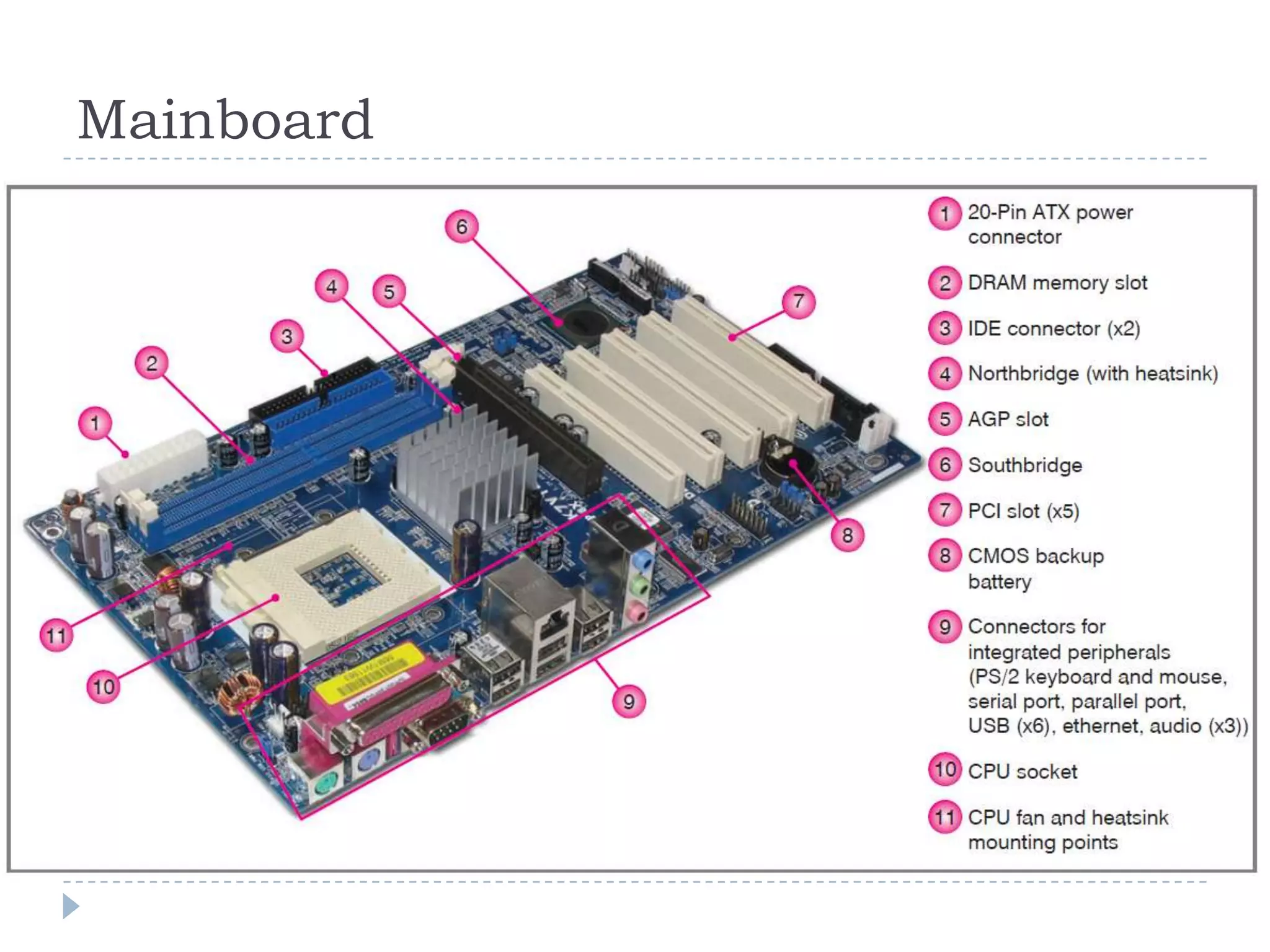
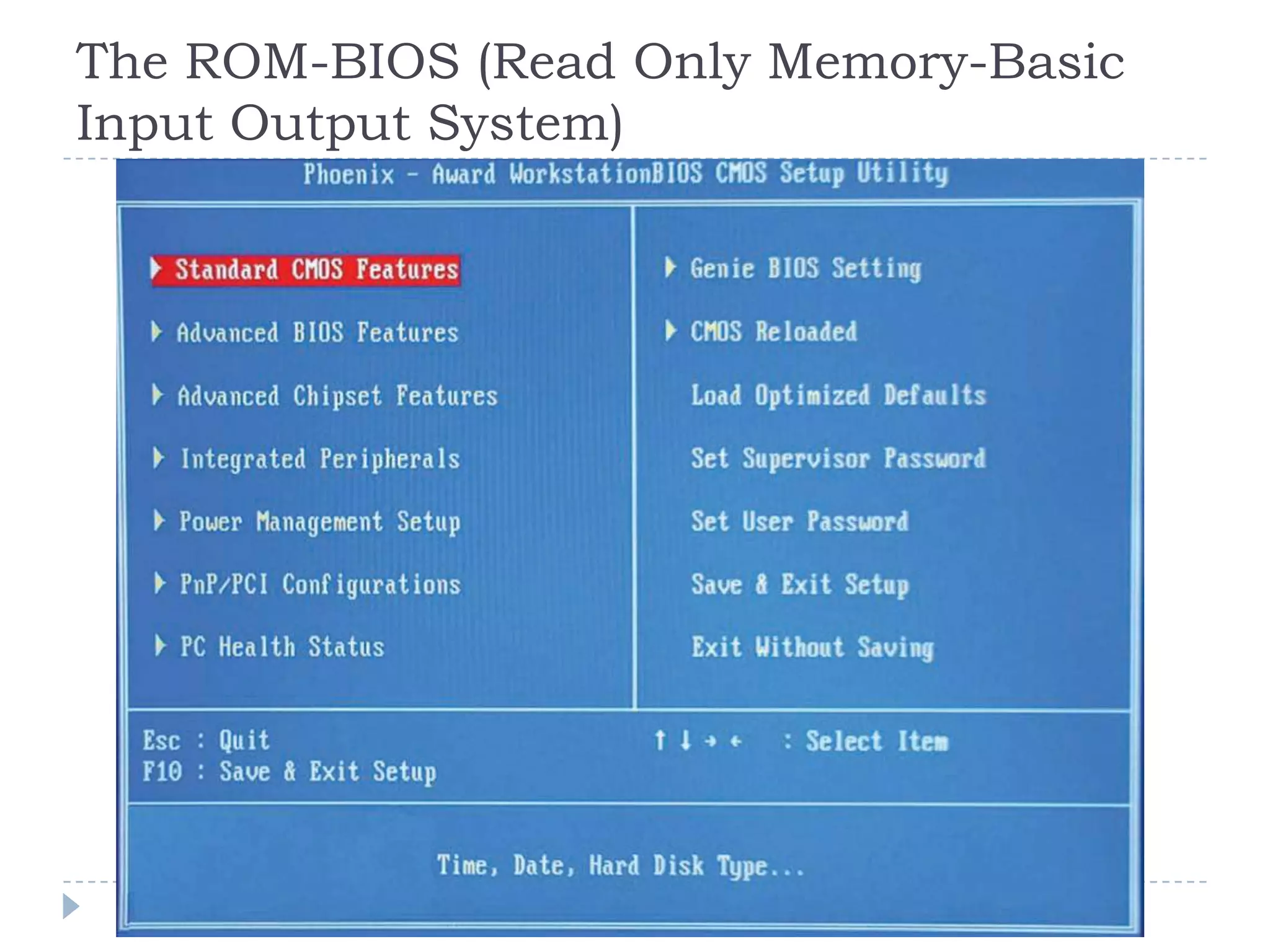
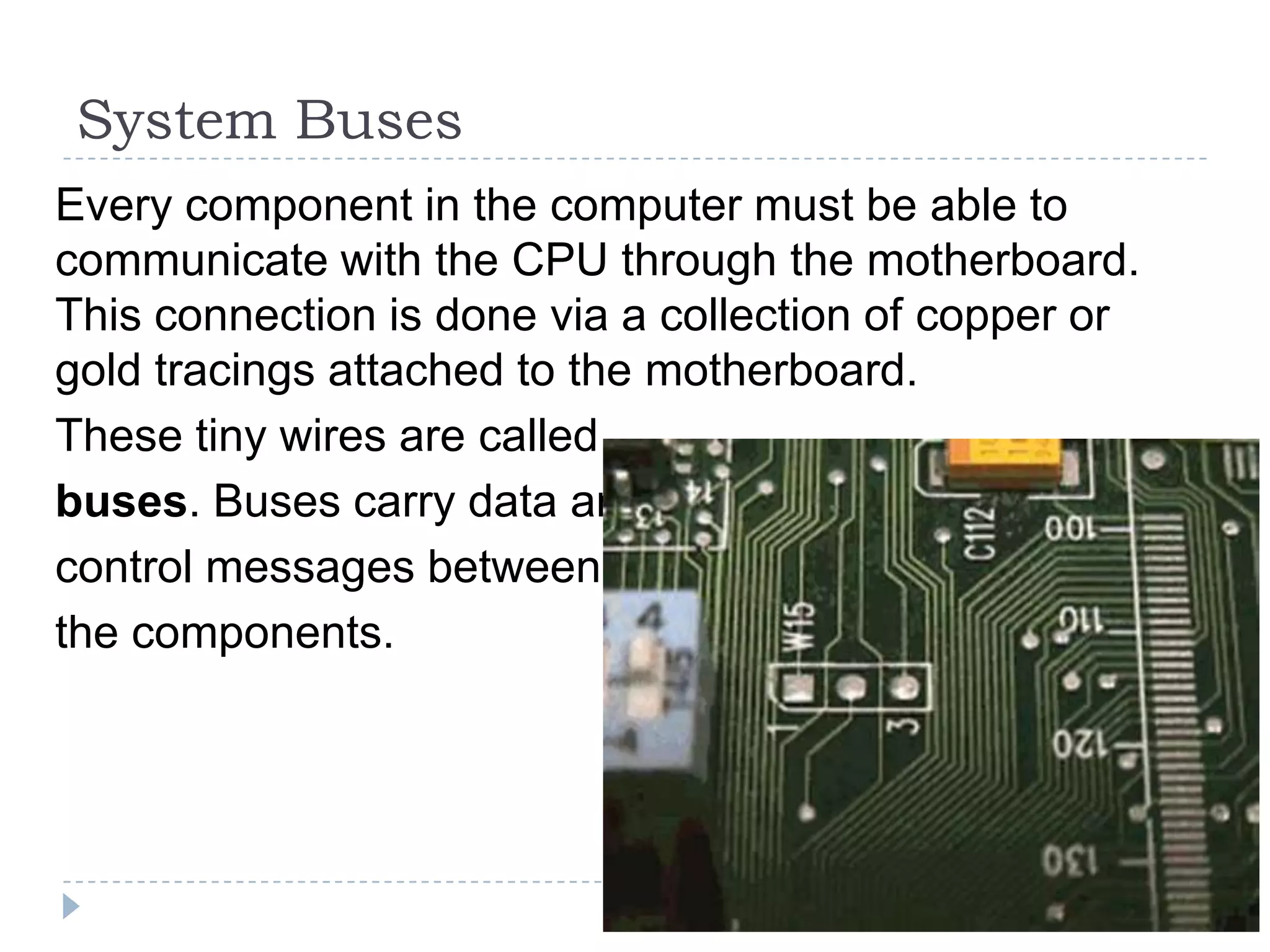
