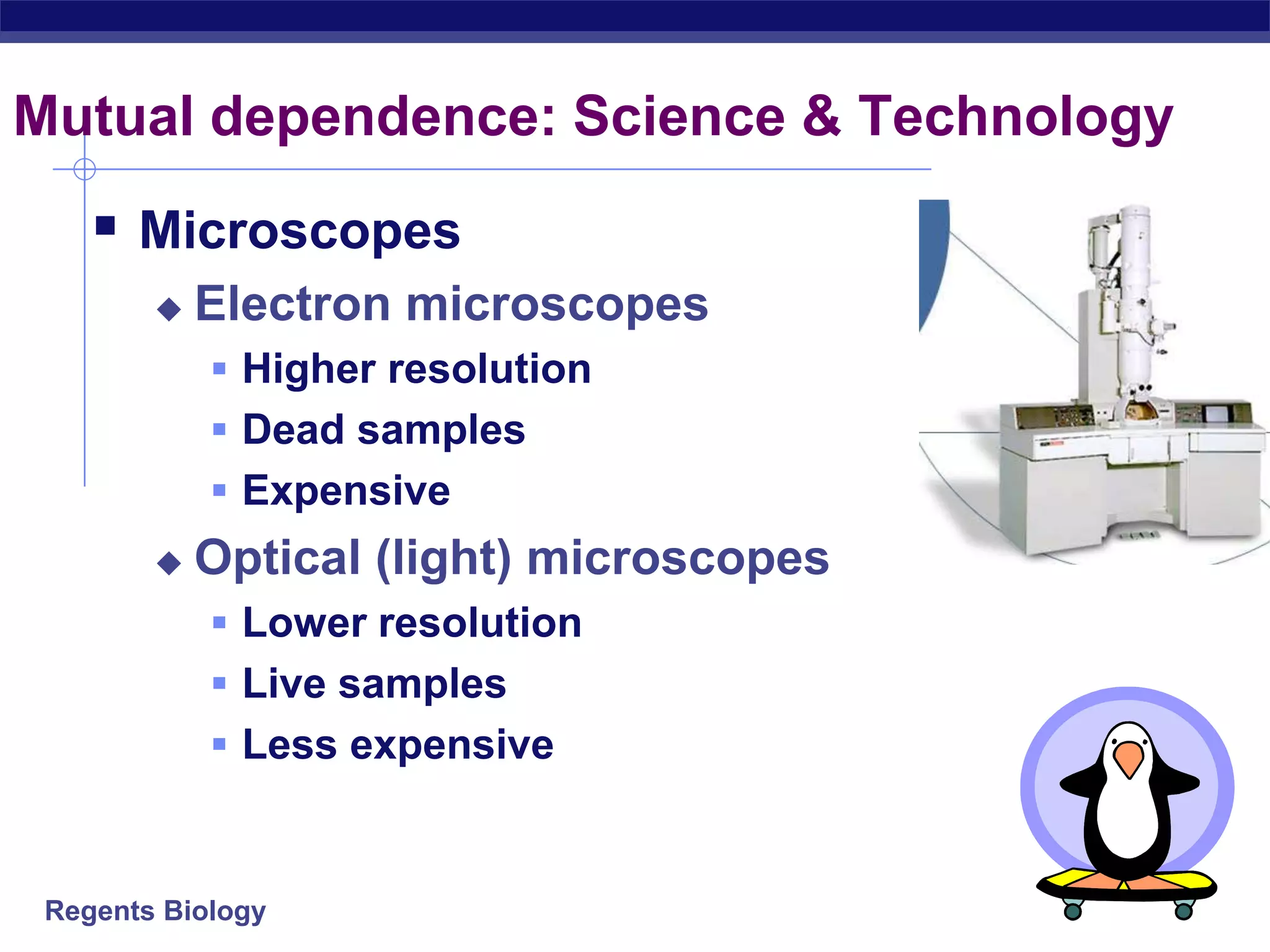
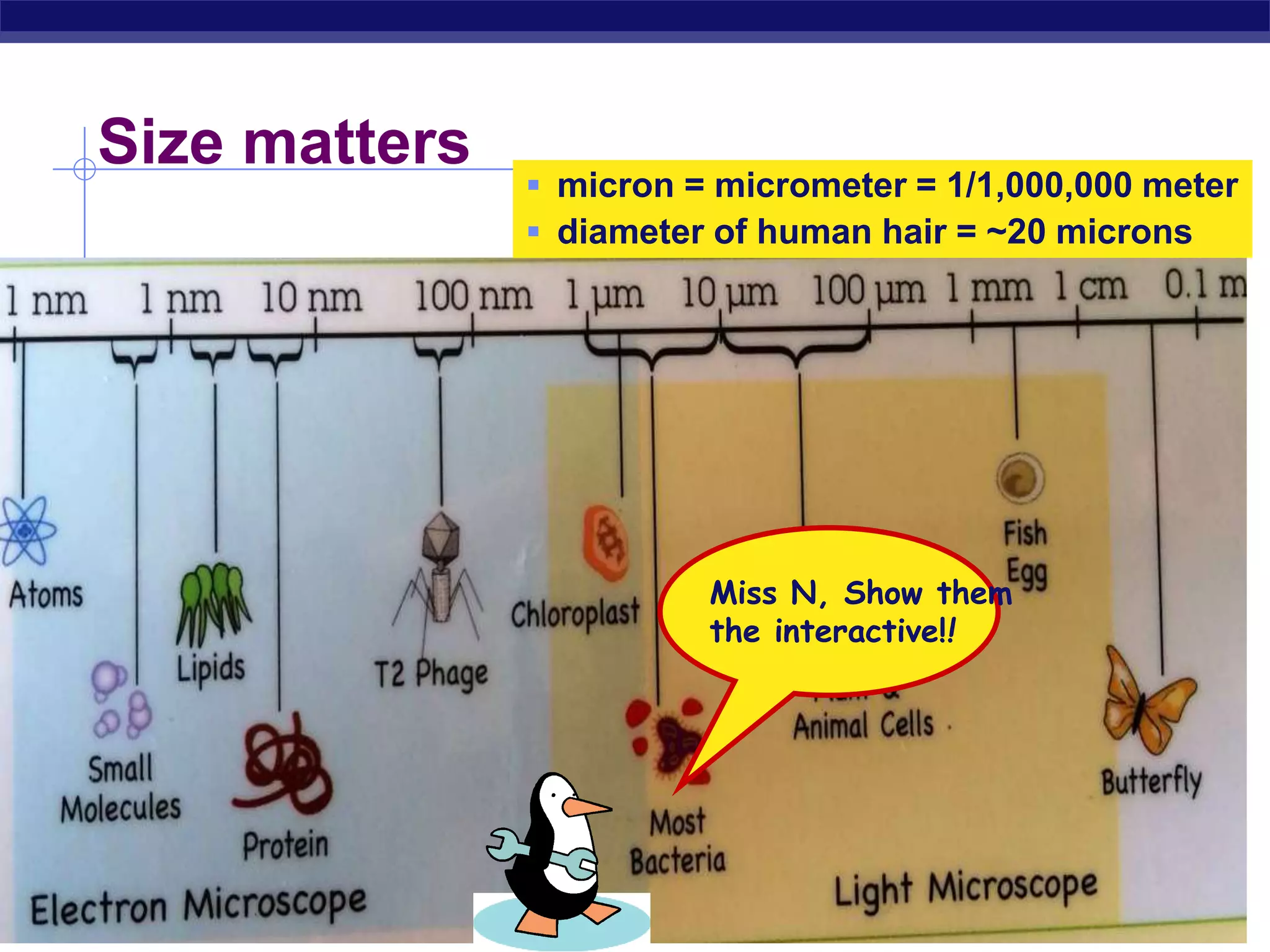
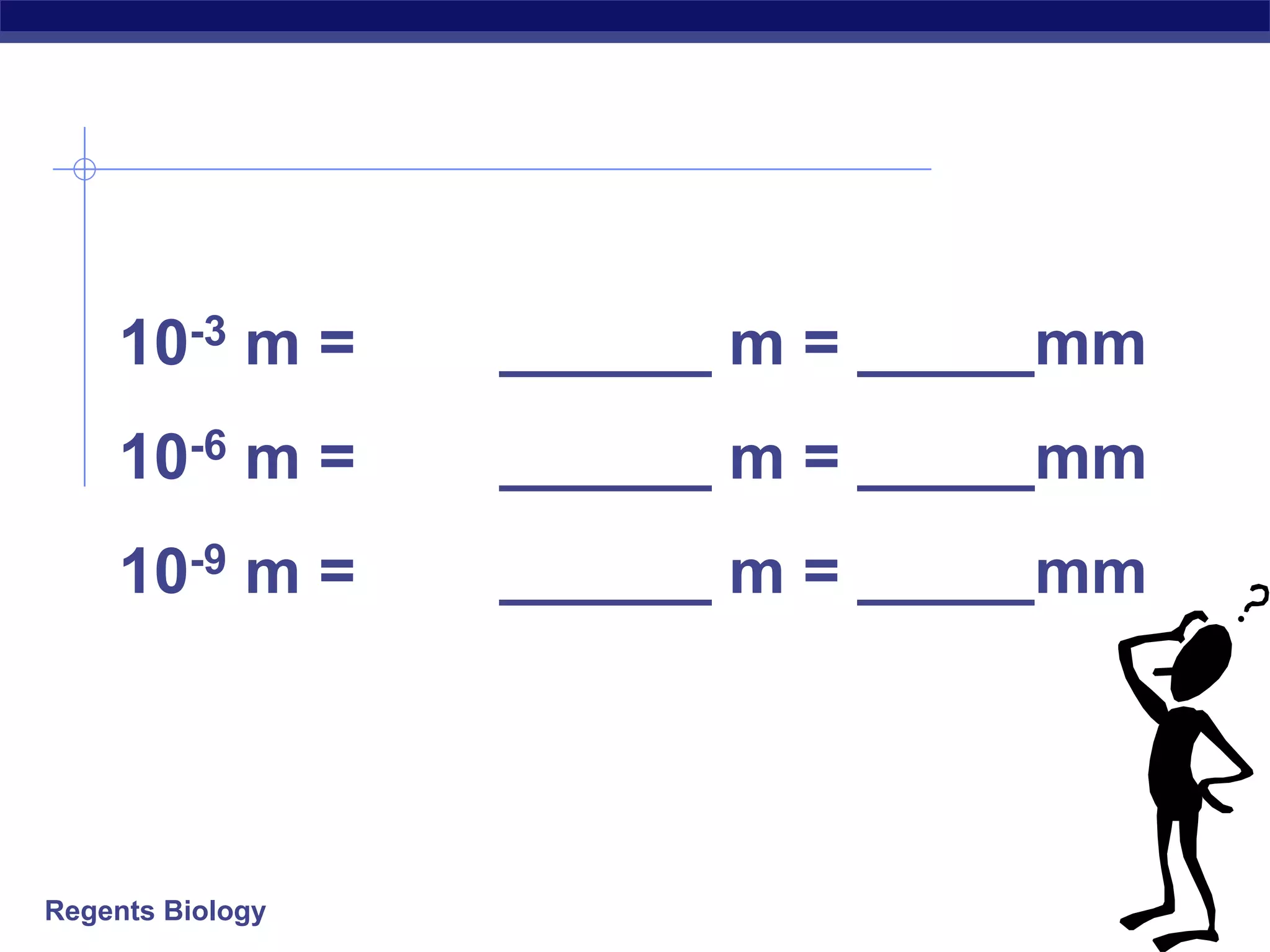
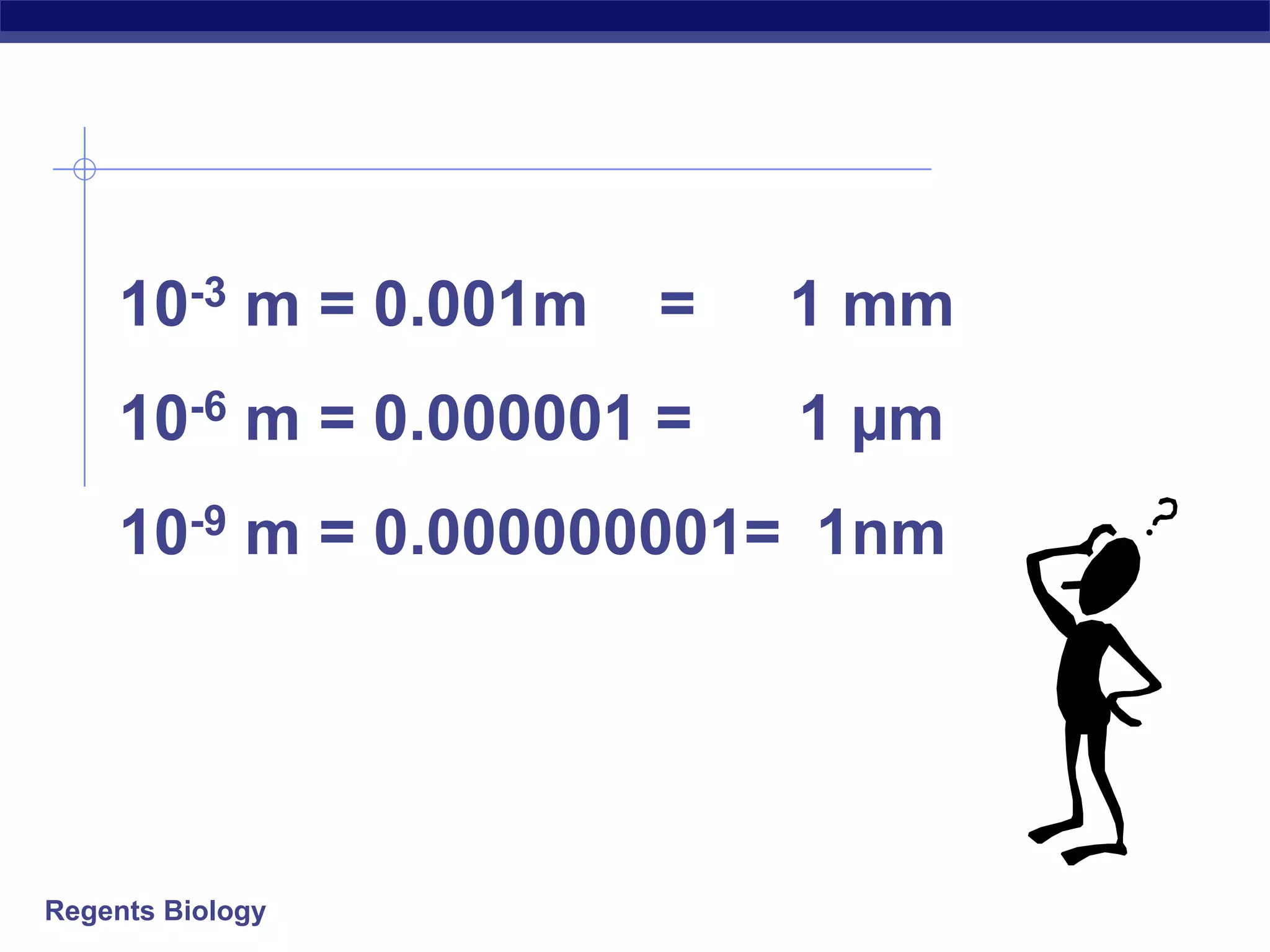
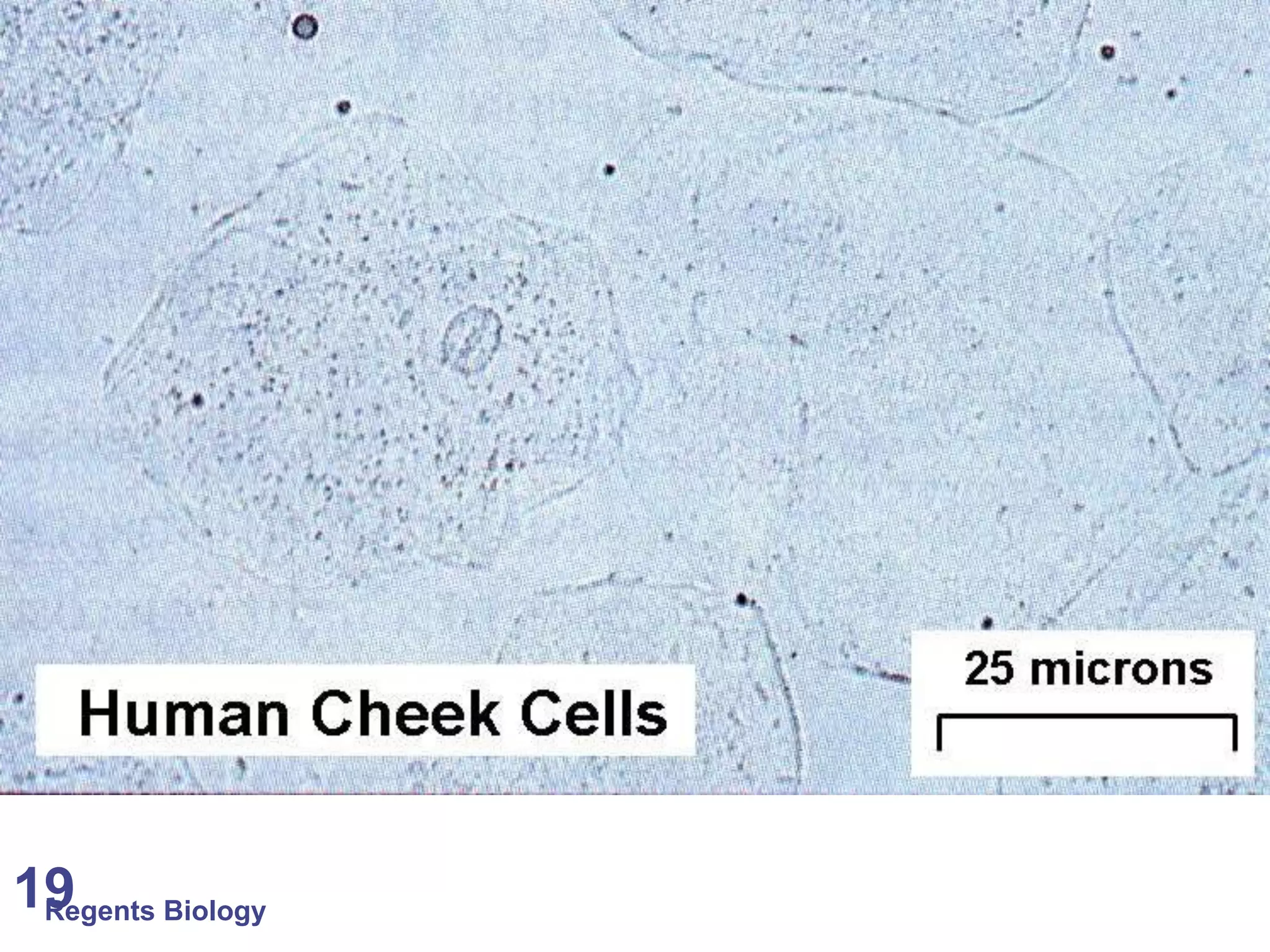
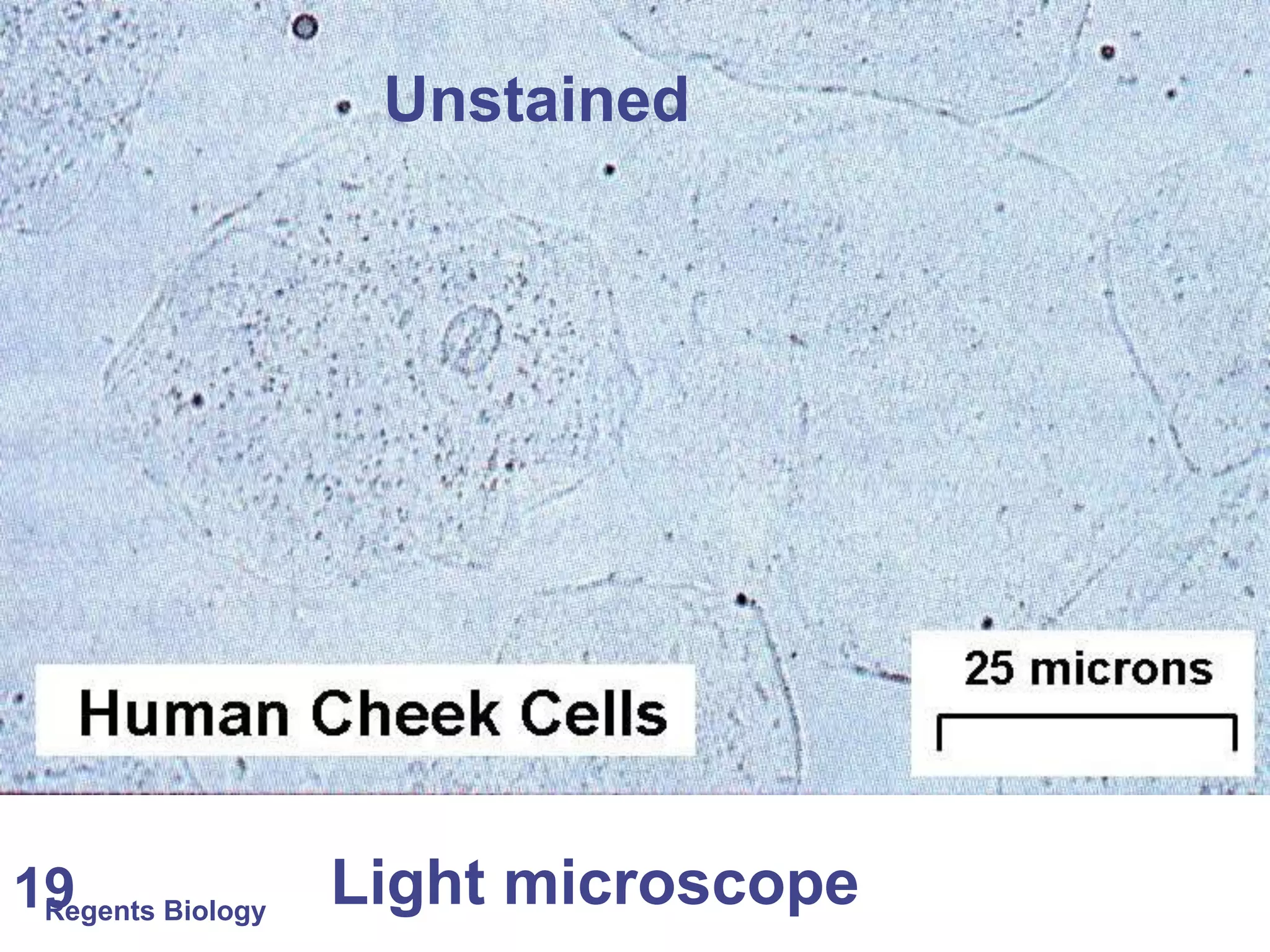
