TRIANGLES_OF_THE_NECK.pptx
- 1. Dr. NDAYISABA CORNEILLE CEO of CHG MBChB,DCM,BCSIT,CCNA TRIANGLE OF THE NECK Supported BY
- 2. objectives • To define the neck • To outline the structures found in the neck • To describe the boundaries and contents of the triangles of the neck. • To describe the fasciae of the neck DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
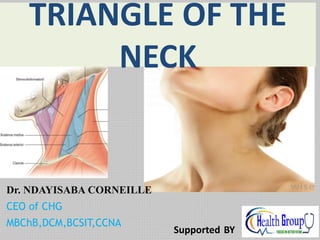
- 3. The neck • Part of the body between the head and the thorax • Contains a number of vessels, nerves and structures connecting the head to the trunk and upper limbs • These include the esophagus, trachea, brachial plexus, carotid arteries, jugular veins, vagus and accessory nerves, lymphatics among others DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 8. Superficial neck muscles Three in number namely • Platysma • Sternocleidomastoid • Trapezius DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 9. Platysma • A thin wide subcutaneous sheet of muscle located in superficial fascia • Upper attachment is to inferior border of the mandible and skin of the face • Lower attachment is to fascia over the pectoralis major and deltoid muscles. • Nerve supply: cervical branch of facial nerve • Action: draws corners of the mouth inferiorly, and depression of the mandible. DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 11. Clinical importance of platysma • Muscle of facial expression • Can be used to express sadness, horror or fright • Can be paralysed in injuries of facial nerve. Skin falls from the neck in slack folds • Should be protected in dissections of the neck to prevent gaping injuries DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 13. Sternocleidomastoid • A broad strap like muscle that is a key land mark in the neck. • Runs superolaterally from the clavicle and sternum to the mastoid process • Divides the neck into anterior and posterior traingles • It is crossed by platysma and the external jugular vein. • Covers and protects the great vessels of the neck and the cervical plexus DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 23. Clinical importance • Can be injured during birth leading to congenital torticollis • Can follow breech presentation • Trauma and heamorrhage leads to healing by fibrosis hence shortening of the muscle • Most are corrected in early child hood hence not seen in adults DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 24. Breech delivery DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 26. Congenital torticolis DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 27. • Sternocleidomastoid muscle also prevents injury to blood vessels and nerves in deep neck lacerations especially in people who attempt suicide by cutting their necks. DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 29. Trapezius The muscle provides a direct attachment of the pectoral girdle to the trunk. This large, triangular muscle covers the posterior aspect of the neck and the superior half of the trunk). It was given its name because the muscles of the two sides form a trapezium (G. irregular four-sided figure). DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 30. Attachments of Trapezius Muscle origin insertion Nerve supply Action Trapezius Medial third of superior nuchal line; external occipital protuberance; nuchal ligament; spinous processes of C7 to T12 vertebrae Lateral third of clavicle; acromion and spine of scapula Accessory nerve (CN XI) (motor fibers) and C3, C4 spinal nerves (pain and proprioceptiv e fibers) Descending part elevates; ascending part depresses; and middle part (or all parts together) retracts scapula; descending and ascending parts act together to rotate glenoid cavity superiorly DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 32. Triangles of the neck • Has 2 major triangles, the anterior & the posterior. • The anterior is further divided into 4, the digastric(submandibular), submental, carotid, mascular triangles • The posterior has the supraclavicular, and occipital triangles. DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 35. The anterior cervical triangle The boundaries are: • Posteriorly: Anterior border of Sternocleidomastoid muscle. • Superiorly: Inferior border of the mandible. • Anteriorly: midline of neck. • Apex is by the jugular notch This triangular region is the major surgical approach to the trachea, esophagus, thyroid gland among others. DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 36. Contents of the anterior triangle • Muscles: supra and infrahyoid muscles Suprahyoid muscles: digastrics, mylohyoid, genihyoid, stylohyoid Infrahyoid muscles (strap muscles): omohyoid, sternohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid • Arteries: common carotid and its branches • Veins: internal jugular vein and tributaries • Viscera: trachea, esophagus, thyroid, parathyroid glands • lymphnodes DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 37. Muscle Origin Insertin Nerve supply Action mylohyoid Mylohoid line of the mandible Raphe and body of hyoid Nerve to mylohoid(from inferior alveolar) Elevation of hyoid, floor of the mouth and tongue(swallo wing) Geniohyoi d Inferior mental spines of mandible Body of hyoid C1 via hypoglossal nerve Pulls hyoid anteroposterior , shortens floor of mouth, widens