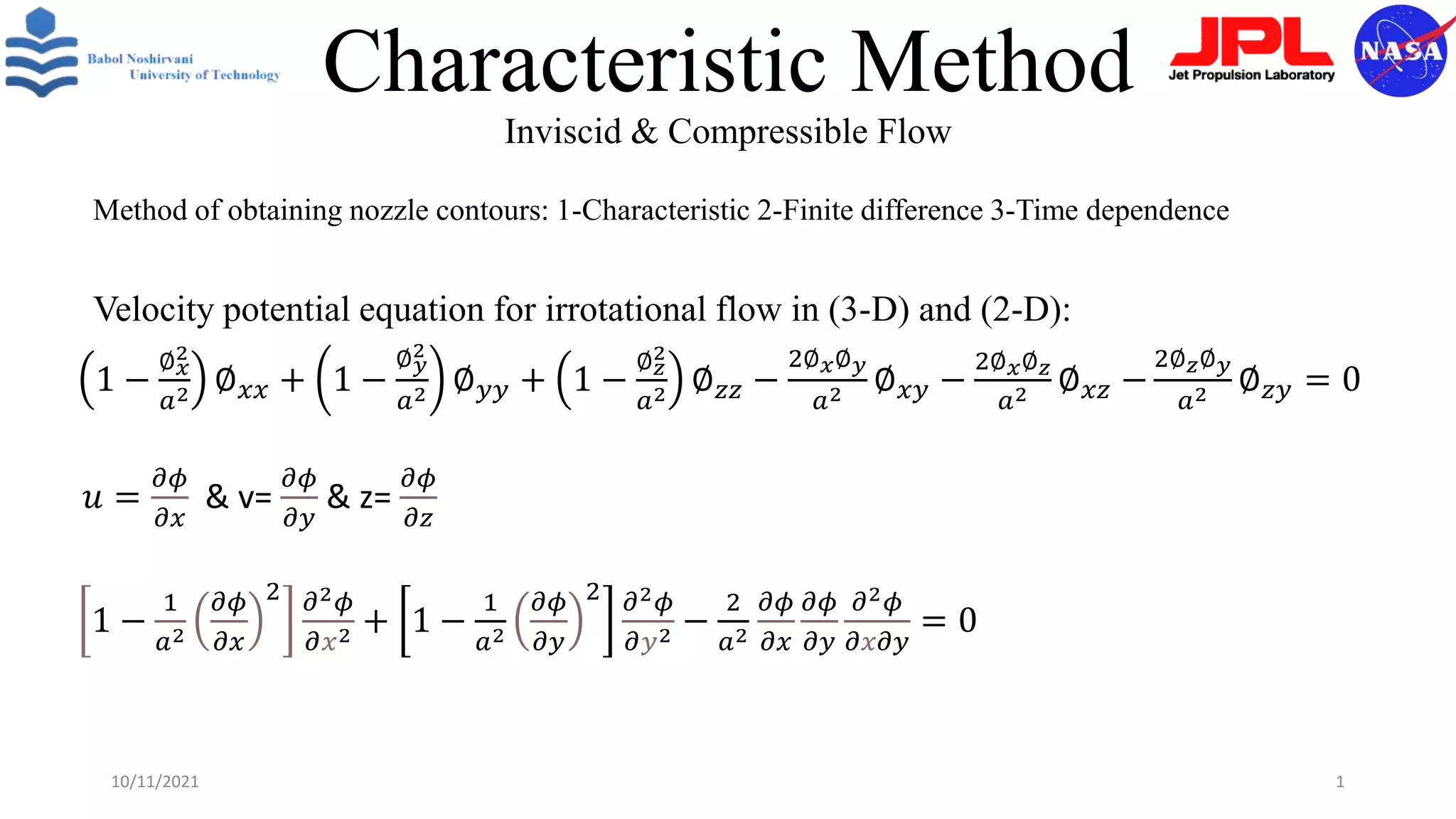
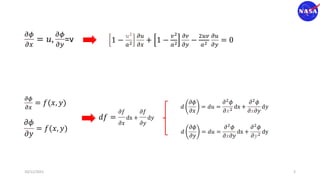
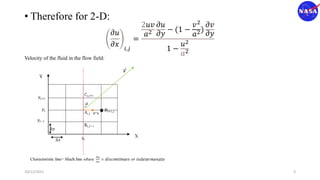
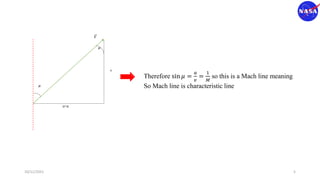
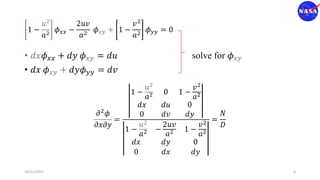
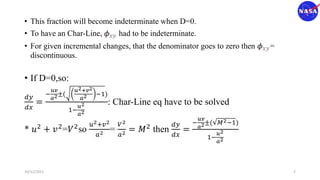
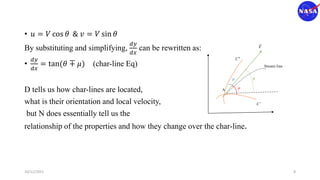
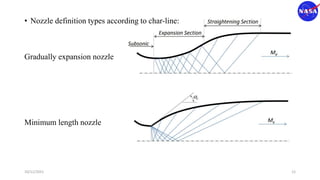
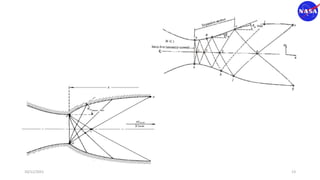
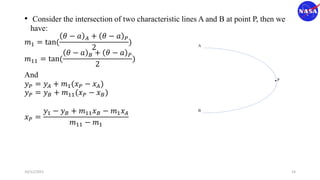
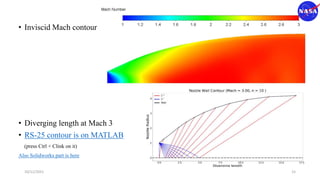
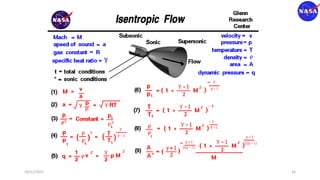
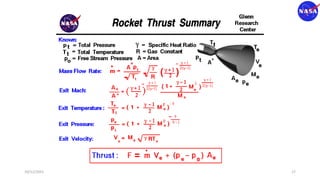
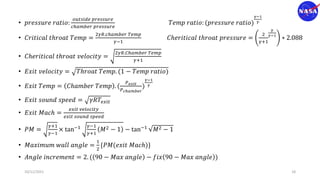
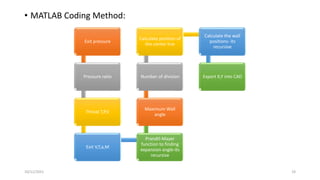
This document discusses characteristic methods for analyzing inviscid and compressible flows. It describes the velocity potential equation and how characteristics lines are derived from it. Characteristic lines represent solutions along which the velocity potential is discontinuous. They are used to determine flow properties like Mach number and expansion wave angles. The document also discusses how to define nozzle contours based on characteristic lines and properties like pressure ratios in converging-diverging nozzles.