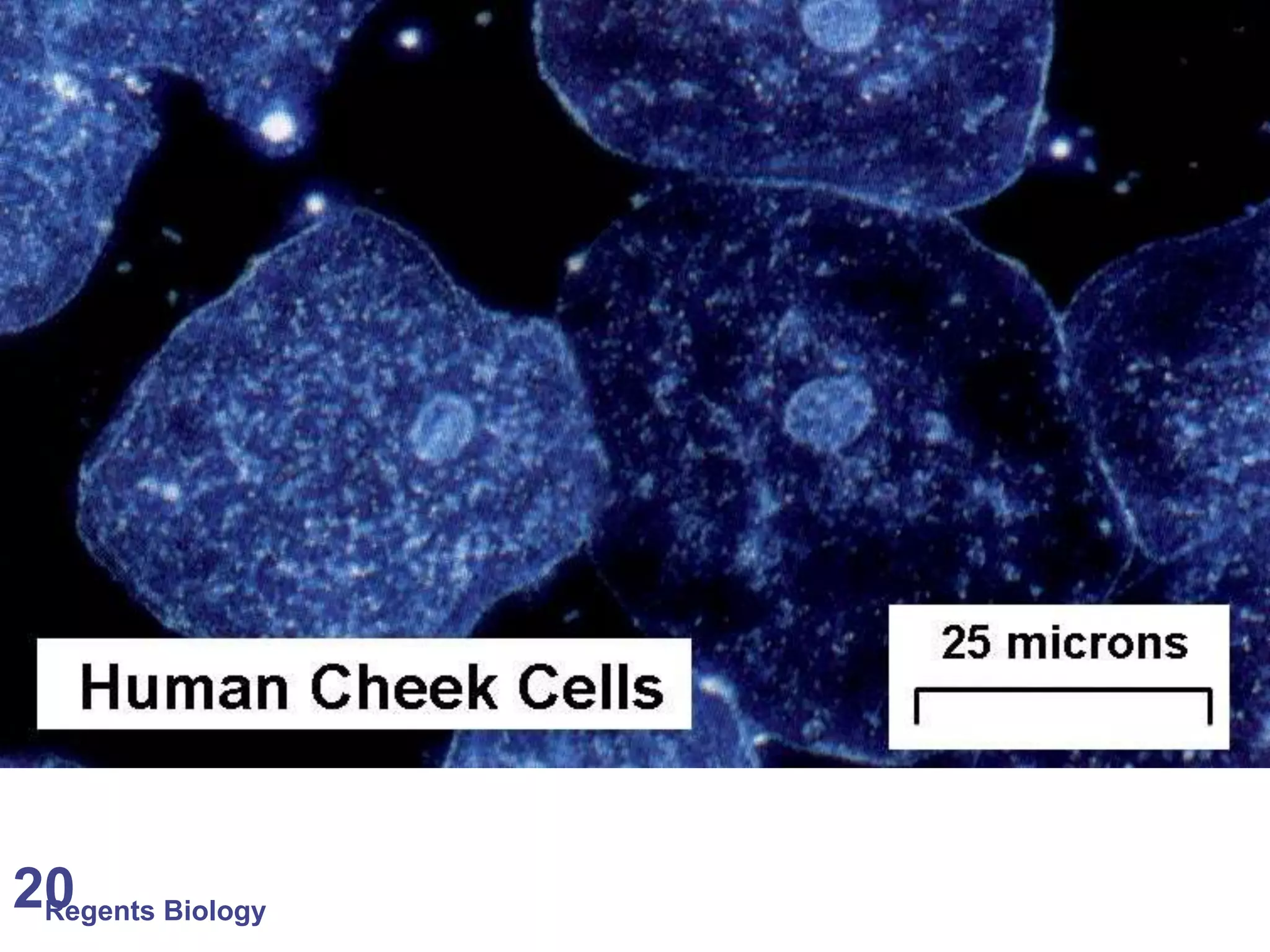
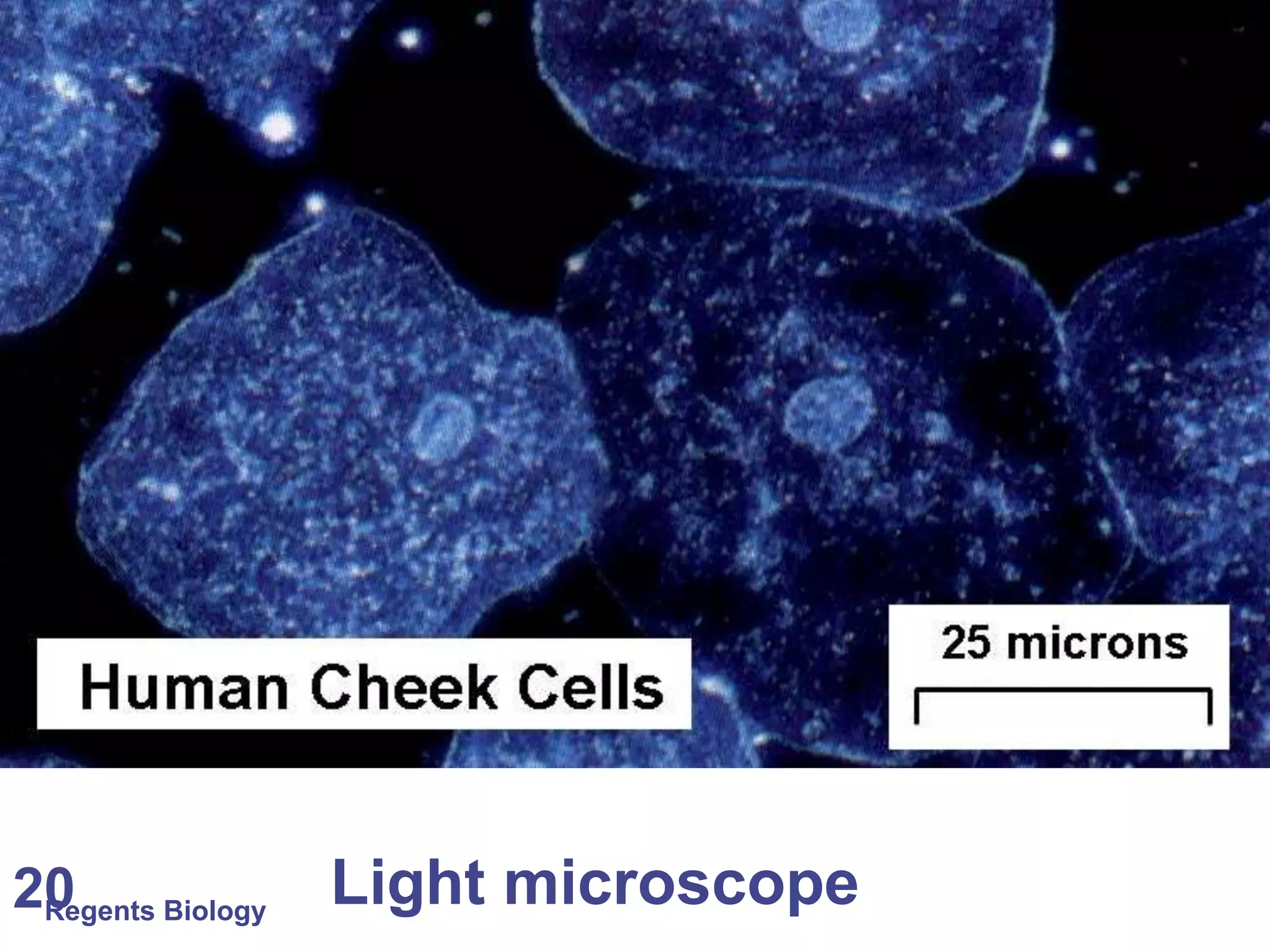
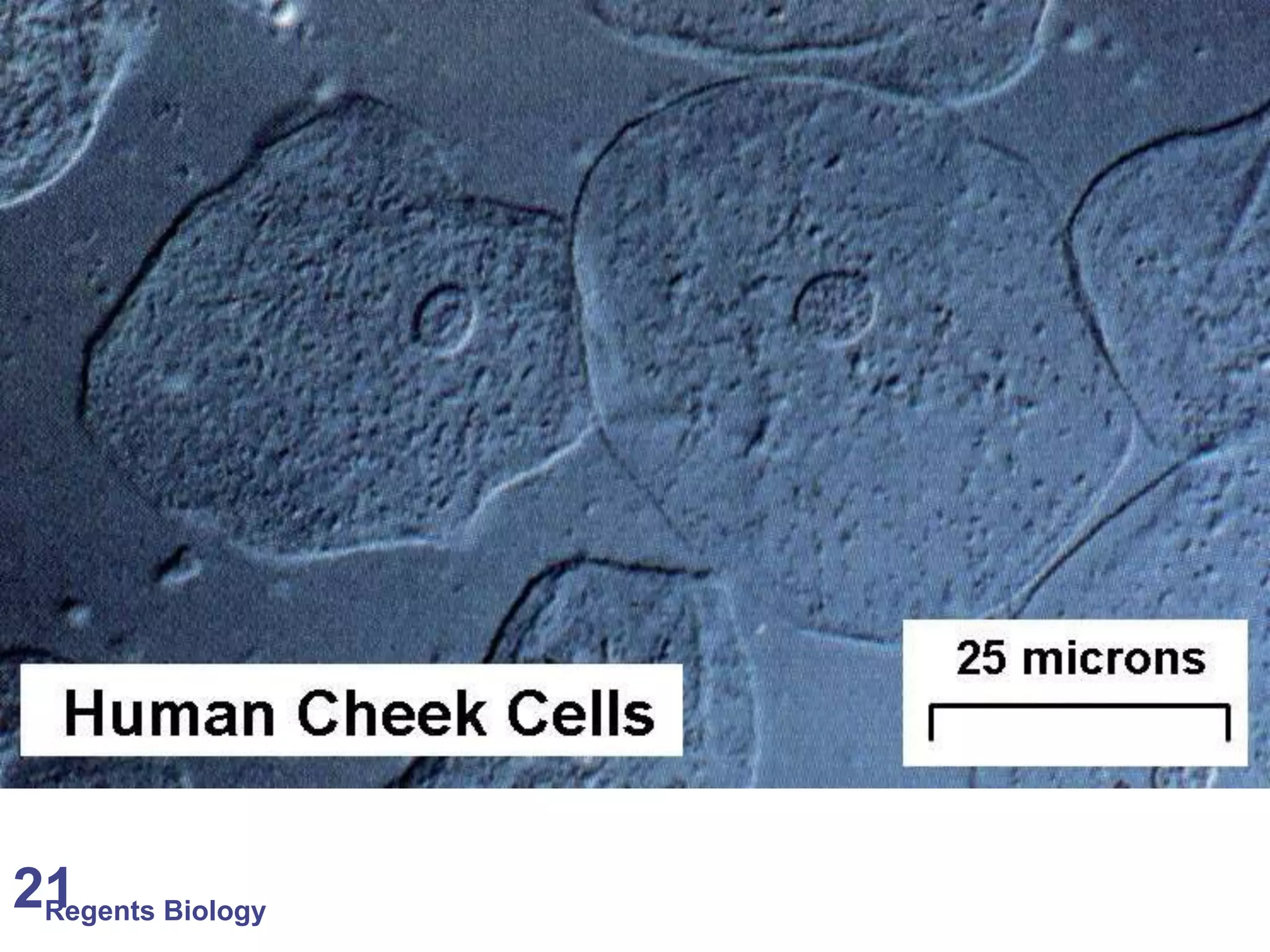
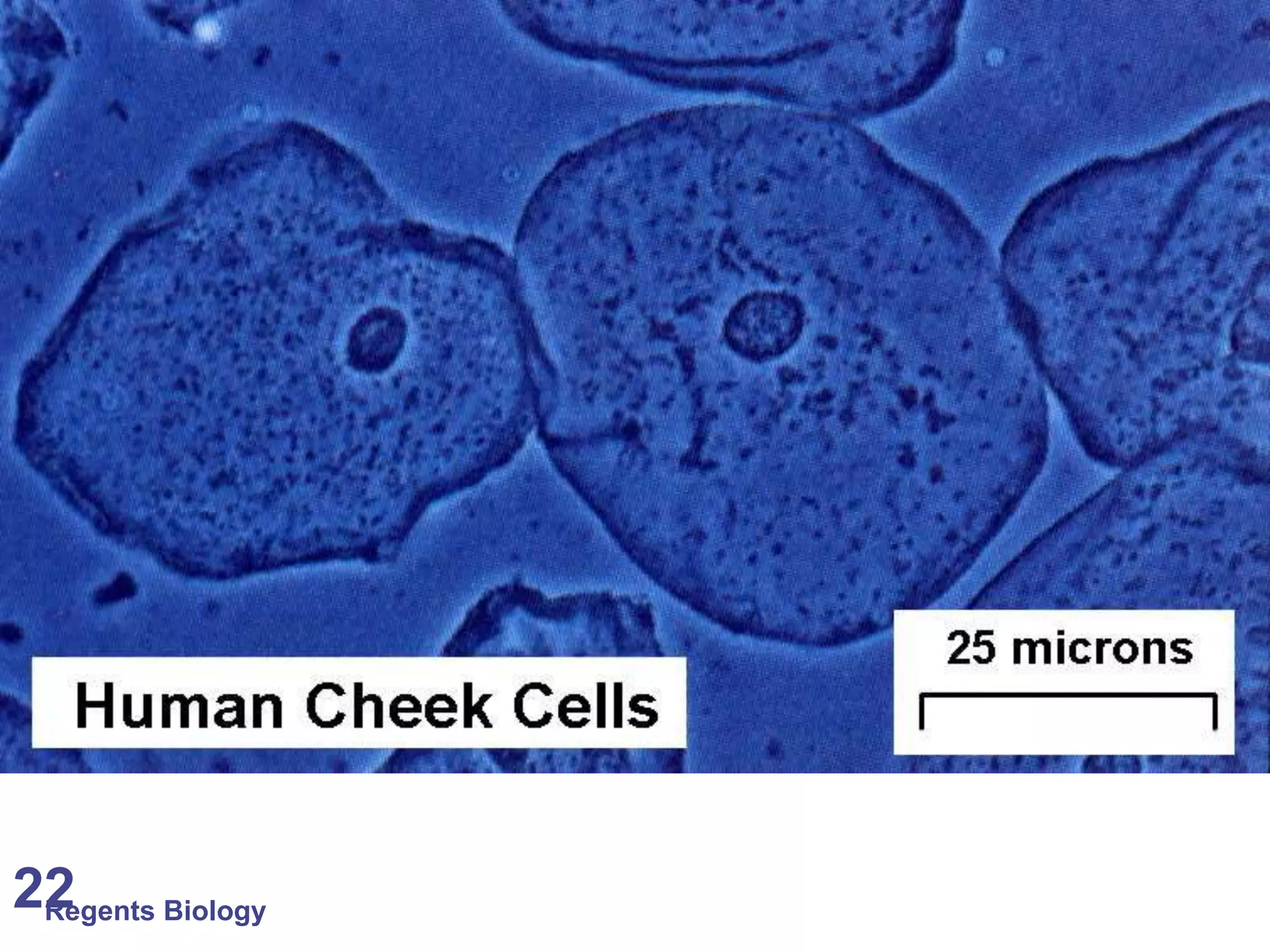
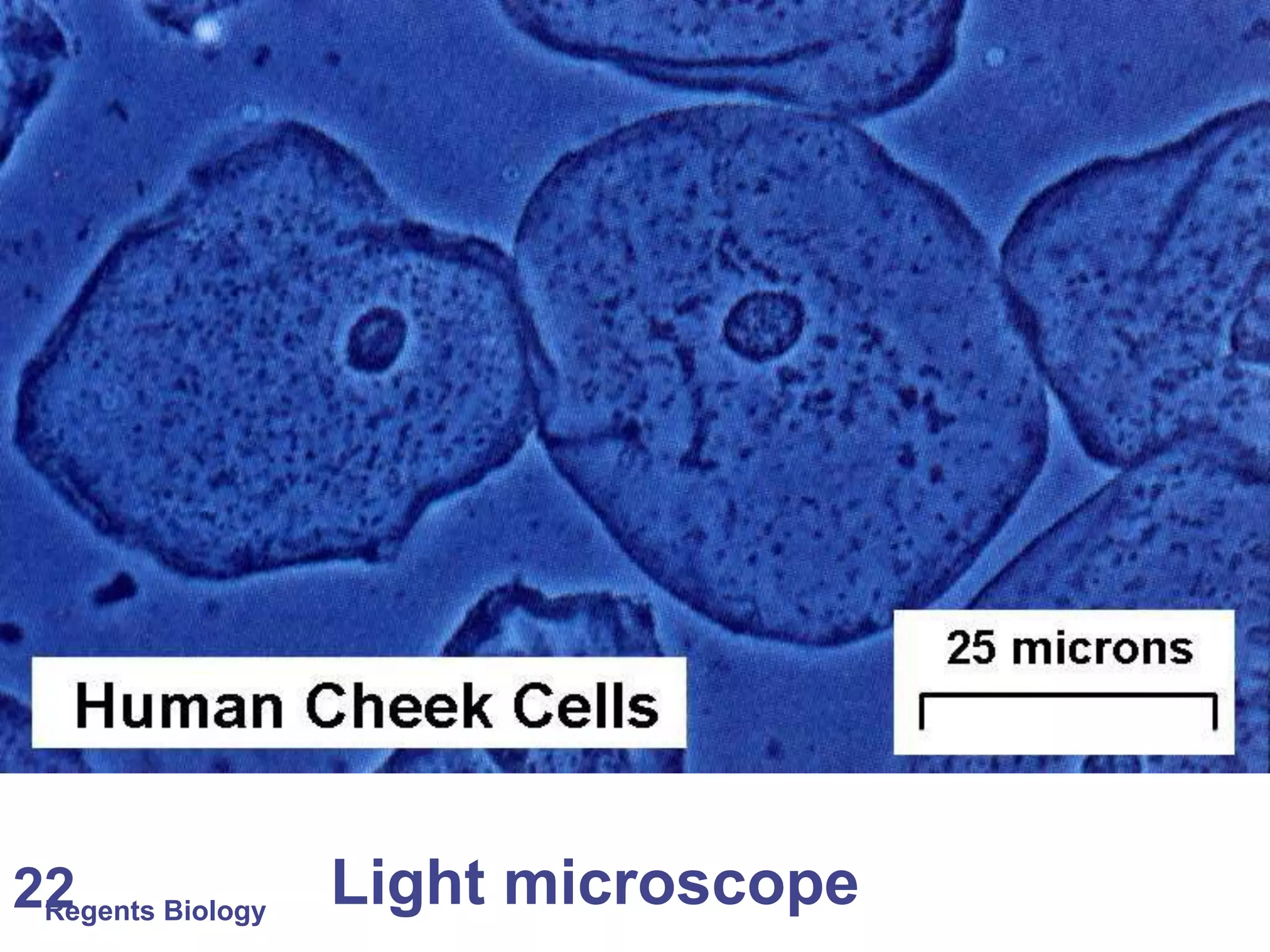
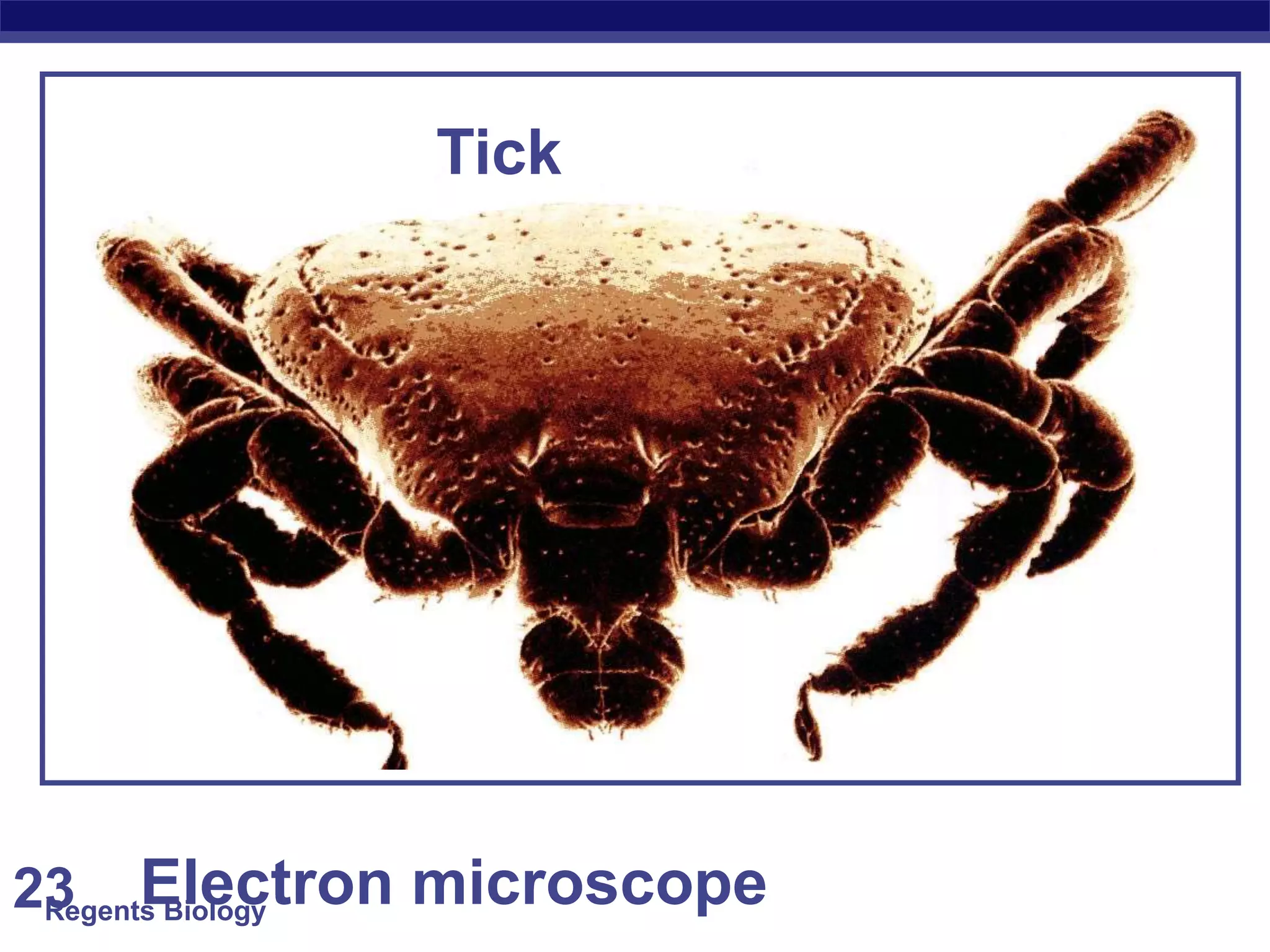