pharynx Digastrics Ant belly: mandible Post belly: mastiod process Btn body and greater horn of hyoid Ant belly: nerve to mylohoid Post belly: cervical branch of facial Depression of mandible, elevation of hyoid bone Stylohoid Styloid process of mandible Body of hyoid Cervical branch of facial Elevation and retraction of hyoid DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 38. Infrahyoid muscles DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 39. Suprahyoid muscles DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 40. Infrahyoid muscles Muscle Origin Insertion Nerve supply Action Sternohyoid Manubrium sternum and clavicle Body of hyoid Ansa cervicalis(C1, C2 C3) Depression of hyoid bone Sternothyroid Manubrium sternum Oblique line on thyroid cartilage C1 via hypoglossal nerve Depression of hyoid bone and larynx thyrohyoid Thyroid cartilage Inferior border of body and greater horn of hyoid bone Ansa cervicalis(C1, C2 C3) Depression of hyoid bone and elevation of larynx Omohyoid Superior border of scapular near suprascapular notch Inferior border of hyoid bone Ansa cervicalis(C1, C2 C3) Depression of hyoid bone DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 41. submandibular (Digastric) triangle Borders Superior(above) : base of the mandible at its projection to the mastoid process Posteriorly: post belly of the digastric & by stylohyoid muscles Anteriorly: ant digastric belly DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 43. submandibular (Digastric) triangle • Roof : skin, superficial fascia, platysma & deep fascia containing branches of the facial & transverse cutaneous cervical nerves • Floor: mylohyoid & hyoglossus. DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 45. Contents Anterior region • Has the submandibular gland with the facial vein superficial & the facial artery deep to it. • Submental & mylohyoid arteries & nerves lie on mylohyoid. • Submandibular LNs receive afferent channels from submental nodes, the oral cavity, and the anterior parts of the face. • Efferent channels drain primarily into the jugulodigastric, jugulocarotid, and juguloomohyoid nodes of the chain accompanying the internal jugular vein (deep cervicalchain). • A few channels pass by way of the sub parotid nodes to the spinal accessory chain. DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 46. Contents cont’d Posterior region: • Lower part of the parotid gland(tail) • External carotid artery, deep to the stylohyoid to curve above the muscle & overlap its superficial surface & ascend deep to the parotid gland later entering it. DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 47. Contents cont’d • Internal carotid artery, internal jugular vein & vagus nerves are deeper & separated from the external carotid artery by styloglossus, stylopharygeous & the glossopharyngeal nerves. • Also contains the hypoglossal nerve DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 49. Submental triangle • Demarcated by the anterior bellies of both digastric muscles. • Base: body of hyoid bone • Apex: at the chin • Floor: both mylohyoid muscles • Roof: skin & superficial fascia • Medial: ant midline. DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 50. contents: • LNs & small vessels that unite to form the ant. jugular vein. • The submental lymphnodes receive efferents from the tongue, floor of the mouth, mandibular incisors and associated gingivae and central part of lower lip and skin of chin. • Efferents drain into the submandibular and deep cervical nodes. DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 52. Coronal section through the tongue, the mouth and the body of the mandible opposite the first molar tooth (to illustrate contents of the submental triangle) DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 53. Muscular triangle Boundaries; • Anterior: median line of the neck from the hyoid bone to the sternum inferiorly: anterior margin of sternocledomastoid superiorly: superior belly of the omohyoid DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 54. Contents • omohyoid, sternohyoid, sternothyroid and thyrohyoid (strap/infrahyoid). • Thyroid & parathyroid glands, trachea, oesophagus, sympathetic nerve trunk. DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 56. Carotid triangle Boundaries: • Posterior: Sternocleidomastoid muscle. • Anterior: Anterior belly of omohyoid muscle. • Superior: Posterior belly of digastric muscle. • Floor: Hyoglossus muscle, inferior constrictor of pharynx, thyrohyoid muscle, longus capitis muscle, and middle constrictor of pharynx. • Roof: Investing layer of deep cervical fascia. DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 57. contents • Carotid artery bifurcation • Int. carotid a( no neck branches) • Ext. carotid a branches –sup. thyroid a, superficial. temporal a, post. auricular a, internal maxillary a, occipital a, ascending pharyngeal a, scmd a, lingual a(occasional), external maxillary (occasional) • jugular vein tributaries- superior thyroid v, occipital v, common facial v, the pharyngeal v; DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 58. Contents cont’d • Vagus nerve, • spinal accessory nerve, • hypoglossal nerve, • Ansa hypoglossi, &sympathetic n.s (partially). • Lymphatic drainage is by jugulodigastric