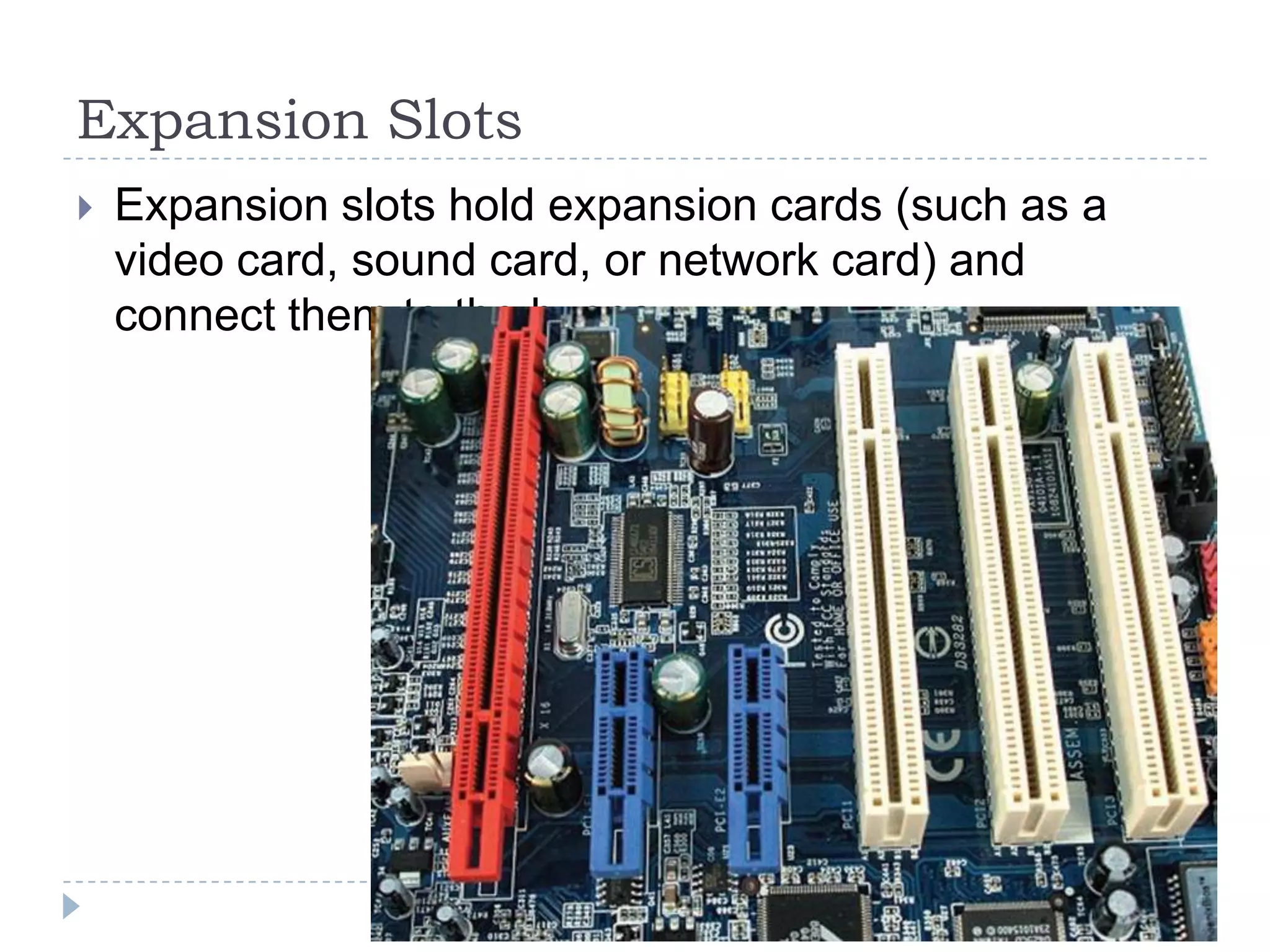
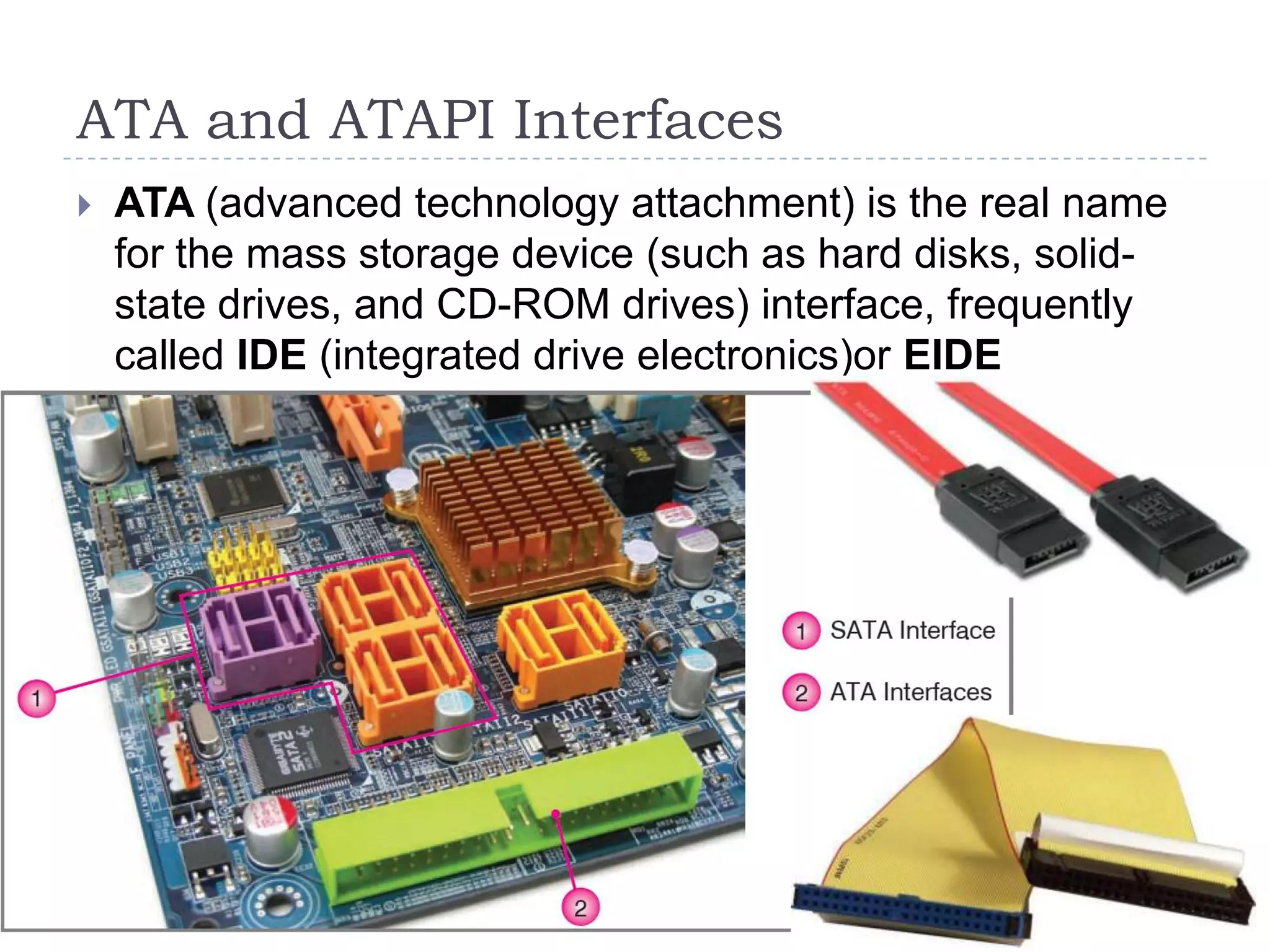