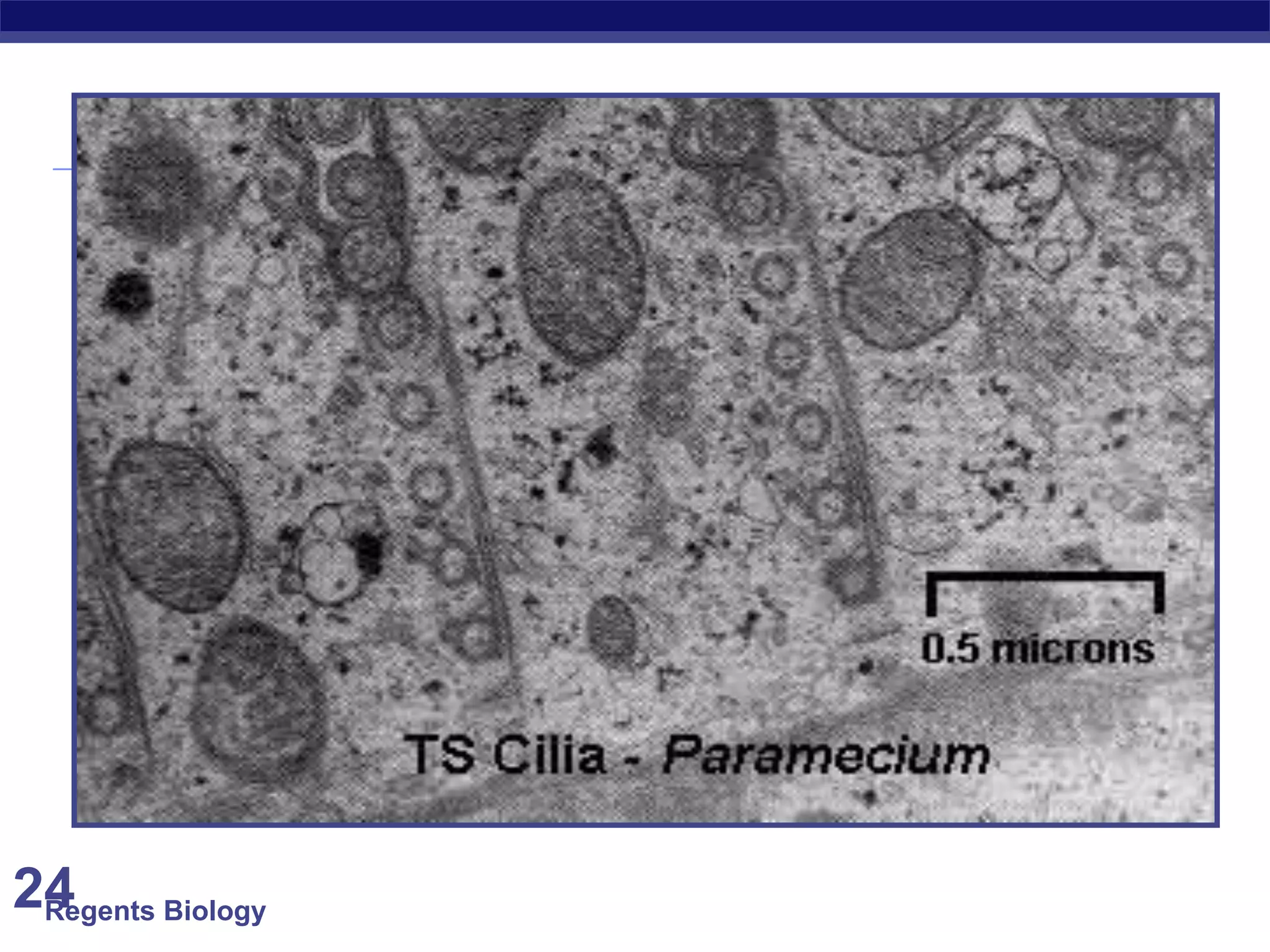
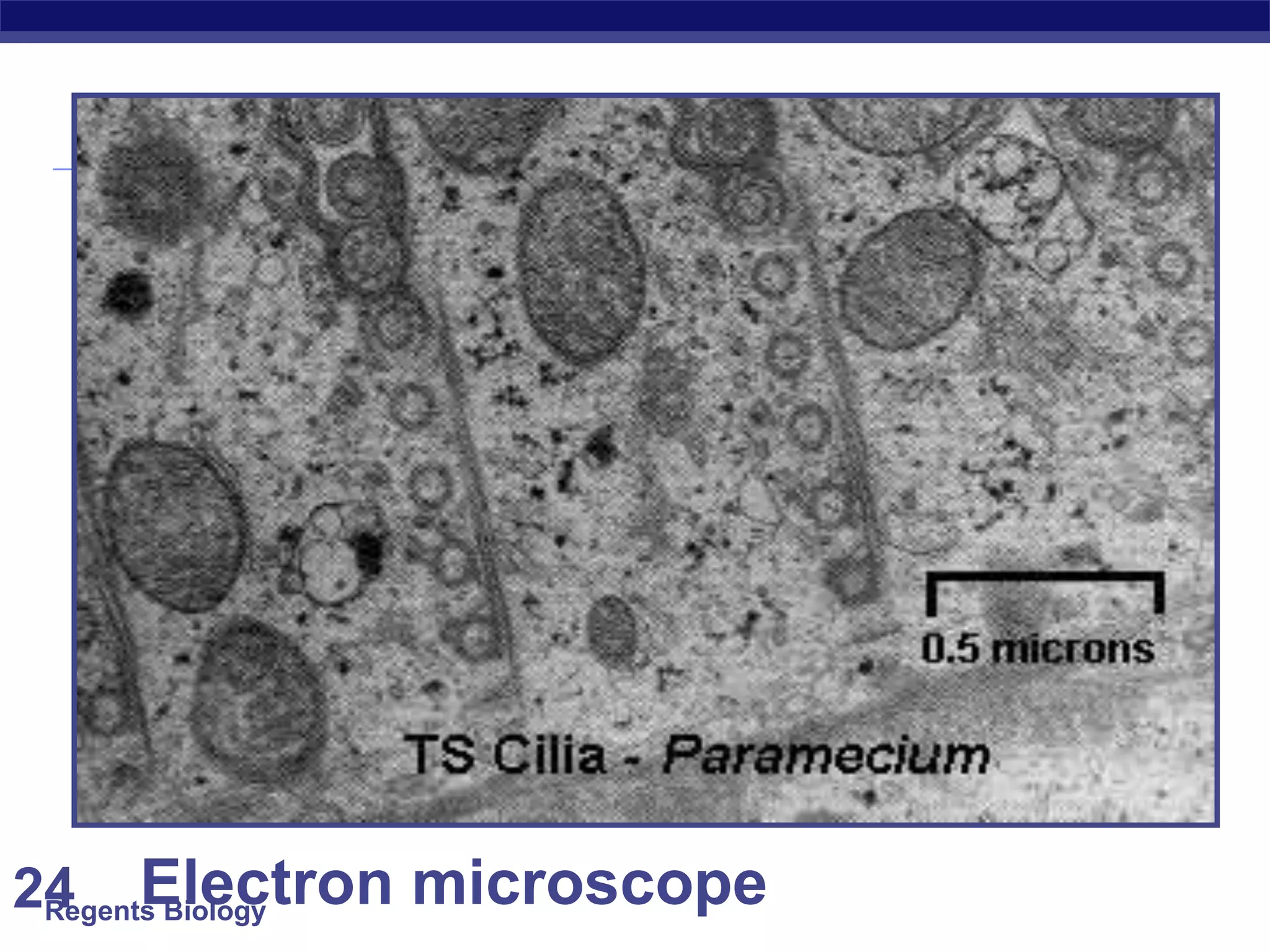
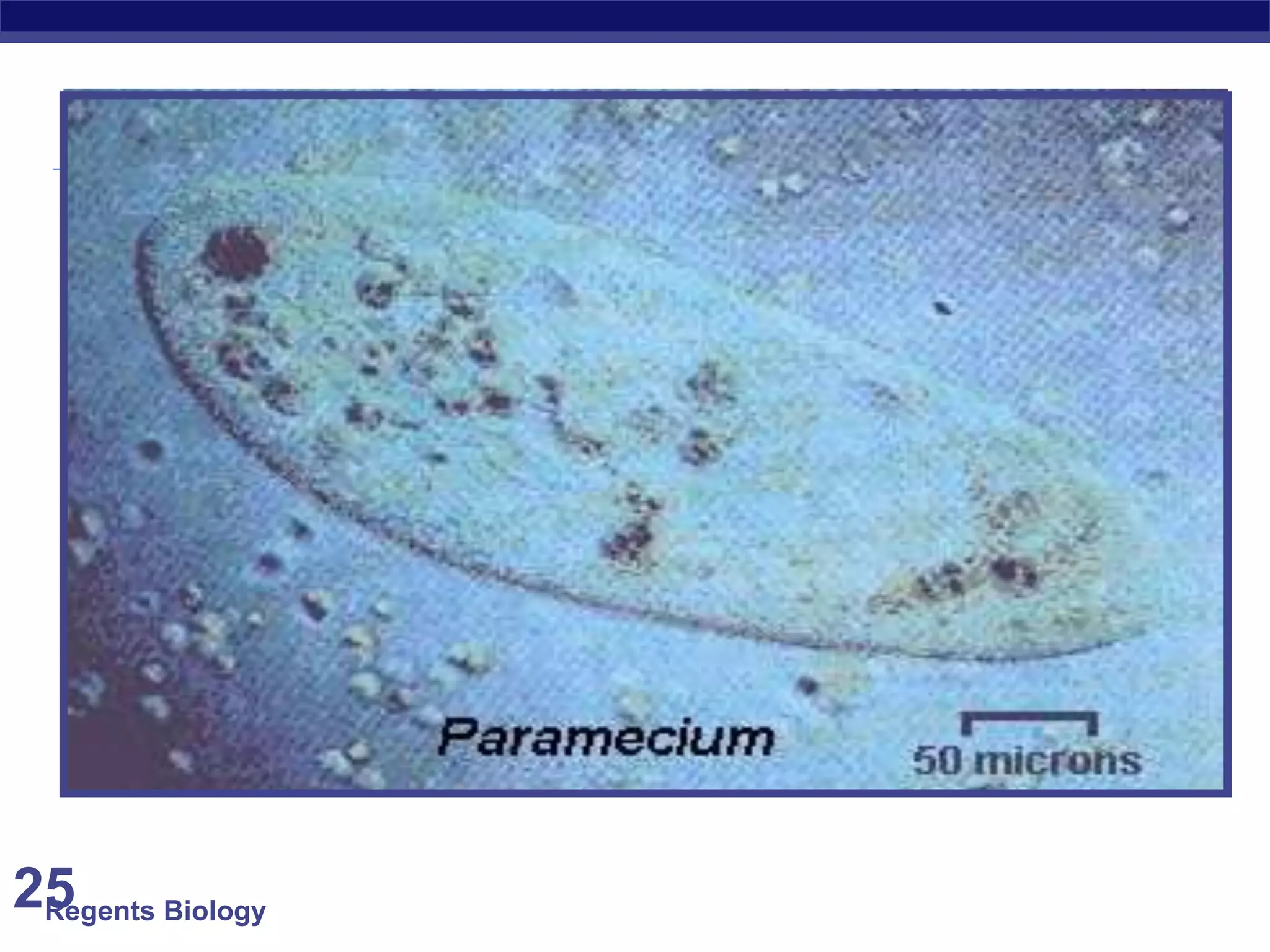
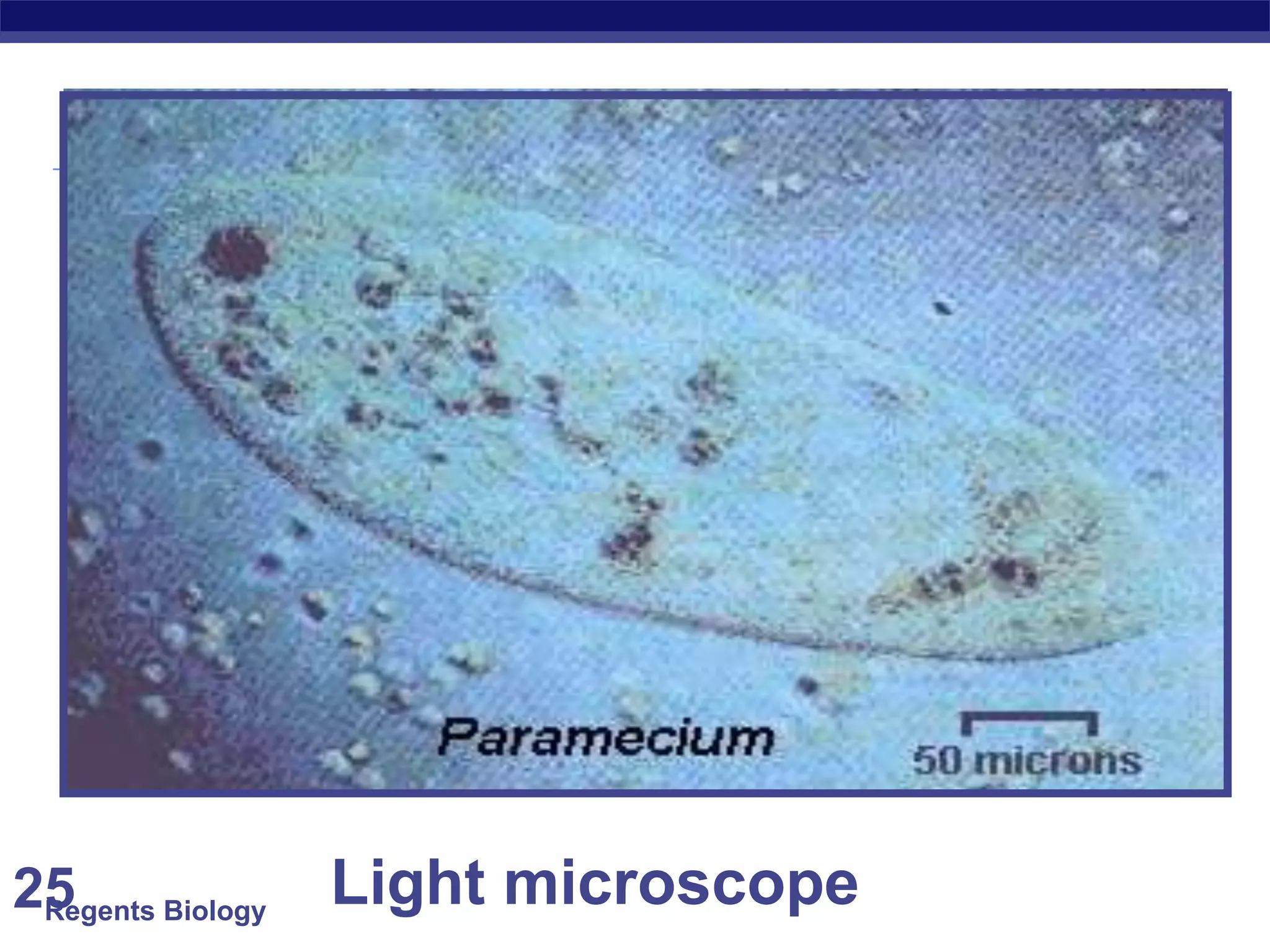
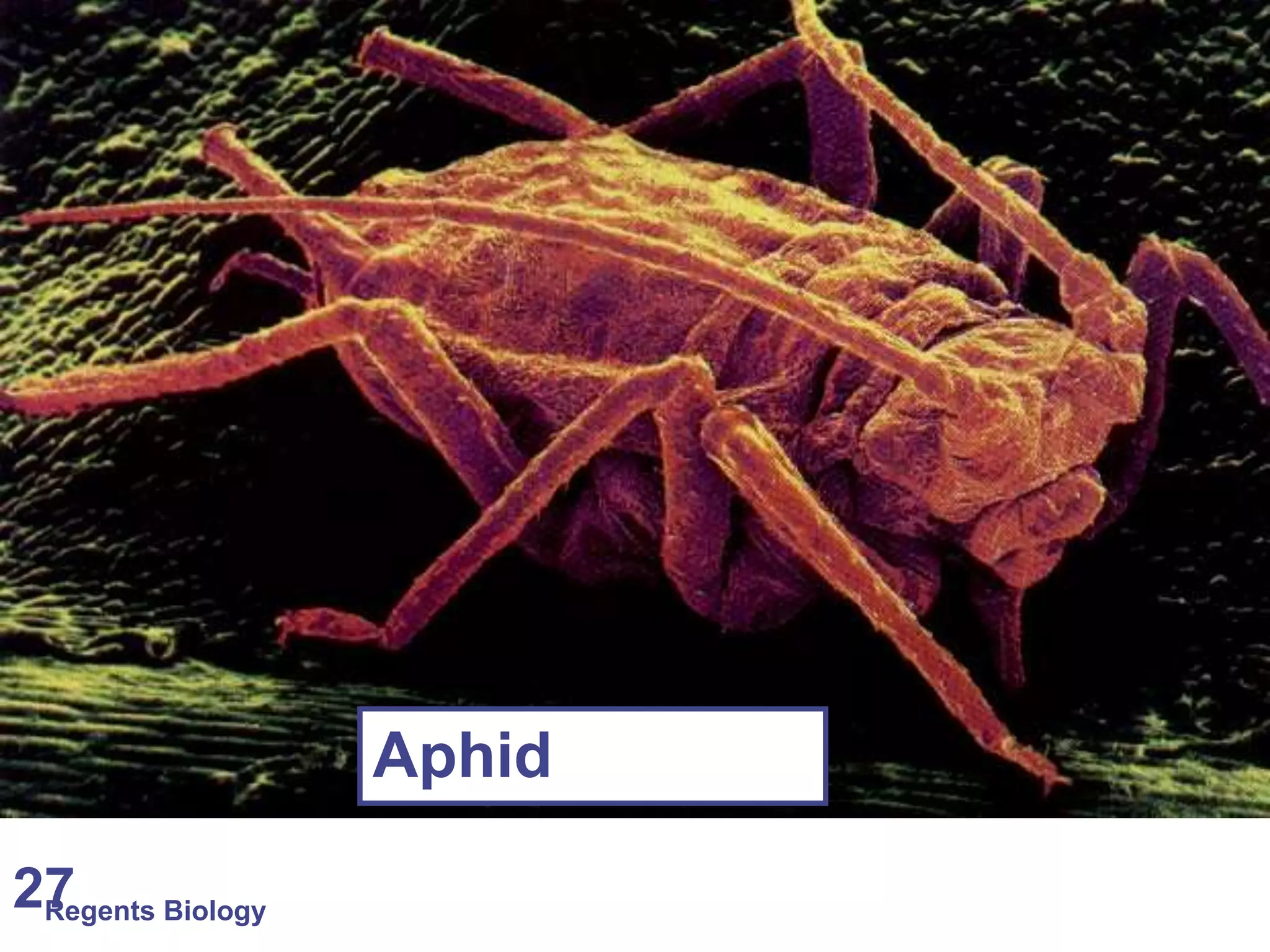
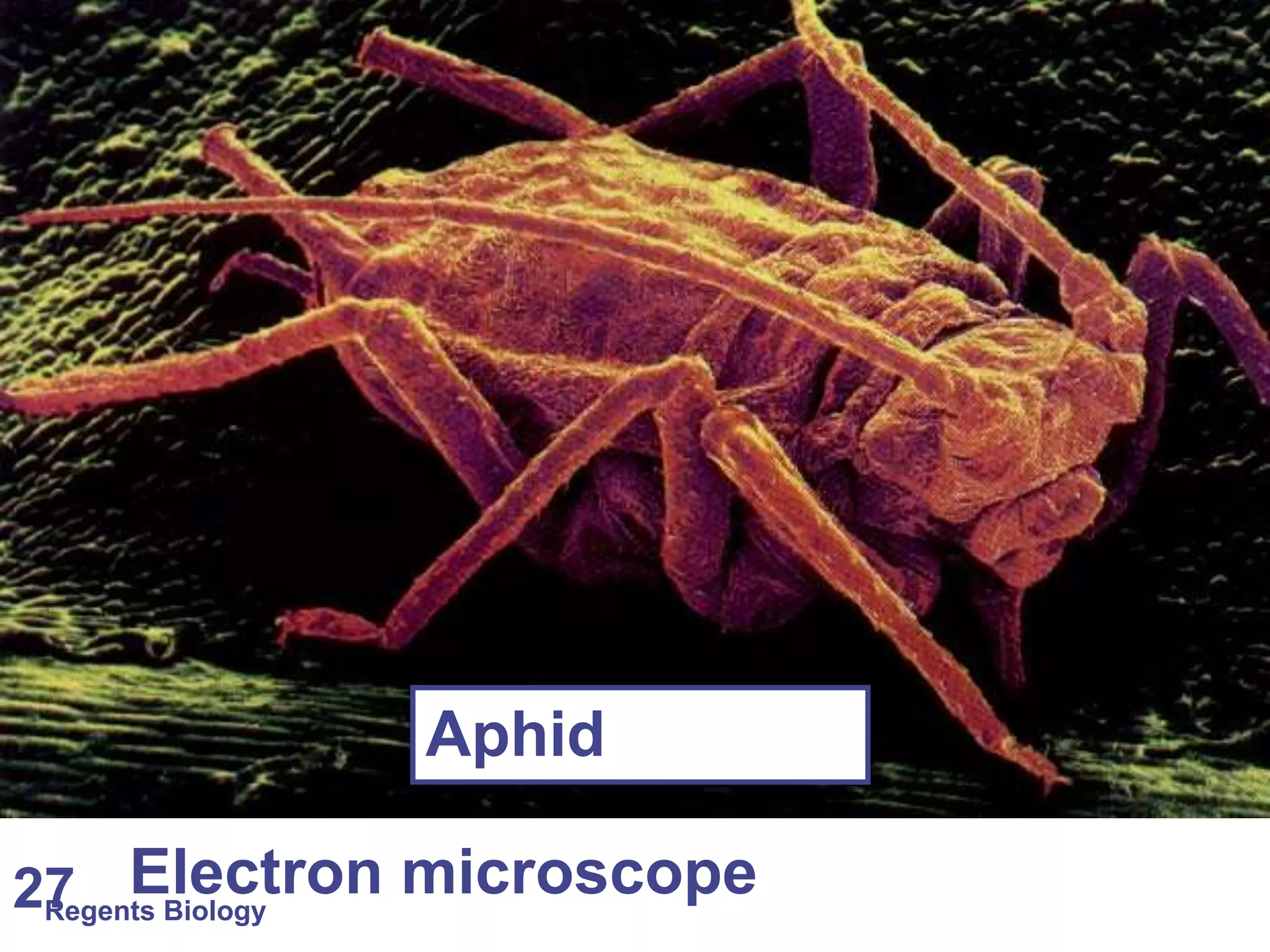
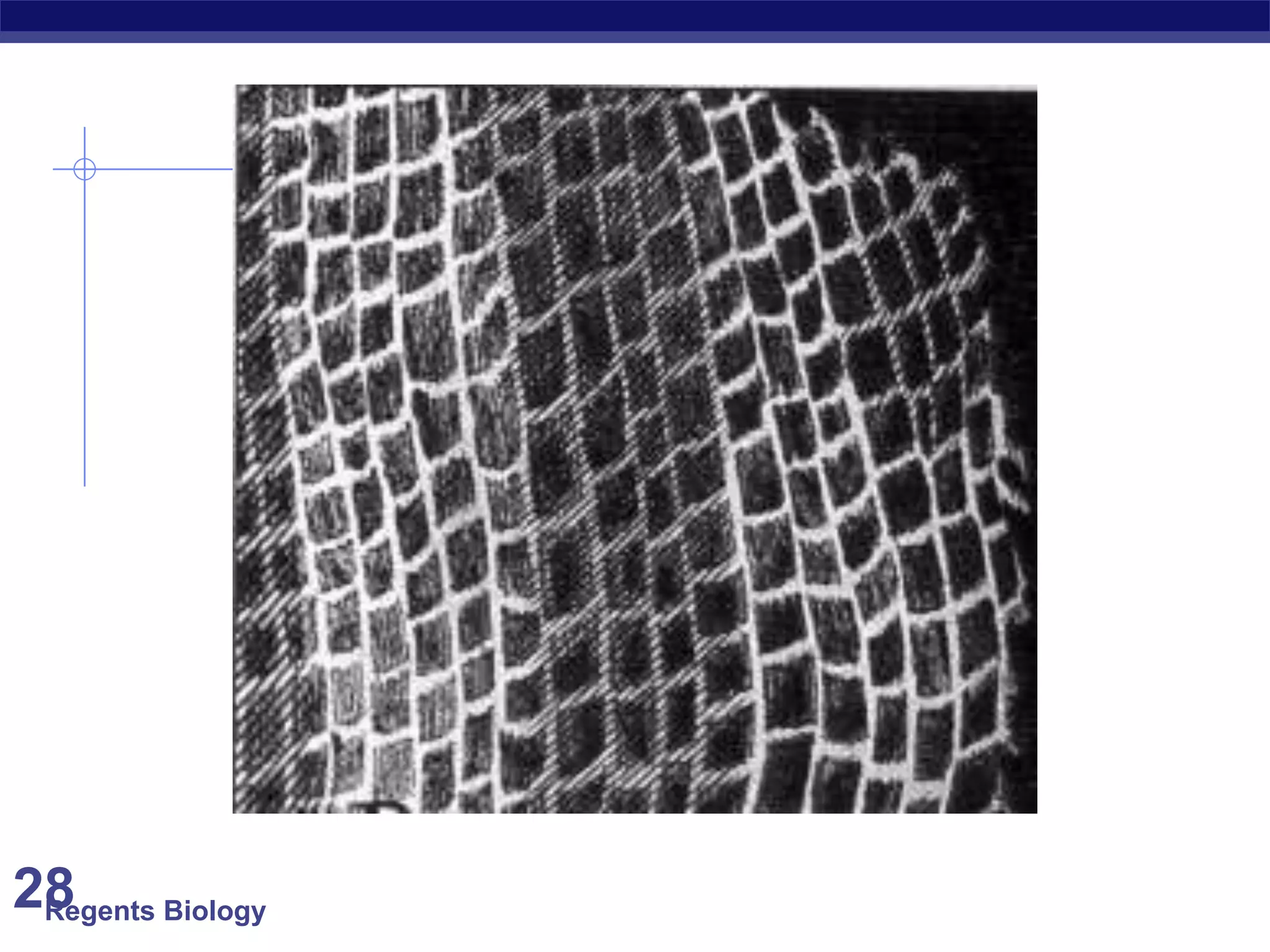
