Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
Similar to Presentation (2) (1).pdf
Similar to Presentation (2) (1).pdf (20)
Presentation on Industrial Automation by Vivek Atalkar 

Presentation on Industrial Automation by Vivek Atalkar
SCADA ... Supervisory control and data acquisition

SCADA ... Supervisory control and data acquisition
Annunciator for Hazard Prevention & Temperature Control

Annunciator for Hazard Prevention & Temperature Control
Recently uploaded
Differences between analog and digital communicationanalog-vs-digital-communication (concept of analog and digital).pptx

analog-vs-digital-communication (concept of analog and digital).pptxKarpagam Institute of Teechnology
Recently uploaded (20)
Fuzzy logic method-based stress detector with blood pressure and body tempera...

Fuzzy logic method-based stress detector with blood pressure and body tempera...
Involute of a circle,Square, pentagon,HexagonInvolute_Engineering Drawing.pdf

Involute of a circle,Square, pentagon,HexagonInvolute_Engineering Drawing.pdf
Presentation on Slab, Beam, Column, and Foundation/Footing

Presentation on Slab, Beam, Column, and Foundation/Footing
Theory of Time 2024 (Universal Theory for Everything)

Theory of Time 2024 (Universal Theory for Everything)
Call for Papers - Journal of Electrical Systems (JES), E-ISSN: 1112-5209, ind...

Call for Papers - Journal of Electrical Systems (JES), E-ISSN: 1112-5209, ind...
analog-vs-digital-communication (concept of analog and digital).pptx

analog-vs-digital-communication (concept of analog and digital).pptx
Instruct Nirmaana 24-Smart and Lean Construction Through Technology.pdf

Instruct Nirmaana 24-Smart and Lean Construction Through Technology.pdf
Developing a smart system for infant incubators using the internet of things ...

Developing a smart system for infant incubators using the internet of things ...
Passive Air Cooling System and Solar Water Heater.ppt

Passive Air Cooling System and Solar Water Heater.ppt
01-vogelsanger-stanag-4178-ed-2-the-new-nato-standard-for-nitrocellulose-test...

01-vogelsanger-stanag-4178-ed-2-the-new-nato-standard-for-nitrocellulose-test...
History of Indian Railways - the story of Growth & Modernization

History of Indian Railways - the story of Growth & Modernization
Presentation (2) (1).pdf
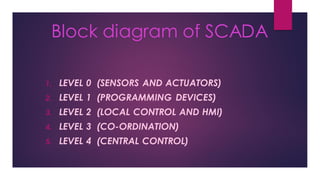
- 1. Block diagram of SCADA 1. LEVEL 0 (SENSORS AND ACTUATORS) 2. LEVEL 1 (PROGRAMMING DEVICES) 3. LEVEL 2 (LOCAL CONTROL AND HMI) 4. LEVEL 3 (CO-ORDINATION) 5. LEVEL 4 (CENTRAL CONTROL)
- 2. LEVEL 0(SENSORS AND ACTUATORS) The ground leveldevices that actually interact with the physical environment ortechnicians in a supervisionsystem. Different types of sensors and actuators come under this level. A sensor is device that can sense the physical changes around it and generate appropriate electrical or electronic signals. For an example we can measure the temperature using a Thermostat.Flow sensor, pressure sensor, LDR and many more sensors are used in a SCADA system. The actuator is a device that makes physical changes when an electrical or electronic signal is applied to it. For example, if we want to control the flow of a liquid solenoid can be used.
- 3. Level 1 (Programming Devices) The programming devicessuch as PLC (Program- mable Logic Controller),RTU (RemoteTerminal Unit) come under this level. These programming devices directlycontrol the ground level devices such as sensors and actuators. A SCADA system can be built with only Local Area Network (LAN) or a combination of the local and Wide Area Networks (WAN). The PLC helps to communicatewith the LAN. On the other hand RTU helps to communicate with the WAN.
- 4. Level 2 (Local Control and HMI) The supervisory computers come under this level.All the programming devices that operate the ground level devices are connected to this computer. SCADA software starts workingfrom the supervisory computers. These computers provide the actual instructions and commands to do the operations. The supervisory computer may be connected to a particular machine or multiple same types of machines or a whole manufacturingplant. These computers are operated by machine operators, plant supervisors and technicians of a manufacturing plant. The main functions of these computers are to observe and control the production, errors etc.
- 5. Level 3 (Co-ordination) Co-ordinating computers comes under this level.Generally these computers are connected to multiple plants. So, it can help to gather data from different plants from one place. At this level,the production planning, scheduling, eventtiming management are done by the plant incharge, managers etc.
- 6. Level 4 (Central Control) It is the top level of the SCADA system. At this level, a central computer is connected to all the plants and machinery. Generally, this is operated and controlled by the management team. All the data and informationare collectedand stored here. Using these data and informationthey can take any decision. From this computer the management team can see all the actions and operations etc.