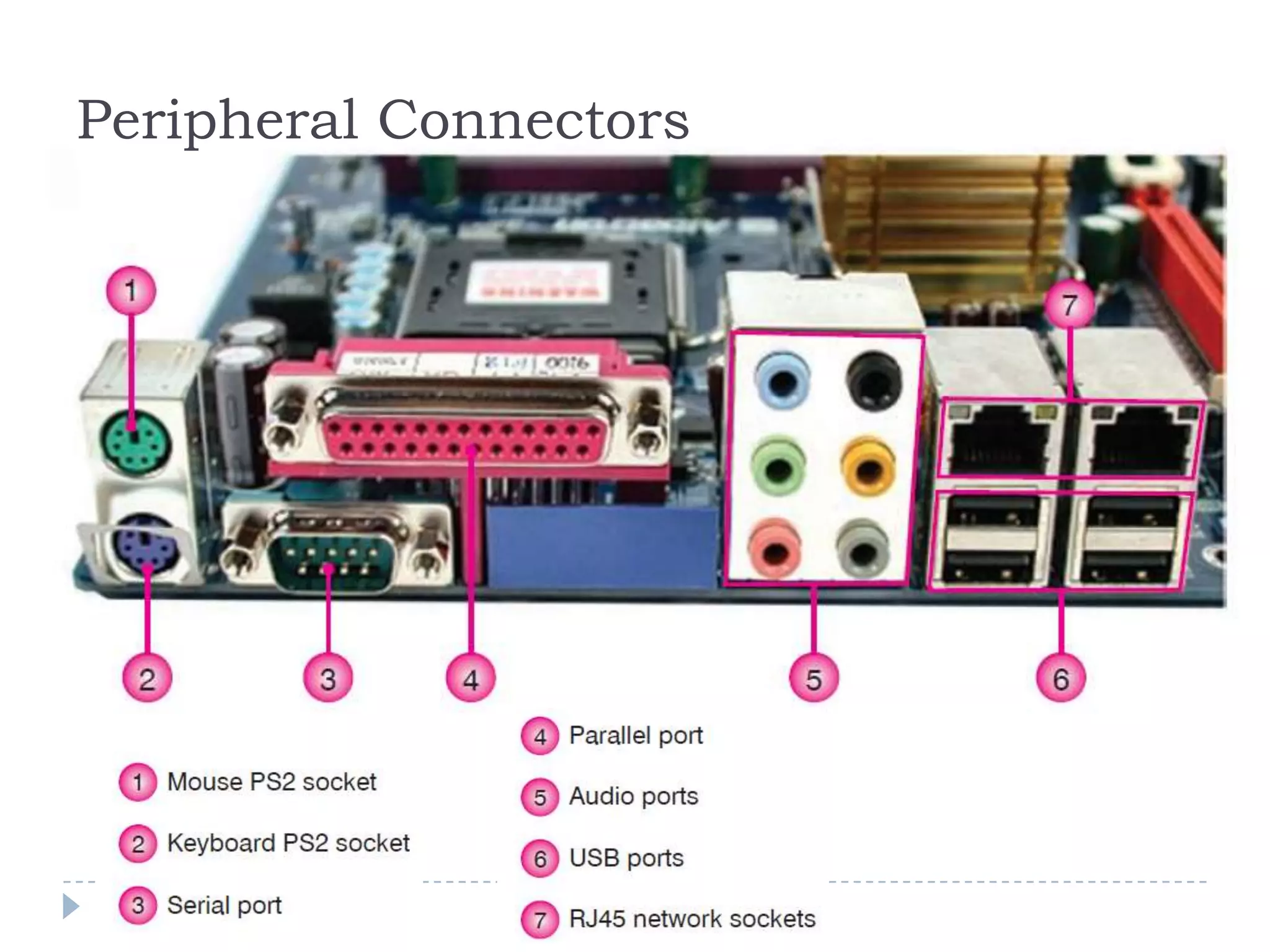
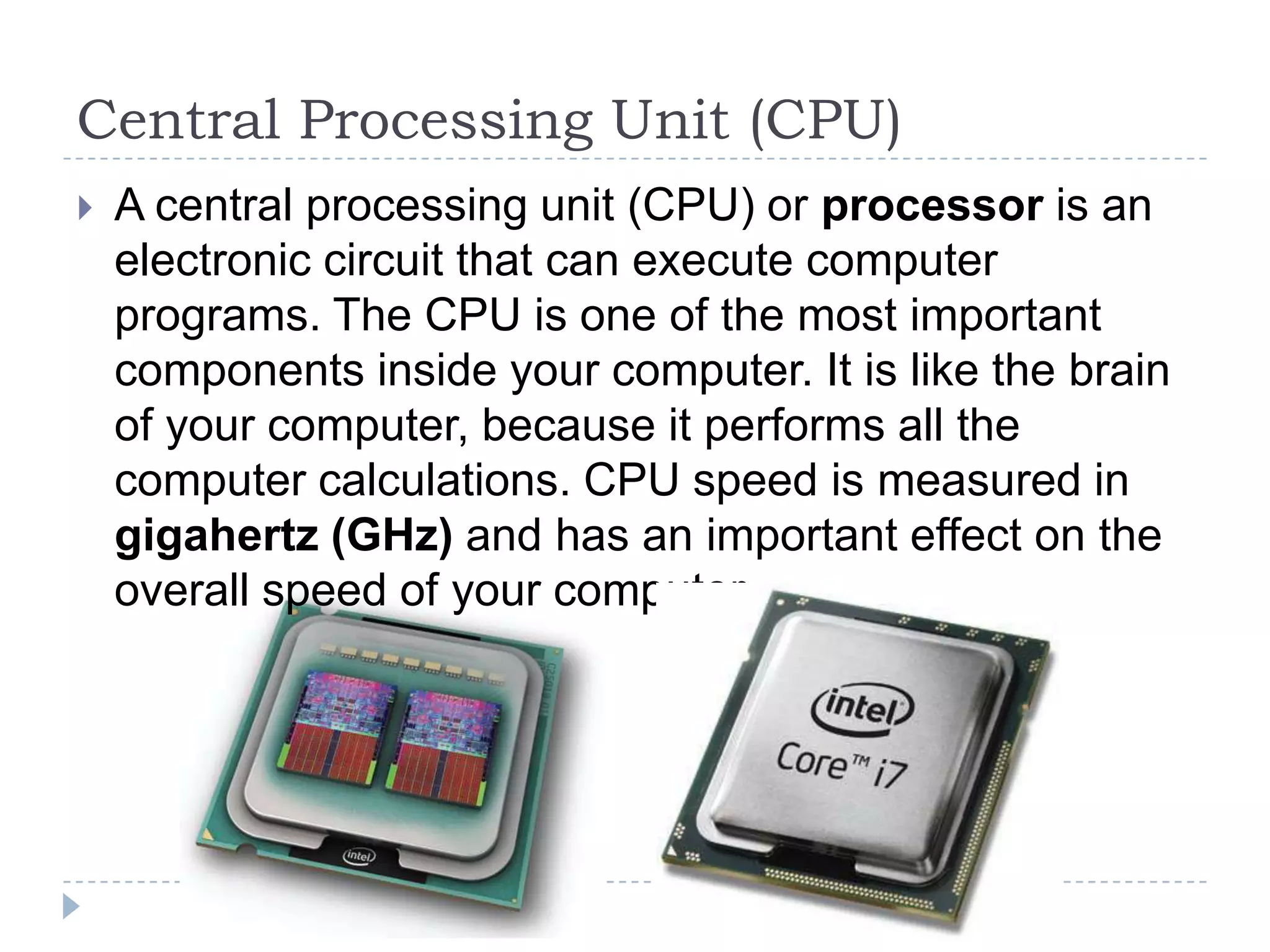
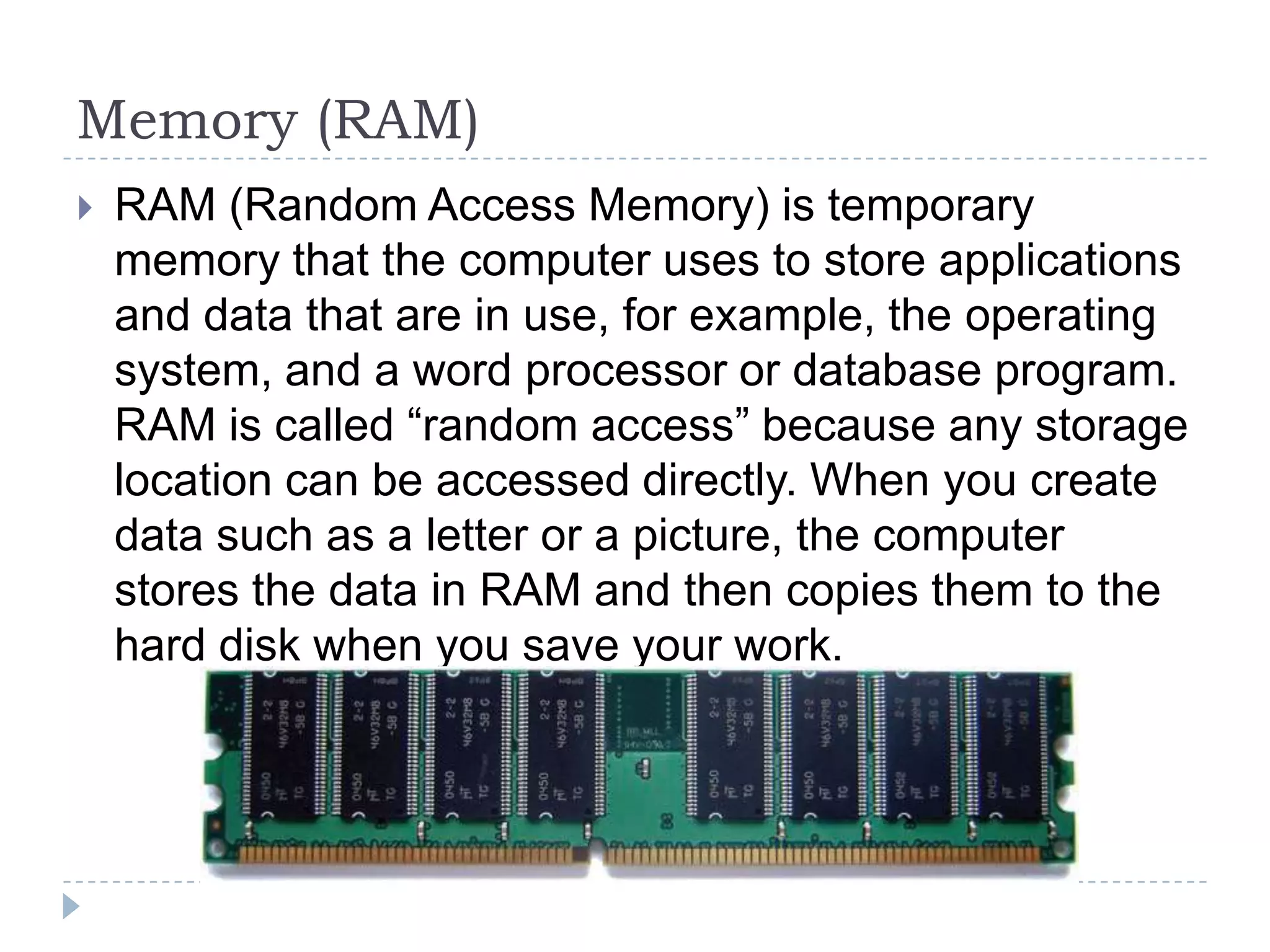