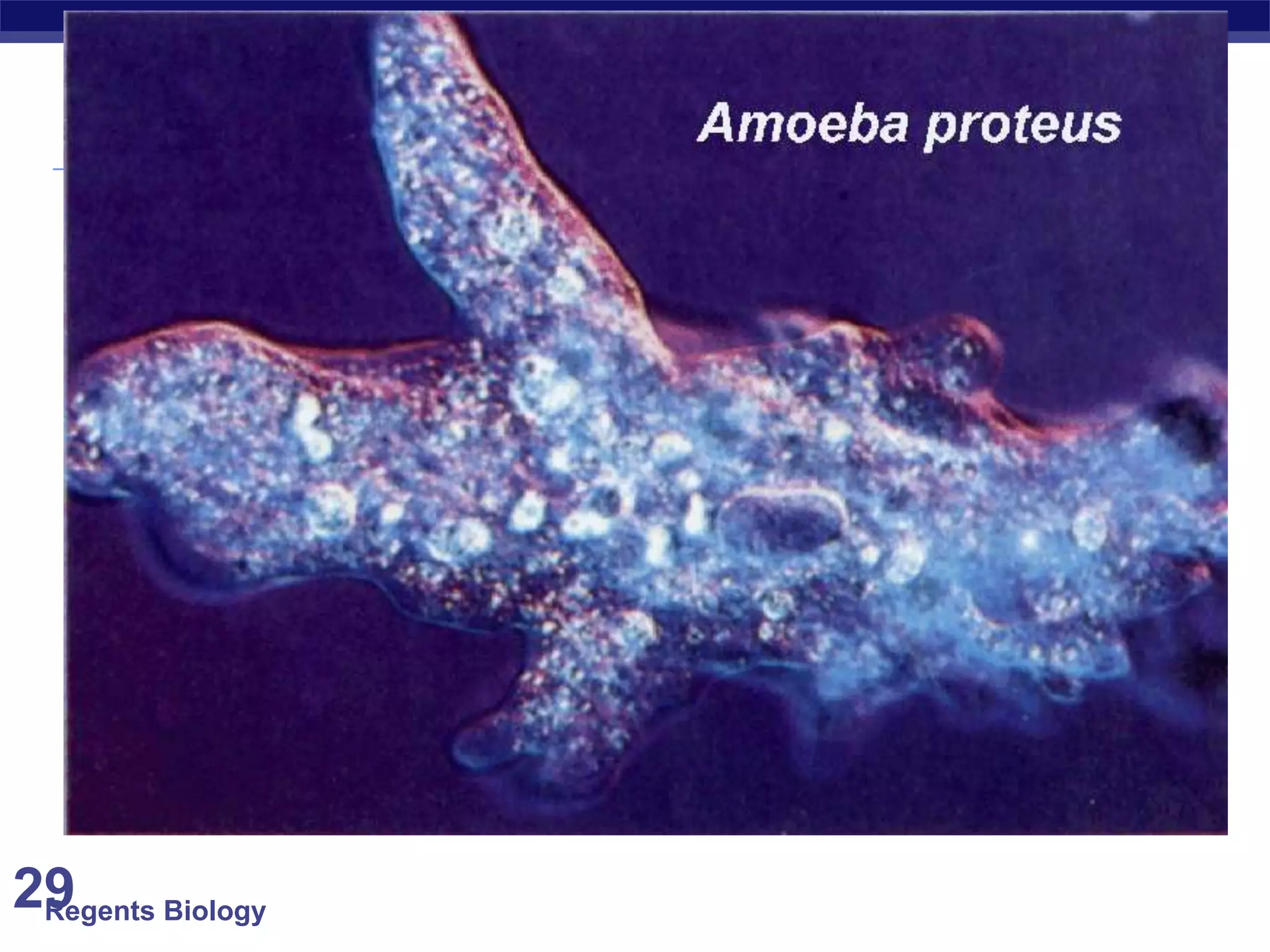
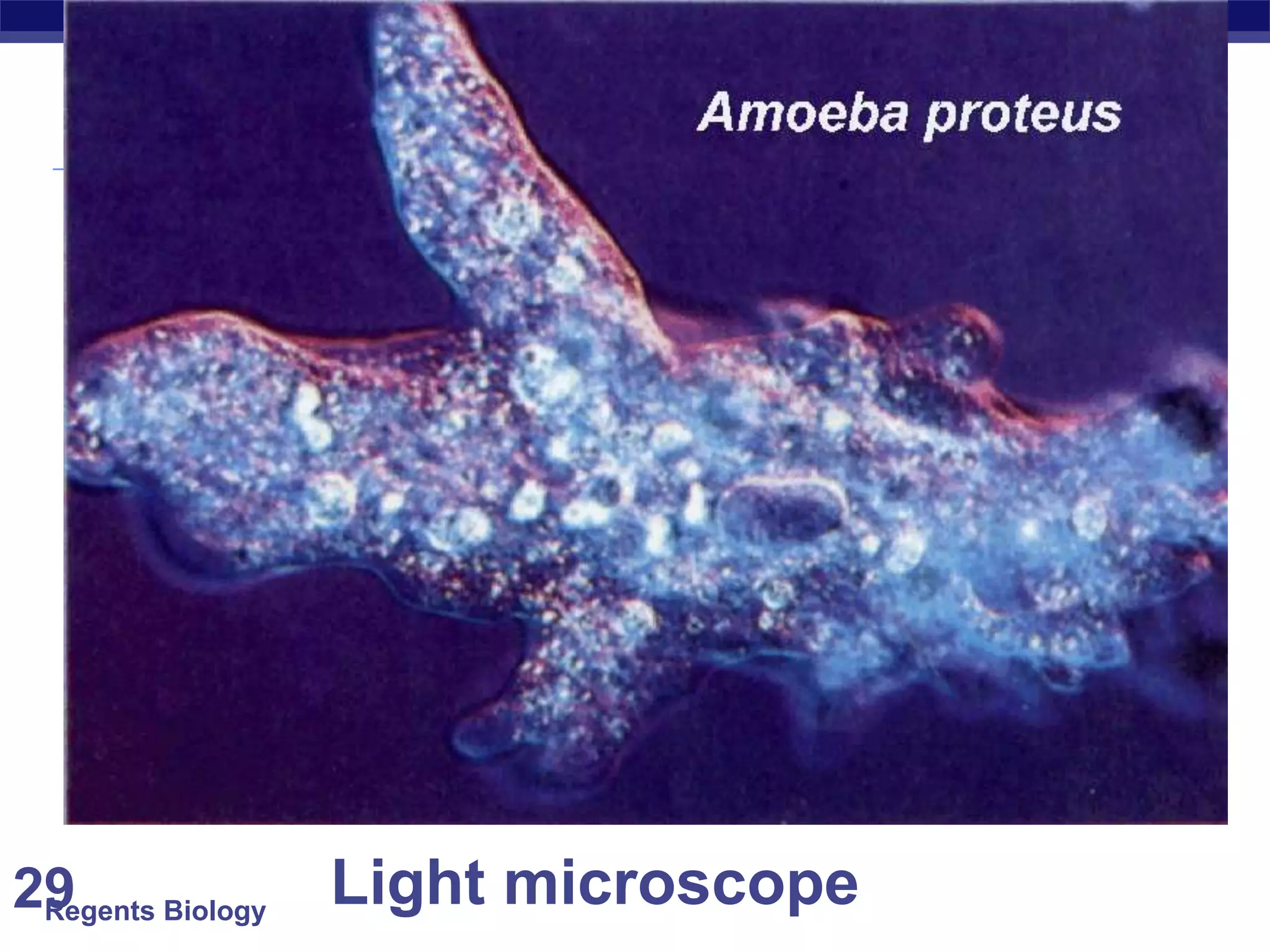
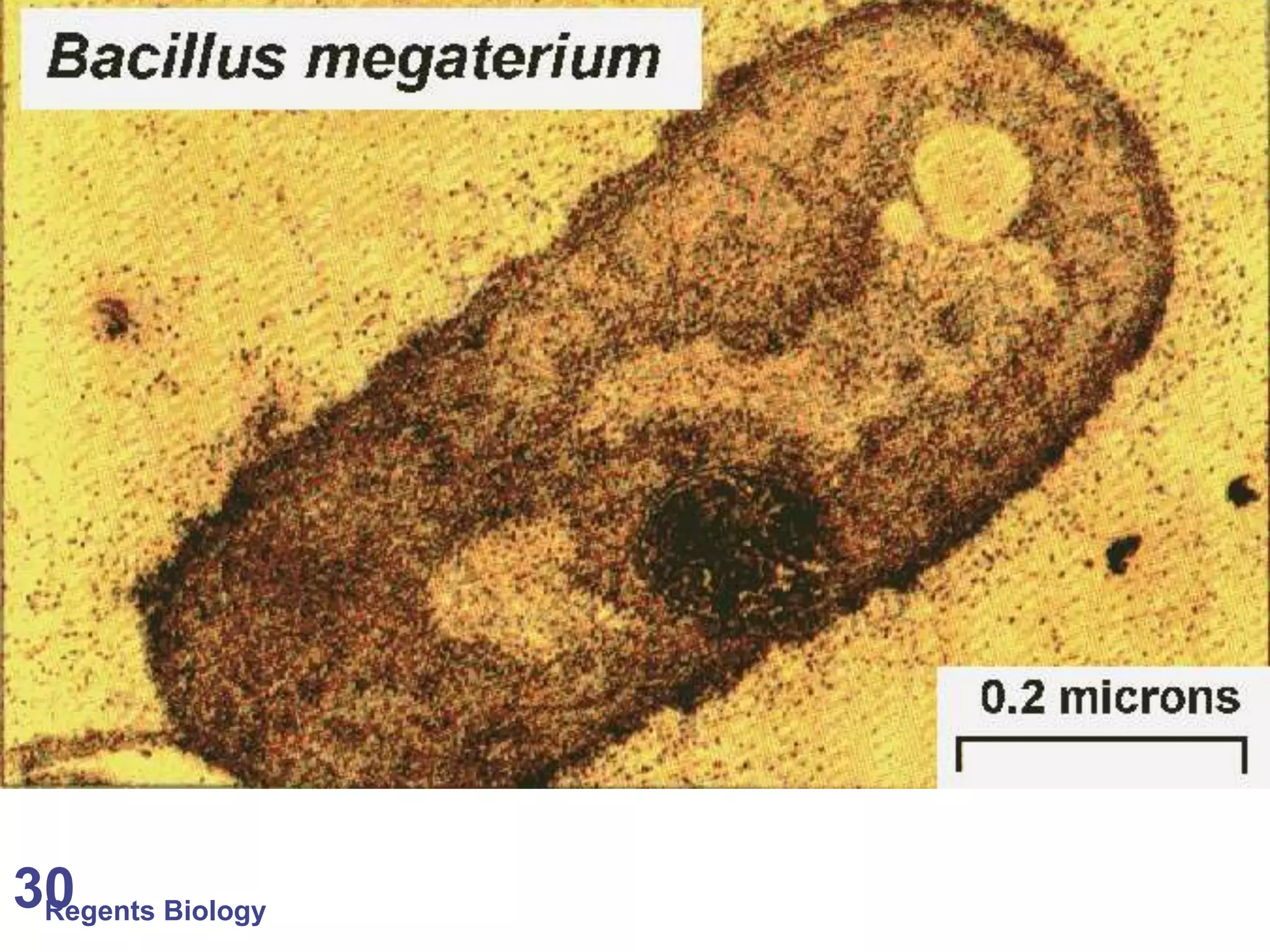
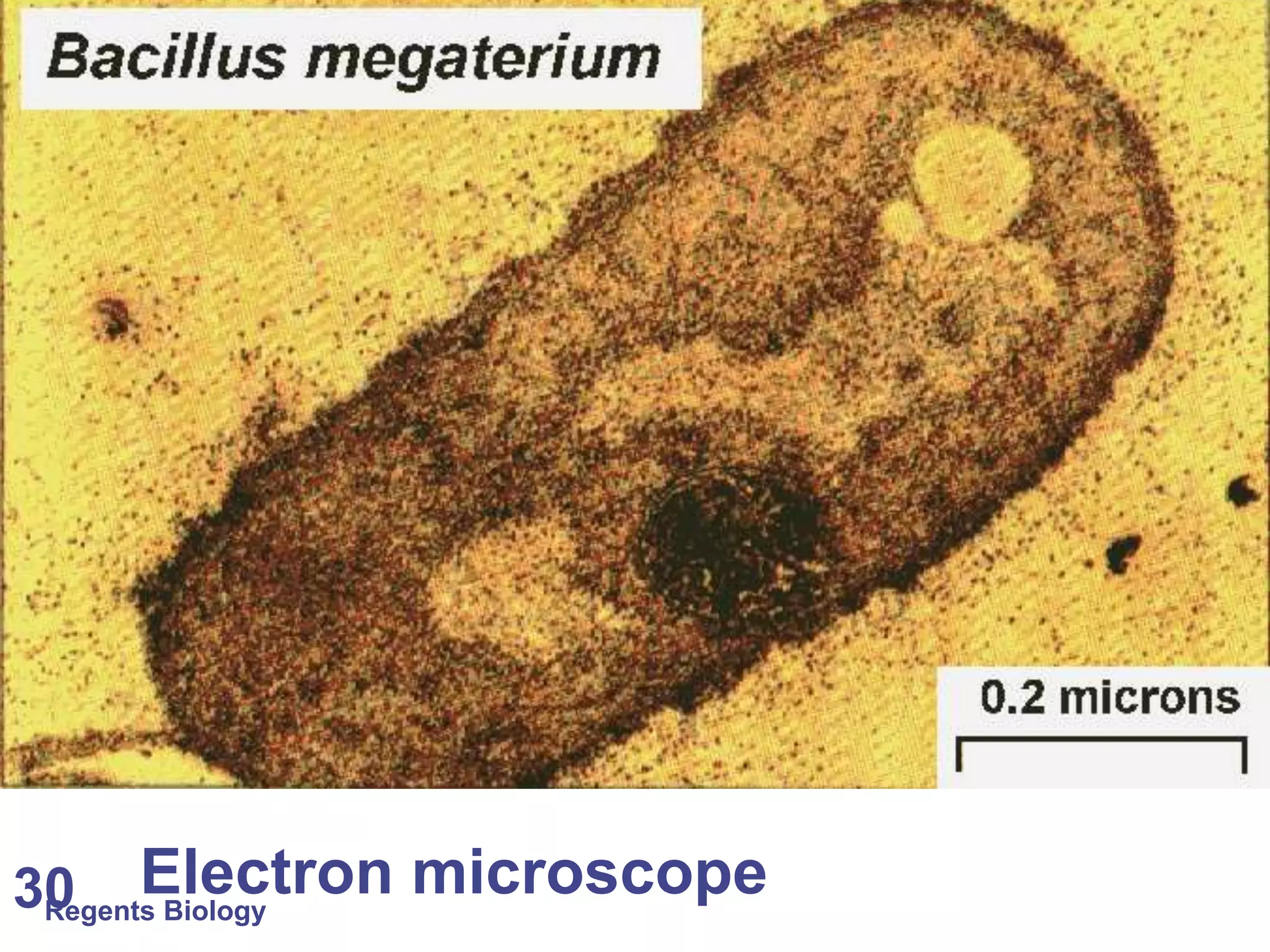
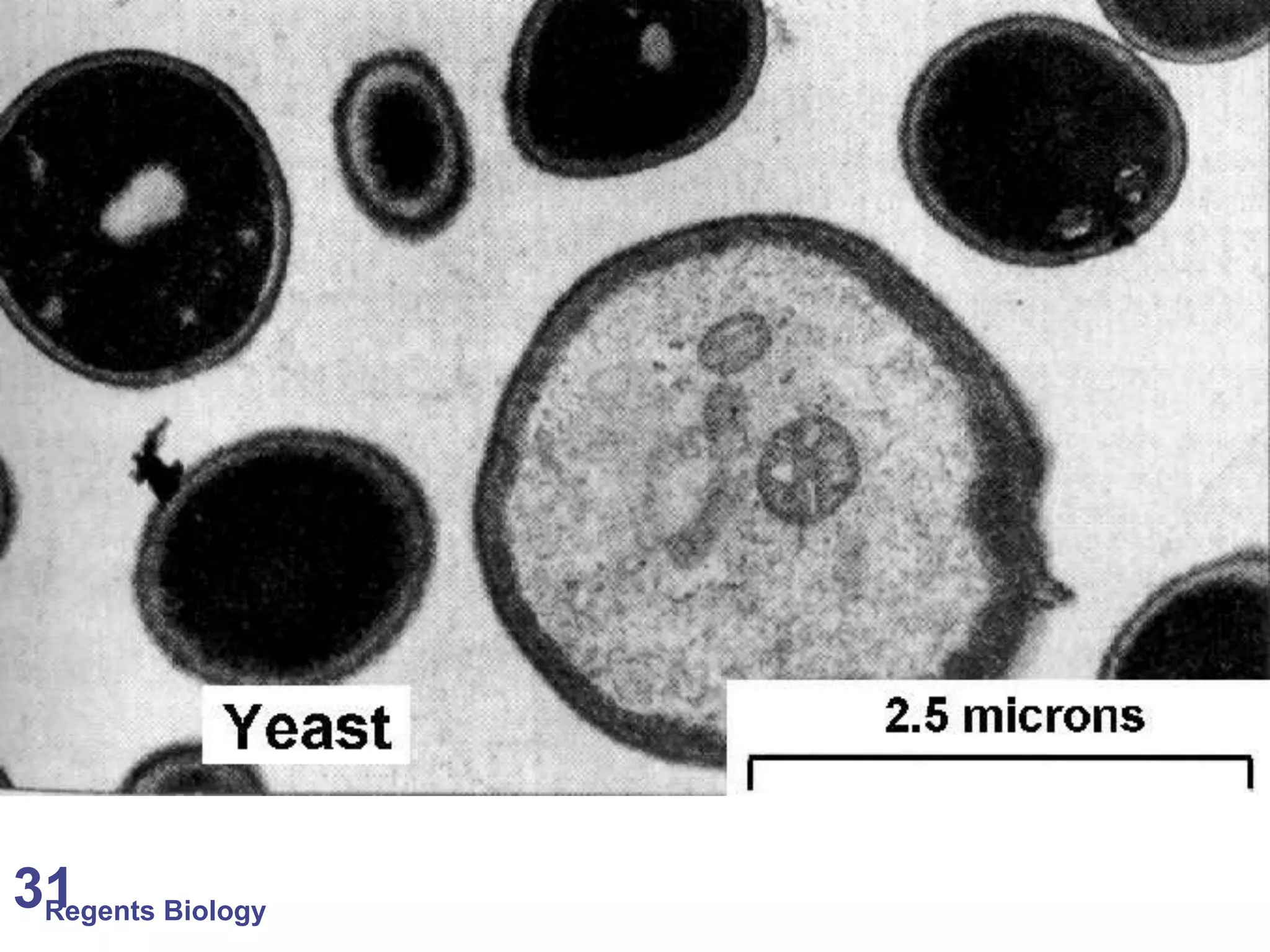
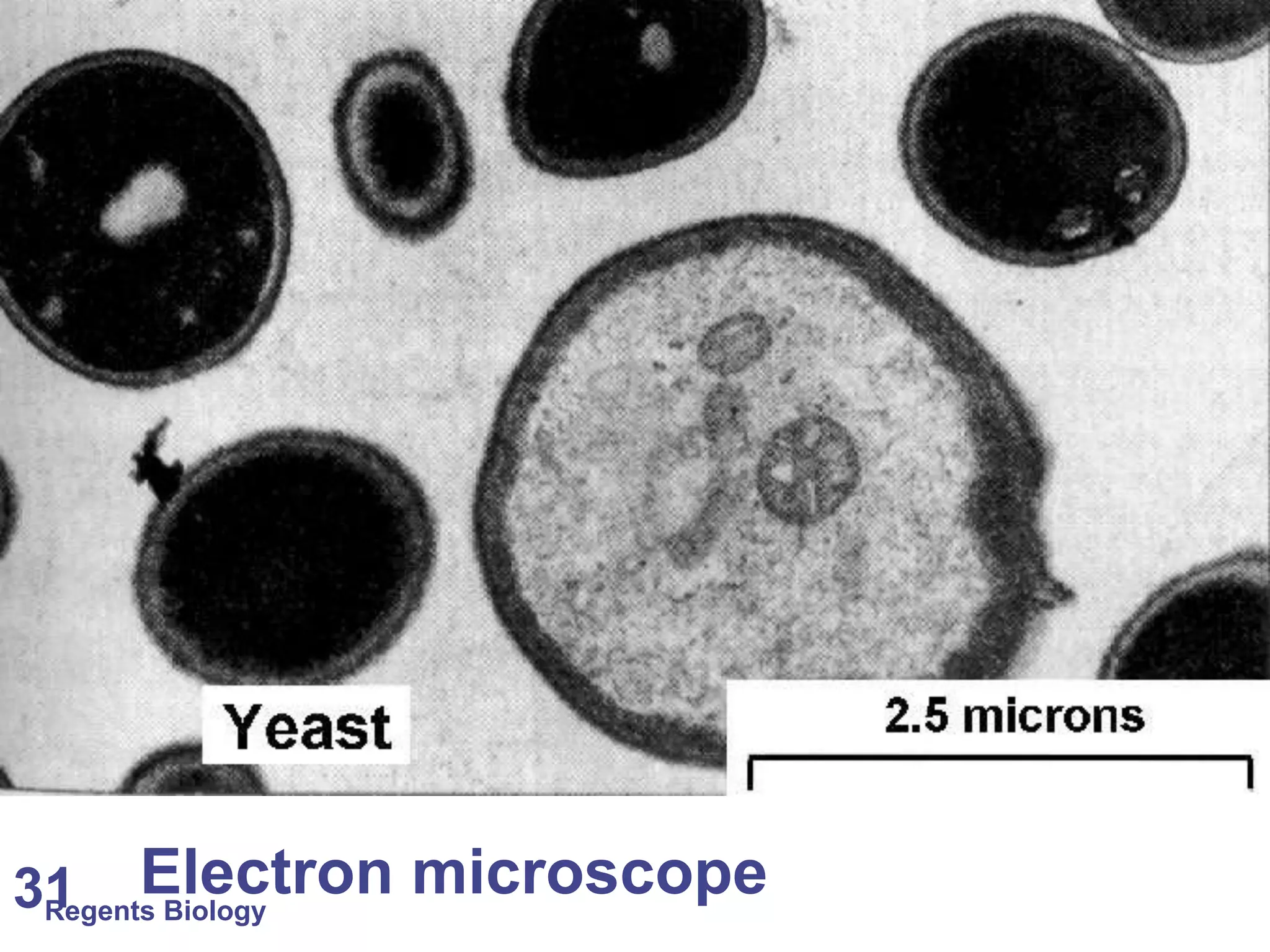