juguloomohyoid , & nodes along the int. jugular v. from submandibular and submental nodes, deep parotid nodes, and posterior deep cervical nodes. DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 59. Cervical LNs DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 60. The branches of the external carotid artery. DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 61. Common carotid artery • Main blood supply to the head, neck, face and brain • The right arises from the brachiocephalic artery while the left from arch of the aorta • Ascends behind the sternoclavicular joint to reach the thyroid cartilage and then divides into external and internal carotid arteries • Embedded in the carotid sheath with the vagus nerve and internal jugular vein DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 62. Common carotid artery • Relations • Anterolaterally: skin, fascia, SCM, sternoyhoid, sternothyroid and superior belly of omohyoid • Posteriorly: transverse processes of C1 to C4, Prevertebral muscles and sympathetic trunk • Medially: larynx, pharynx, trachea, esophagus • Laterally: internal jugular vein, vagus nerve DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 63. External carotid artery • One of the terminal branches of CCA • Supplies skin, face and scalp • Starts at upper border of thyroid cartilage and ends in parotid gland by dividing into maxillary and superficial temporal arteries Relations: Anterolaterally: SCM, skin, fascia, hypoglossal nerve, post belly of digastric, dtylohyoid, facial nerve DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 64. External carotid artery • Medially: pharynx, ICA, stylopharyngeous, glossopharyngeal nerve, vagus nerve(pharyngeal branch) • Branches superior thyroid, acsending pahryngeal, lingual, facial, occipital, posterior auricular, superficial temporal, maxillary DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 65. The posterior triangle; The boundaries are: • Anteriorly: posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid • Posteriorly: anterior border of the trapezius • Inferiorly: middle 1/3rd clavicle • Apex: scm & trapezius to the occiput • Roof: deep cervical fascia(investing layer) , platysma, superficial veins, cutaneous nerves and skin. • Floor: prevertebral fascia overlying splenius capitis, levator scapulae and the scalenus medius and S. posterior muscles. DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 66. Muscular floor of the posterior triangle DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 67. Contents • Fat • lymph nodes • Nerves: spinal accessory nerve, cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus, • Arteries: occipital, transverse cervical and suprascapular arteries, the third part of the subclavian artery • Veins: Subclavian and the external jugular vein. • Muscles: splenius capitis, levator scapulae, scalenus medius and scalenus posterior DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 68. External jugular vein • Drain most of the face and scalp on the same side. • Starts at the angle of the mandible as a union of the posterior auricular vein and the posterior division of the retromandibular vein • Crosses the SCM in the superficial fascia and then pierces deep fascia in the roof of the post triangle, 5cm above the clavicle • End by draining in the subclavian vein 2cm above the clavicle DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 70. External jugular vein Tributaries of external jugular vein include • Posterior auricular vein • Posterior division of the retromandibular vein • Posterior external jugular vein • Transverse cervical vein • Suprascapular vein • Anterior jugular vein DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 71. Subclavian vein • Major venous channel draining the upper limb • A continuation of the axillary vein above the clavicle • An occassional occurance in the posterior triangle DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 72. Subclavian artery • Major blood supply to the upper limb • Has three parts. Only 3rd part is found in post triangle • Begins about a finger breadth above the clavicle and lies in contact with the first rib posterior to scalenous anterior muscle • Can be compressed to control heamorrhages at this point DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 74. Other arteries • Transverse cervical: a branch of the thyrocervical trunk(from subclavian). Lies superficial and lateral across the post triangle, 2 cm above the clavicle deep to omohyoid • Suprascapular artery: another branch of thyrocervical trunk. Lies in inferior part of the triangle above the clavicle • Occipital artery: a branch of external carotid. Enters apex of the triangle and ends by supplying the scalp DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 75. Nerves in the posterior triangle • Accessory nerve: enters triangle btn the superior and middle 1/3 of SCM. Passes posteroinferiorly and disappears deep to ant border of trapezius. Supplies these two muscles • Cervical plexus: gives off the lesser and greater occipital, transverse cervical, phrenic and supraclavicular nerves • Brachial plexus: the three trunks are located in this region DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 76. Nerve of the posterior triangle DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 