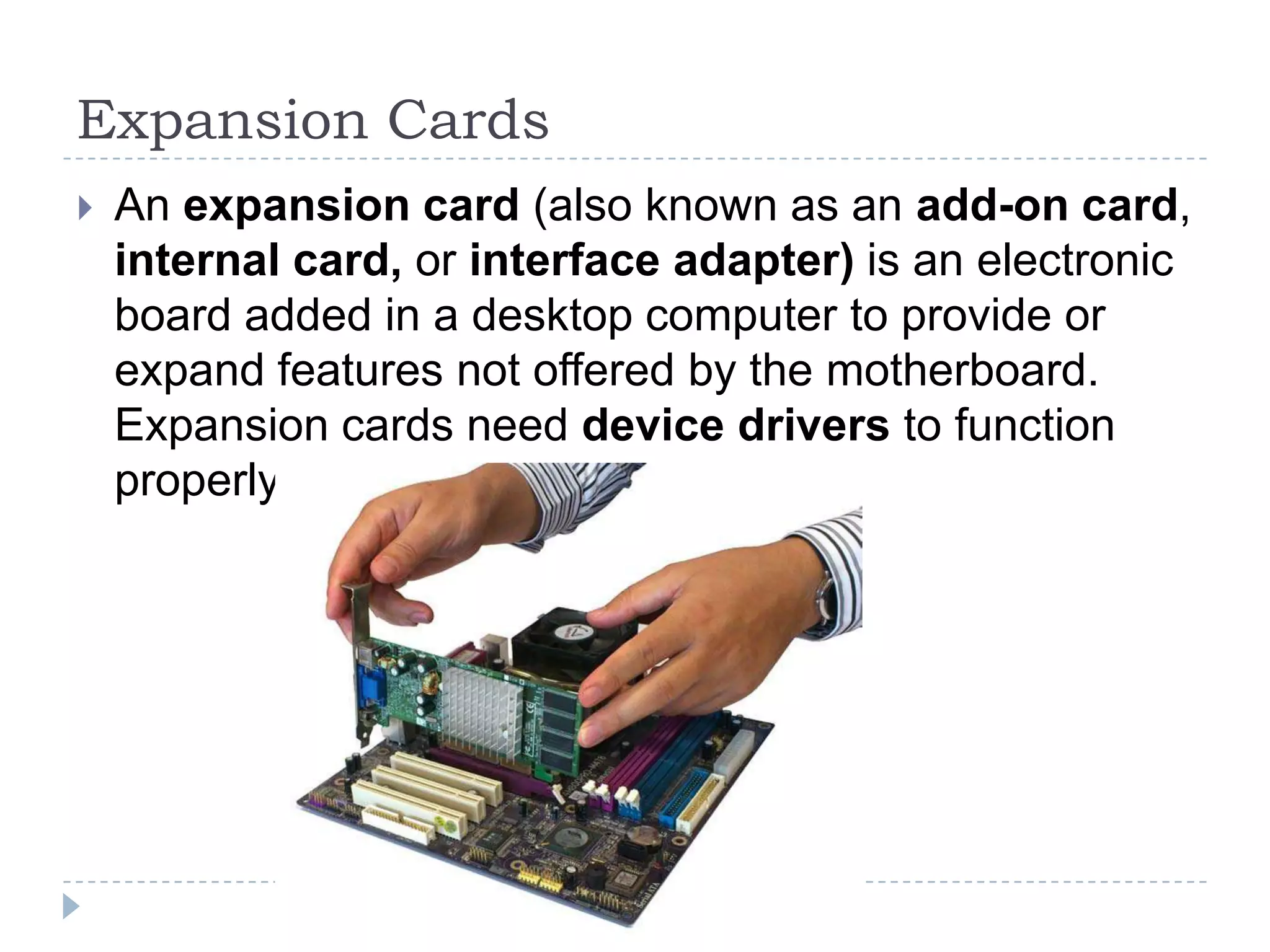
The physical components of a computer can be grouped into four categories: the system unit, input devices, output devices, and storage devices. The system unit contains the main components like the chassis, power supply, motherboard, CPU, memory, and expansion slots. The motherboard connects all the components via buses and contains the BIOS chip which allows the computer to boot. Expansion cards add additional features and connect via slots on the motherboard.