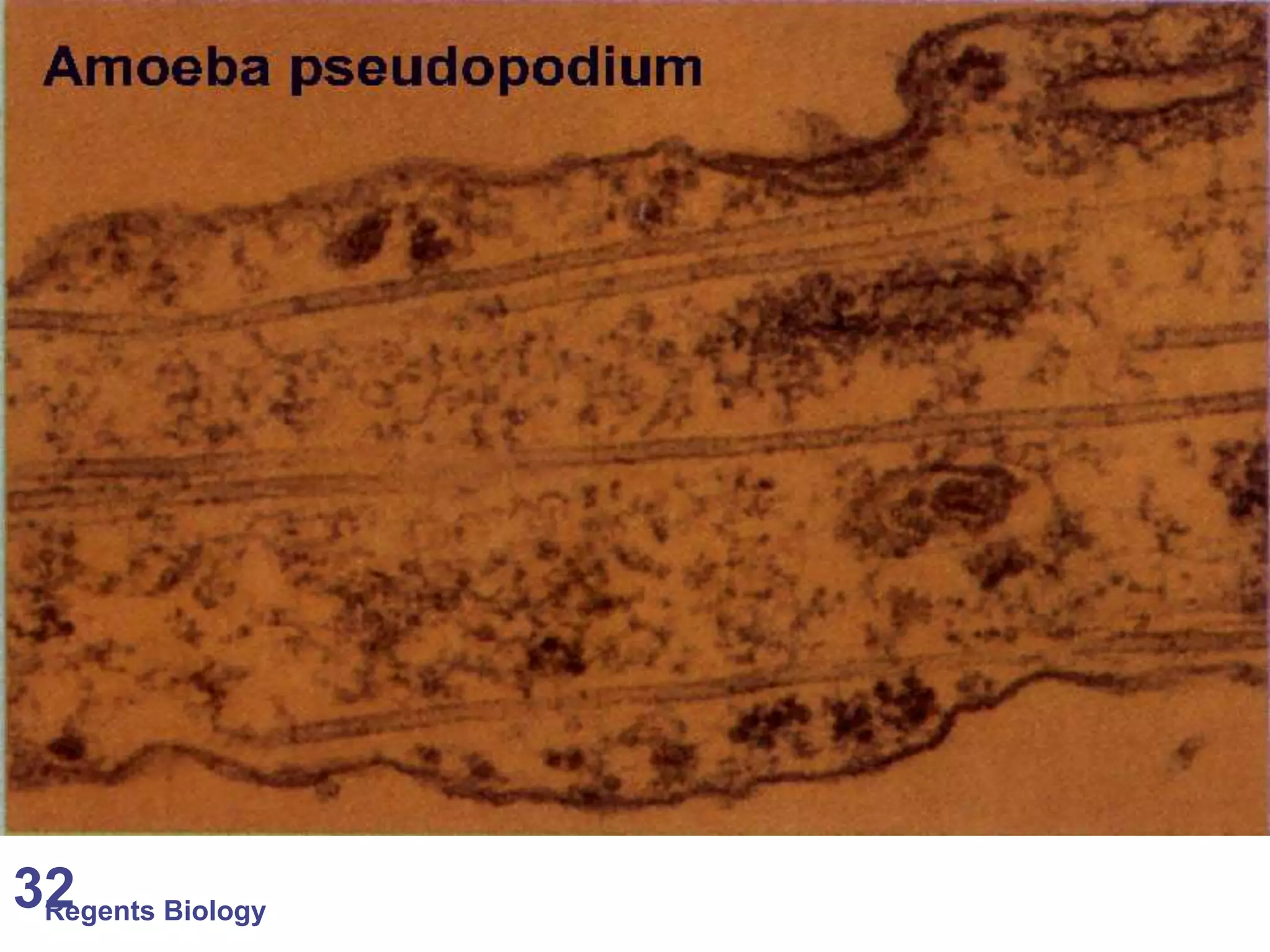
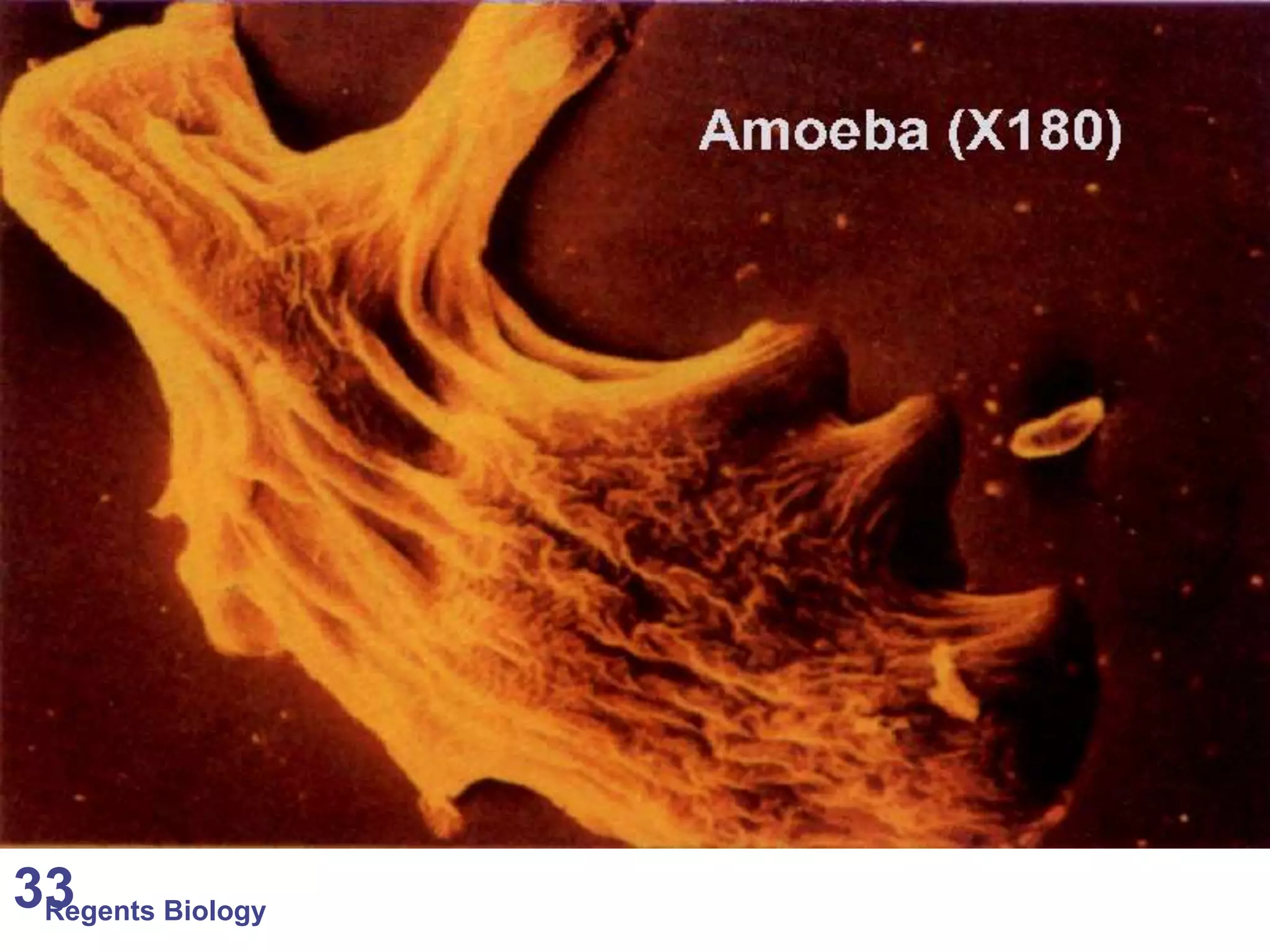
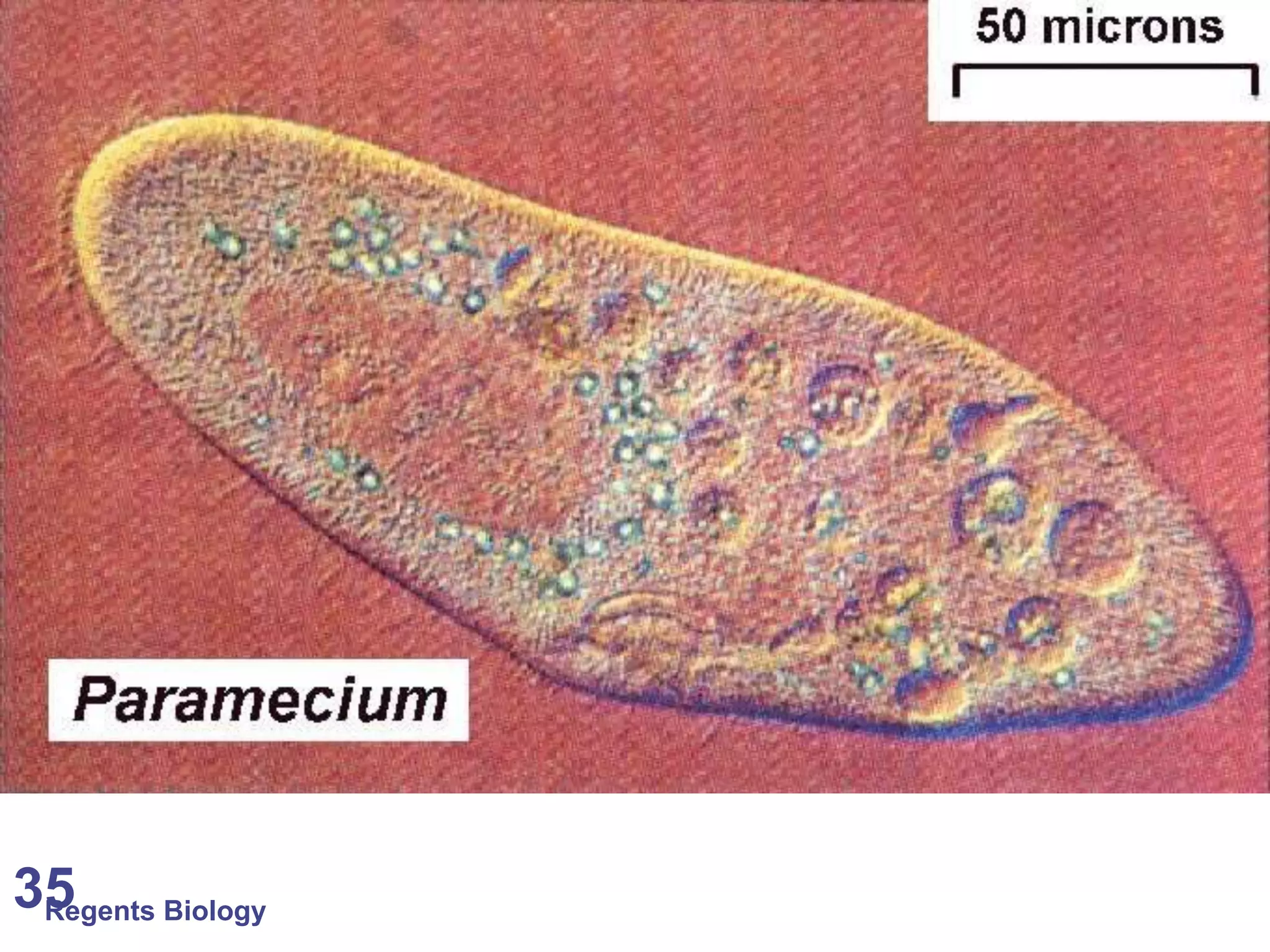
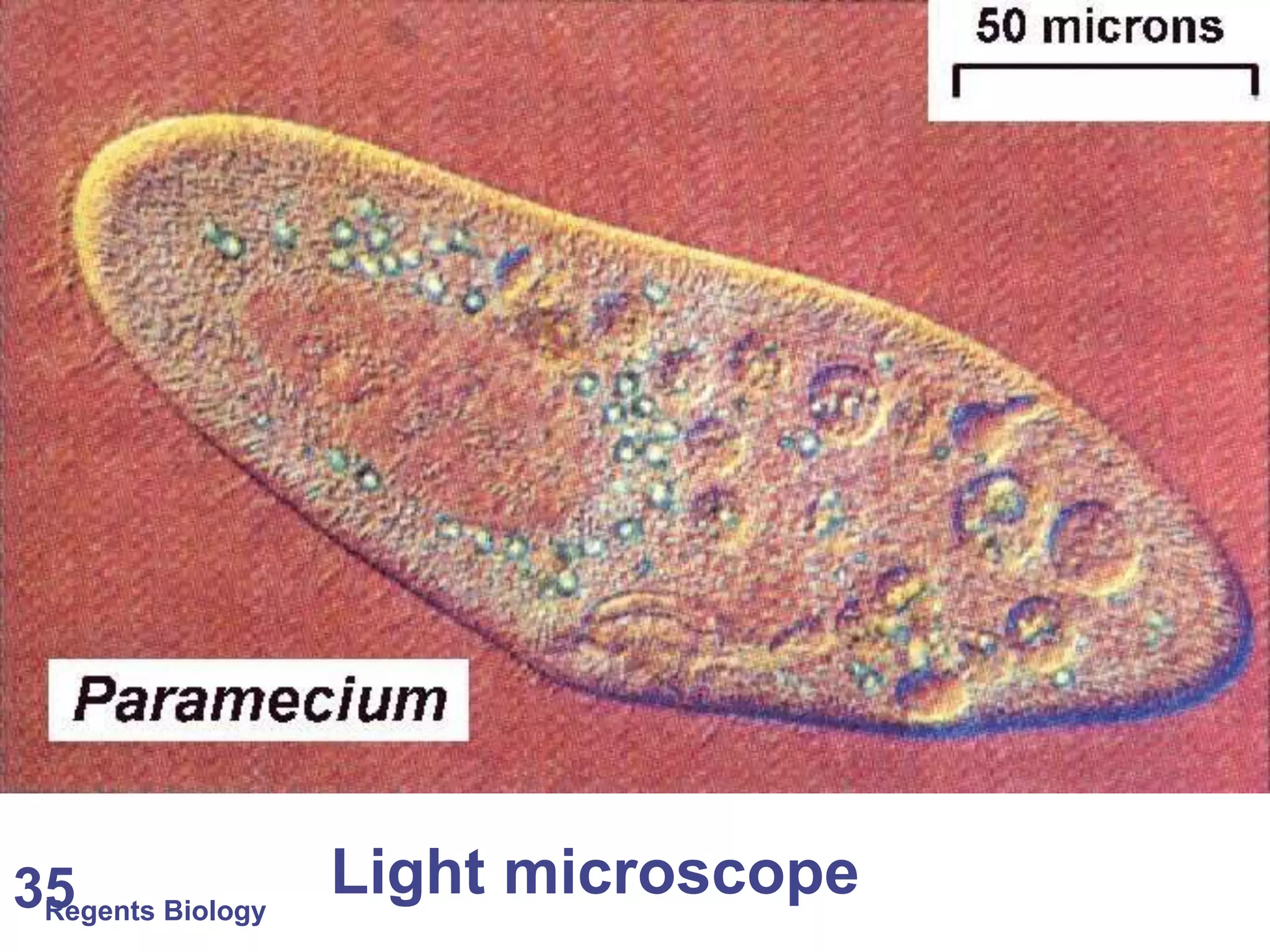
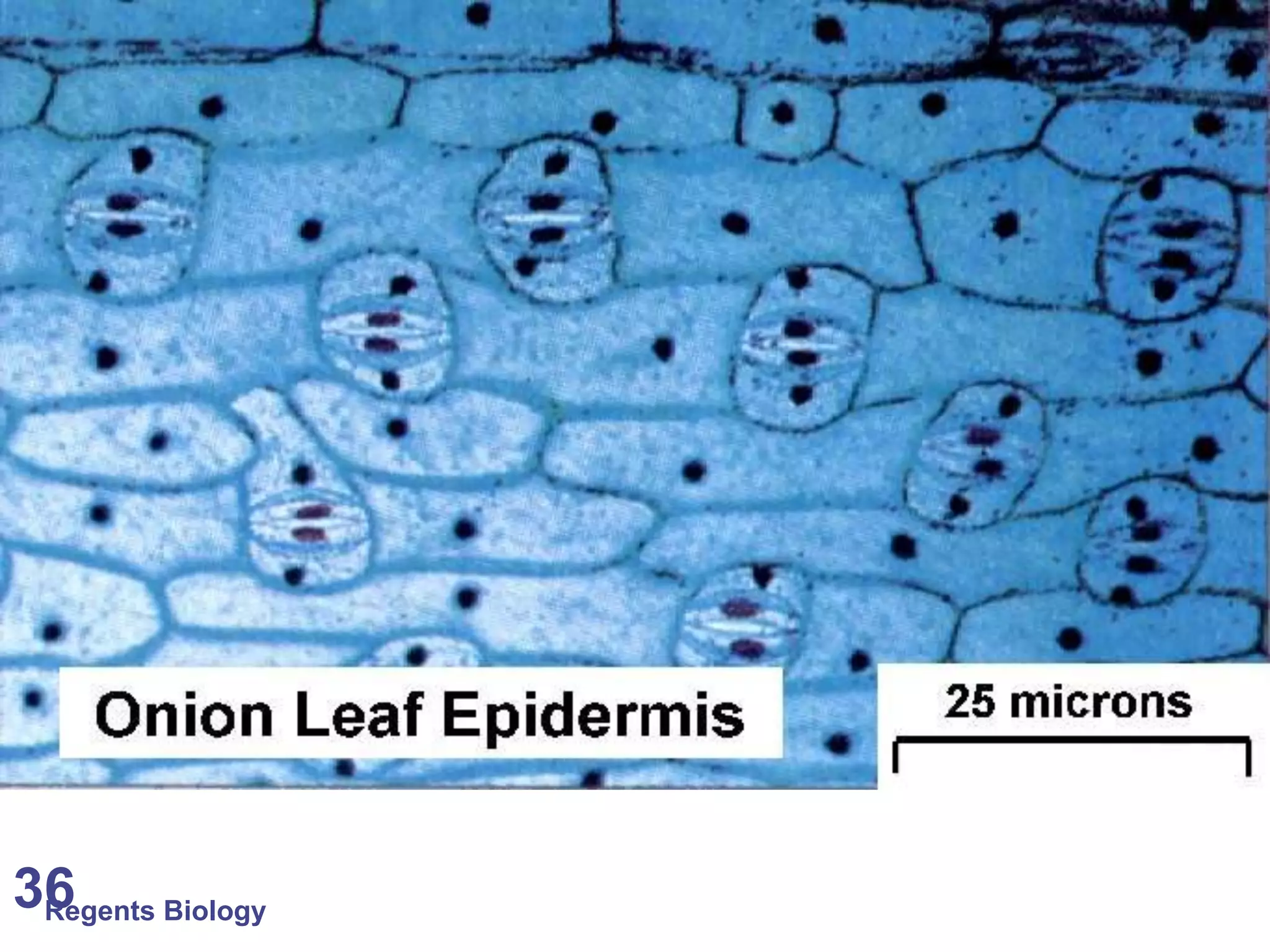
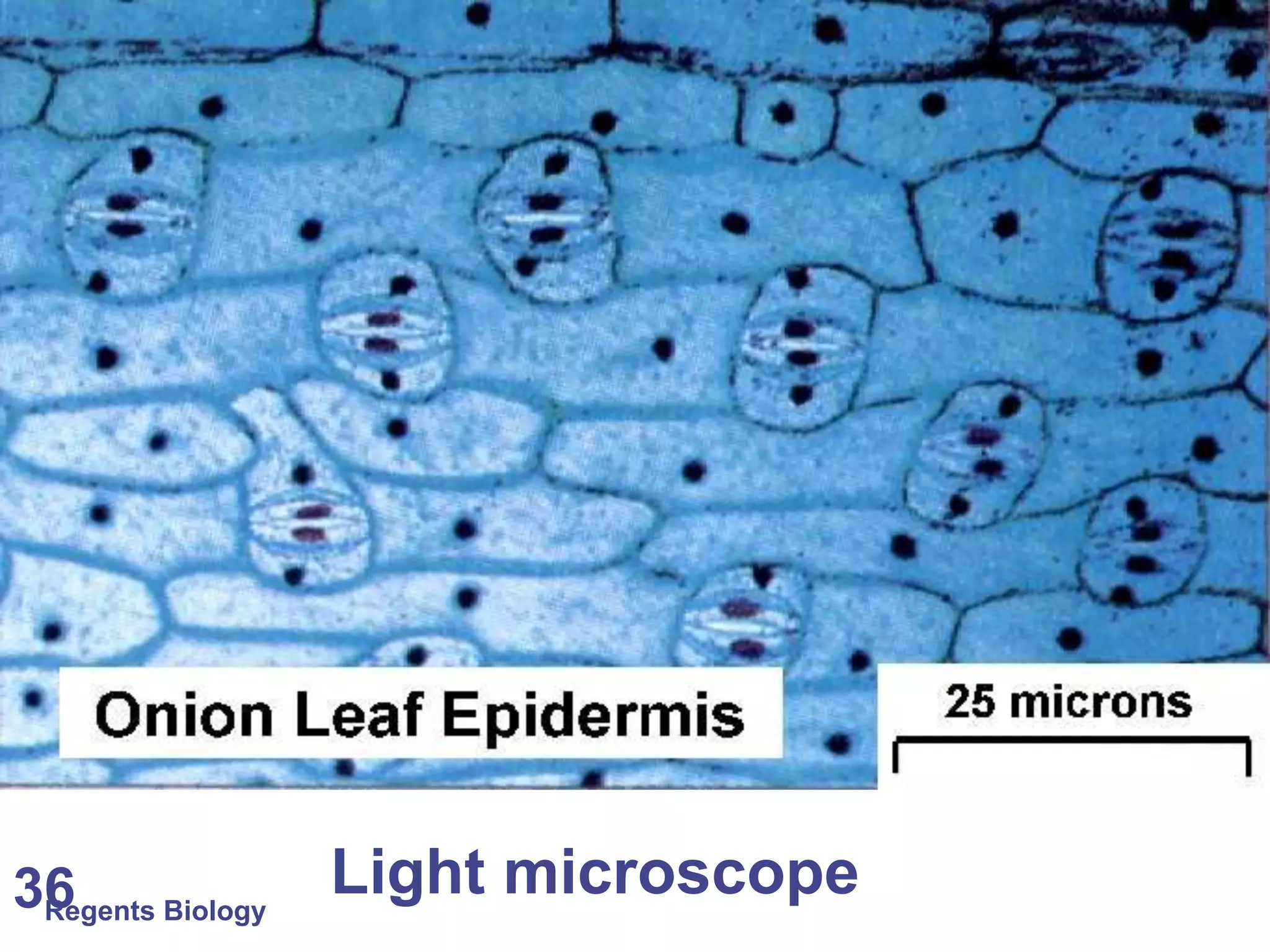