77. Muscles in the posterior triangle • Splenius capitis: occupies upper part of the triangle, serves as a bandage that holds the deeper muscles of the neck • Levator scaplae: a strap like muscle partially covered by SCM and Trapezius. Elevators the scapula • Scalenus medius: longest and largest of the scalenus muscles. Perforated by the dorsal scapular nerve and the two superior roots of the long thoracic nerve. Lies post. to the ant. roots of the brachial plexus and 3rd part of subclavian artery • Scalenous posterior: smallest and most deep of scalene • muscles • Partially fused to scalenus medius DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 78. Muscular floor of the posterior triangle DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 79. Muscles in posterior triangle Muscle origin Insertion Nerve supply Action Splenius capitis Ligamentum nuchae, spines of C1 - C6 Mastoid process Dorsal rami of middle cervical spinal nerve Lateral flexion and rotation of the head Levator scapulae Transverse processes of C1 – C4 scapular Dorsal scapular nerve and cervical plexus Elevation of the scapular Splenius medius Transverse processes of C4 – C6 External border of second rib Ventral rami of cervical plexus( C7 and C8) Lateral flexion of the neck, elevation of 2nd rib during forcefull insipiration Scalenus posterior Transverse processes of C6 and C7 Superior surface of 1st rib Ventral rami of cervical plexus( C3 - C8) Lateral flexion of the neck, elevation of 1st rib during forcefull insipiration DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 80. Splenius capitis DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 81. Lymphnodes in the posterior triangle • Superficial cervical nodes: lie along the external jugular vein • Deep cervical nodes: lie along internal jugular vein • The nodes receive efferents from the parortid, occipital and mastoid lymphnodes, muscles and skin • Efferents pass to the supraclavicular nodes in the subclavian triangle DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 82. Lymphnode groups in the neck DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 83. Subdivisions of the posterior triangle • Divided by inferior belly of omohyoid into a larger superior occipital and a smaller supraclavicular triangle • Occpital triangle: mainly contains the occpital artery and the accessory nerve • Supralavicular triangle: mainly has the external jugular vein, the suprascapular artery and subclavian artery(hence also called subclavian triangle) DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 85. Occipital triangle Boundaries; • Ant: post belly of sternocleidomastoid • post: ant border of trapezius, • inferiorly by the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle. • Floor: splenius capitis, levator scapulae, and scaleni medius and posterior; semispinalis capitis occasionally appears at the apex. • Roof: skin, superficial & deep fasciae & inferiorly by the platysma . DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 86. Contents • The spinal accessory nerve pierces sternocleidomastoid and crosses levator scapulae obliquely downwards and backwards to reach the deep surface of trapezius. (surface marking: jxn of sup 1/3rd & inf 2/3rds of the scmd to the jxn of inf 1/3rd & sup 2/3rds of trapezius ) • Cutaneous & muscular branches of the cervical plexus emerge at the posterior border of scmd. • Inferiorly; supraclavicular nerves ,cervical vessels & uppermost part of the brachial plexus cross the triangle. • Lymphnodes DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 87. Supraclavicular triangle boundaries; • Superior: inf belly of omohyoid • Anterior : post. border of the SCM • Inferior: sup middle 1/3rd boarder of the clavicle. • & communicates with the greater supraclavicular fossa • Floor; 1st rib, scalenus medius, 1st slip of serratus anterior. • Roof; skin, superficial & deep fasciae & platysma crossed by the supraclavicular nerves. DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 88. Contents • 3rd part of subclavian artery, vein.. Usually not but may rise as high as the artery. , • brachial plexus partly sup & post to the artery. • Suprascapular vessels pass tranversely behind the clavicle, below the transverse cervical artery and vein. • The ext. jugular vein drains into the subclavian vein following the post boarder of the scmd. DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 89. Contents cont’d • It receives the transverse cervical & supra scapular veins to later form a plexus anterior to the 3rd part of the subclavian artery. Occasionally, a small branch from the cephalic vein is received. • Nerve to the subclavius • Lymphnodes DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 90. Illustration (posterior triangle) DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 91. Clinical significance • Brachial plexus trunk palpation • Arterial flow control of the subclavian artery by retroclavicular compression. • Communication with the greater supraclavicular fossa…….. • Lymphnodes DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE
- 92. END Dr Ndayisaba Corneille THANKS FOR LISTENING By DR NDAYISABA CORNEILLE MBChB,DCM,BCSIT,CCNA Contact us: amentalhealths@gmail.com/ ndayicoll@gmail.com whatsaps :+256772497591 /+250788958241