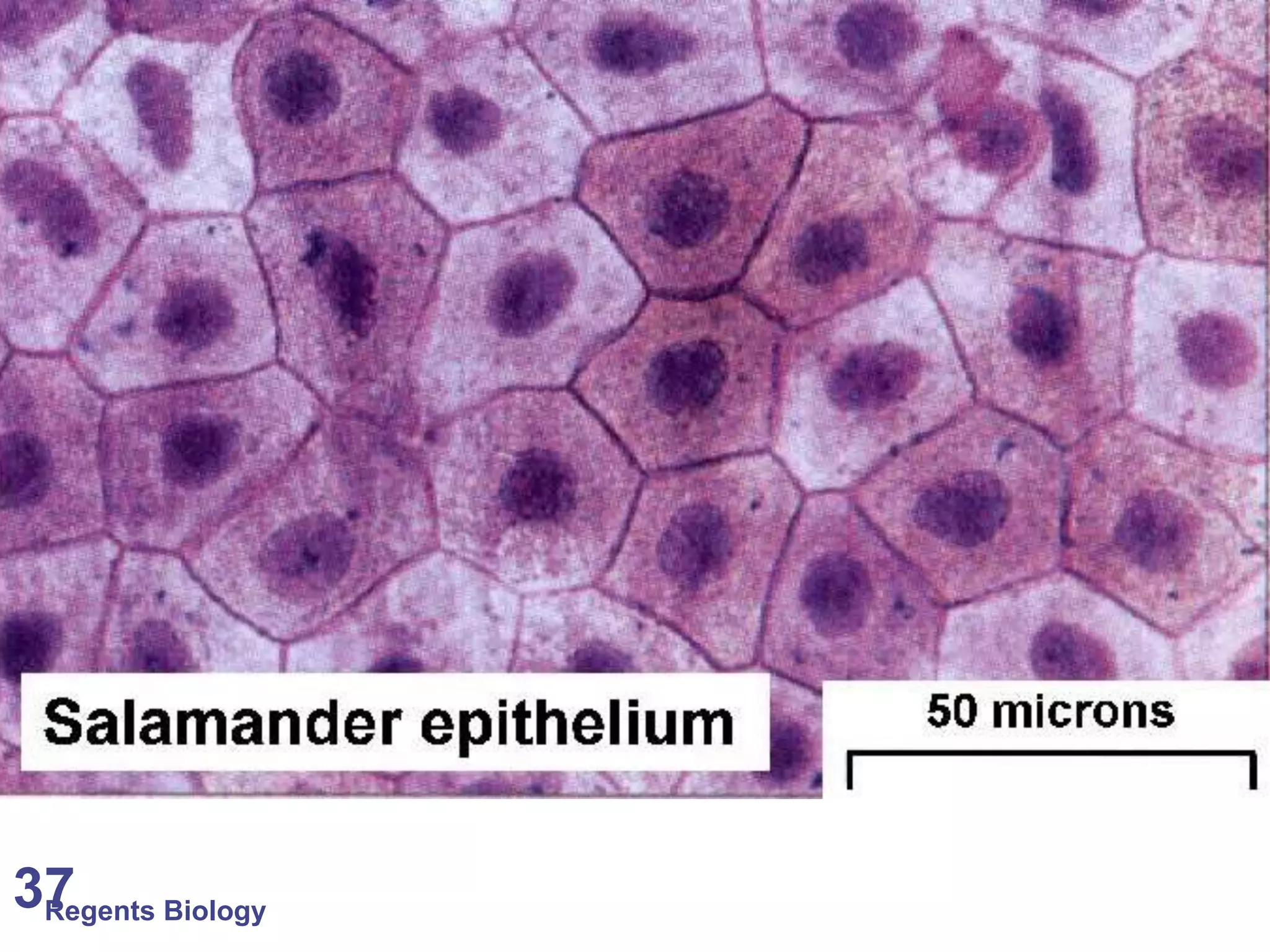
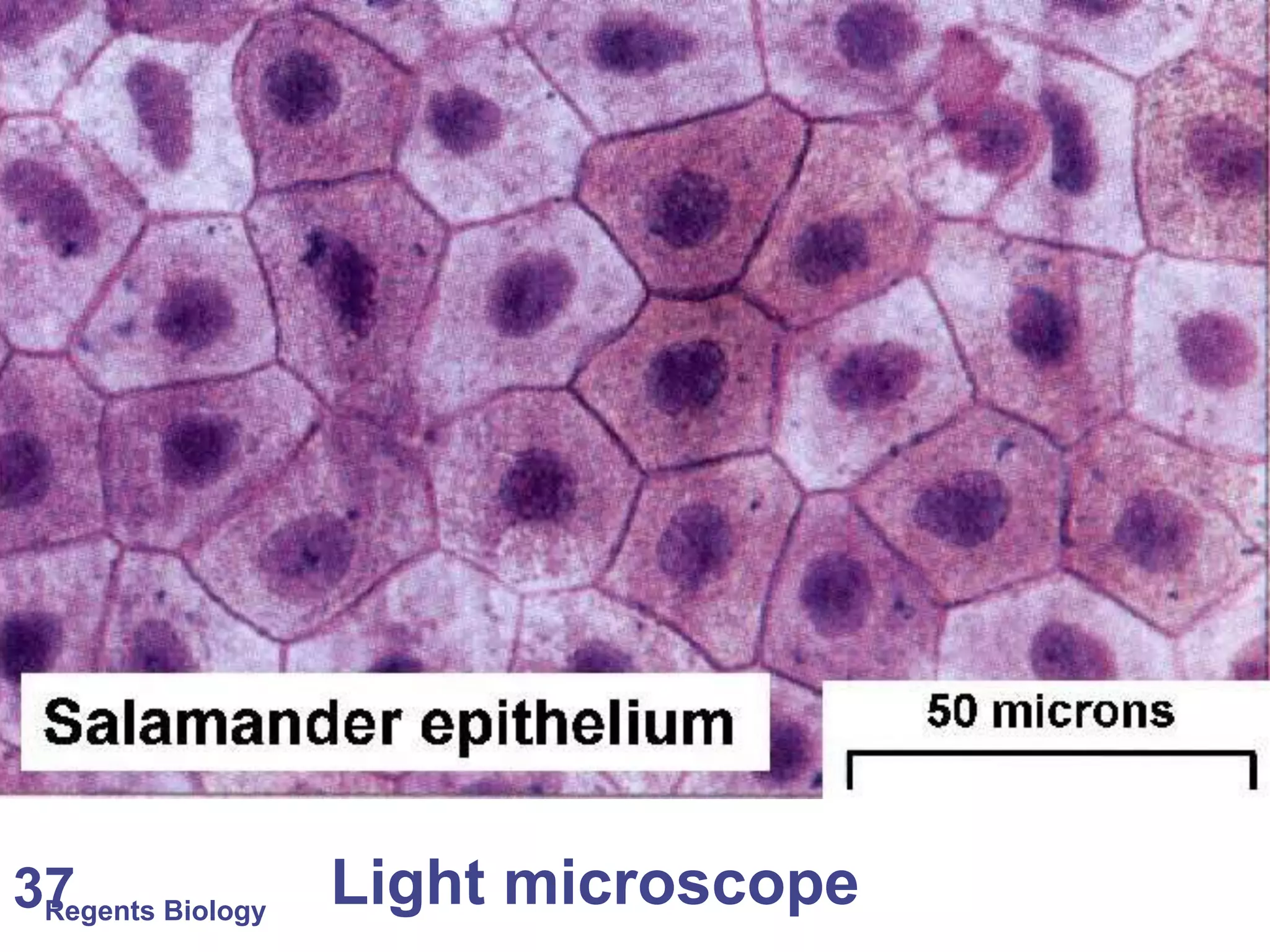
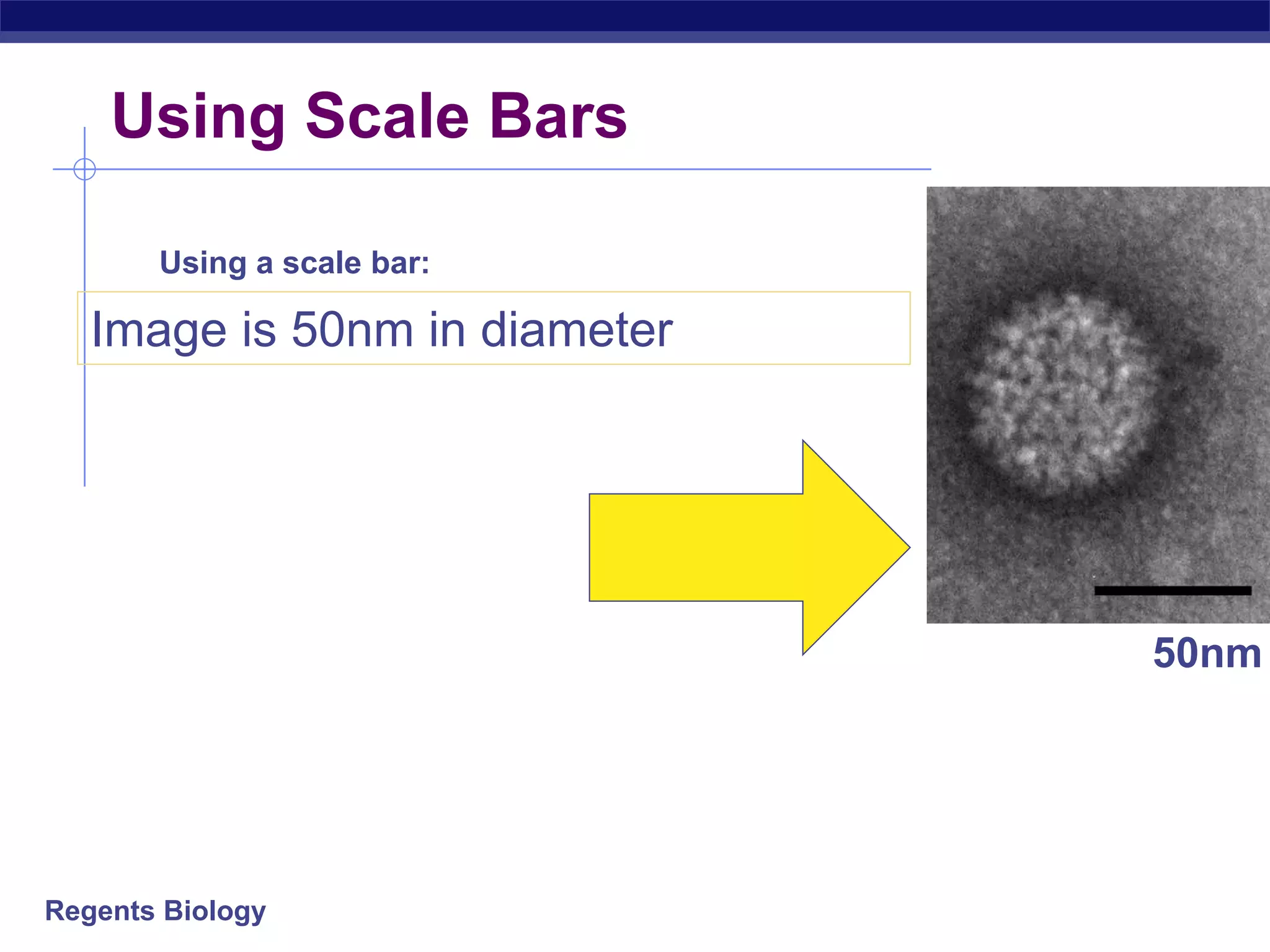
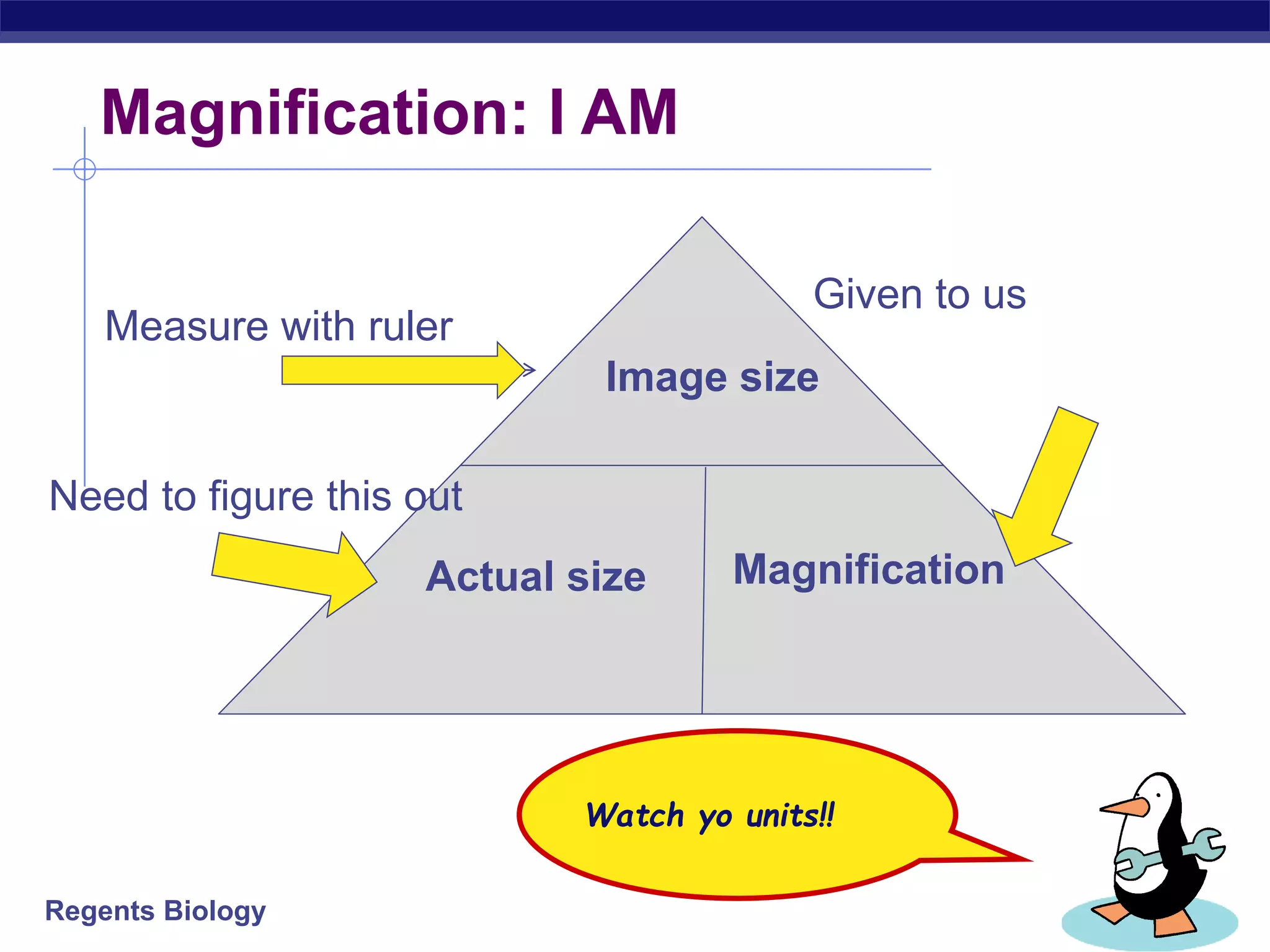
The document discusses microscopes and microscopic units of measurement. It explains that electron microscopes have higher resolution than optical light microscopes but require dead samples, while light microscopes can be used to view live samples and are less expensive. Various micrographs are shown at different magnifications from light microscopes and electron microscopes. The document also reviews the ranges of measurement for electron microscopes, light microscopes, and the unaided human eye, as well as how to calculate total magnification and actual size using a microscope's scale.