The document provides an overview of the banking industry in India. It discusses key points:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) acts as the central bank and regulates monetary policy, banking supervision, foreign exchange and more.
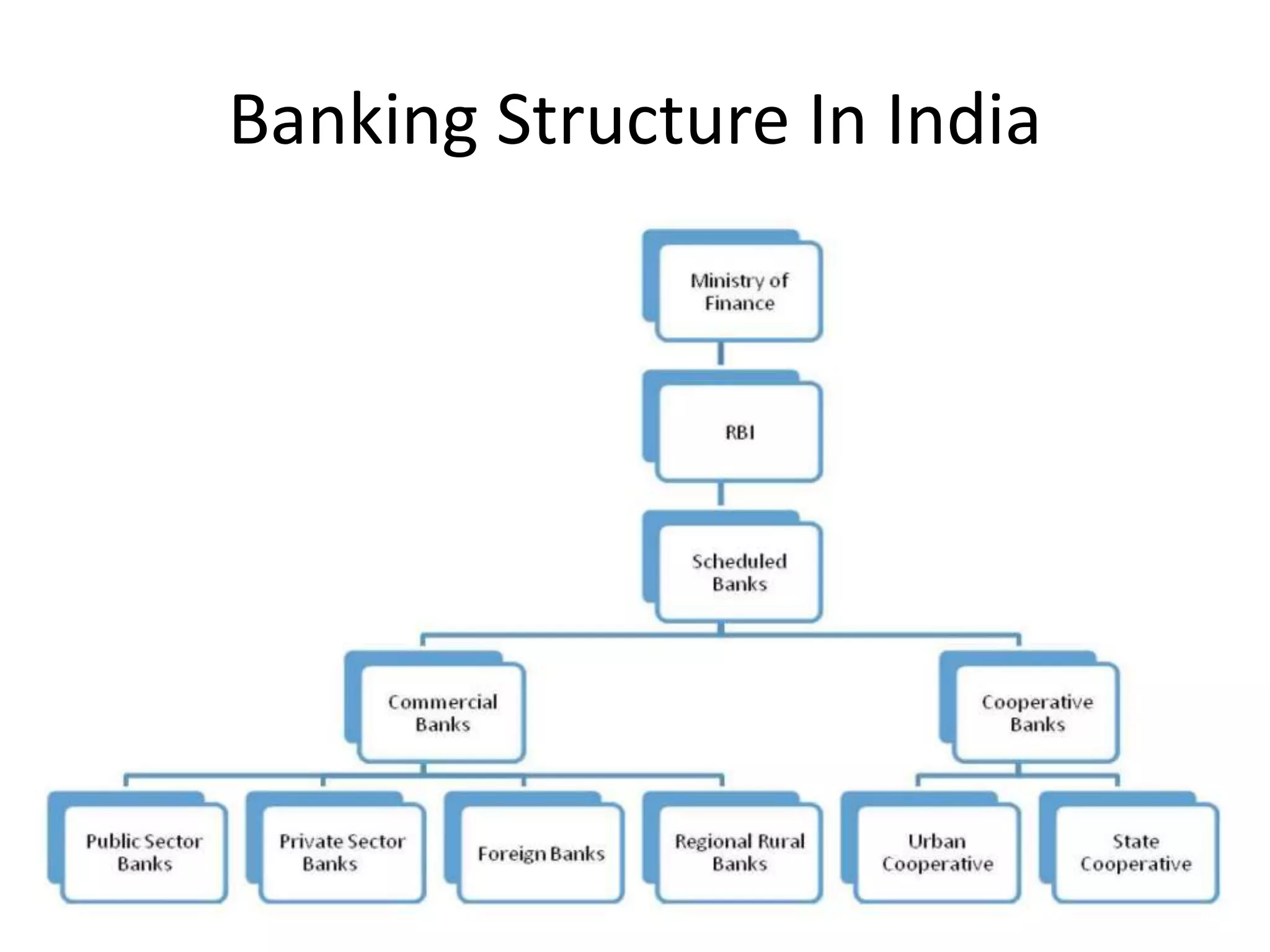
- India has a multi-tiered banking structure including retail banking for consumers, international banking, and wholesale banking for large corporations.
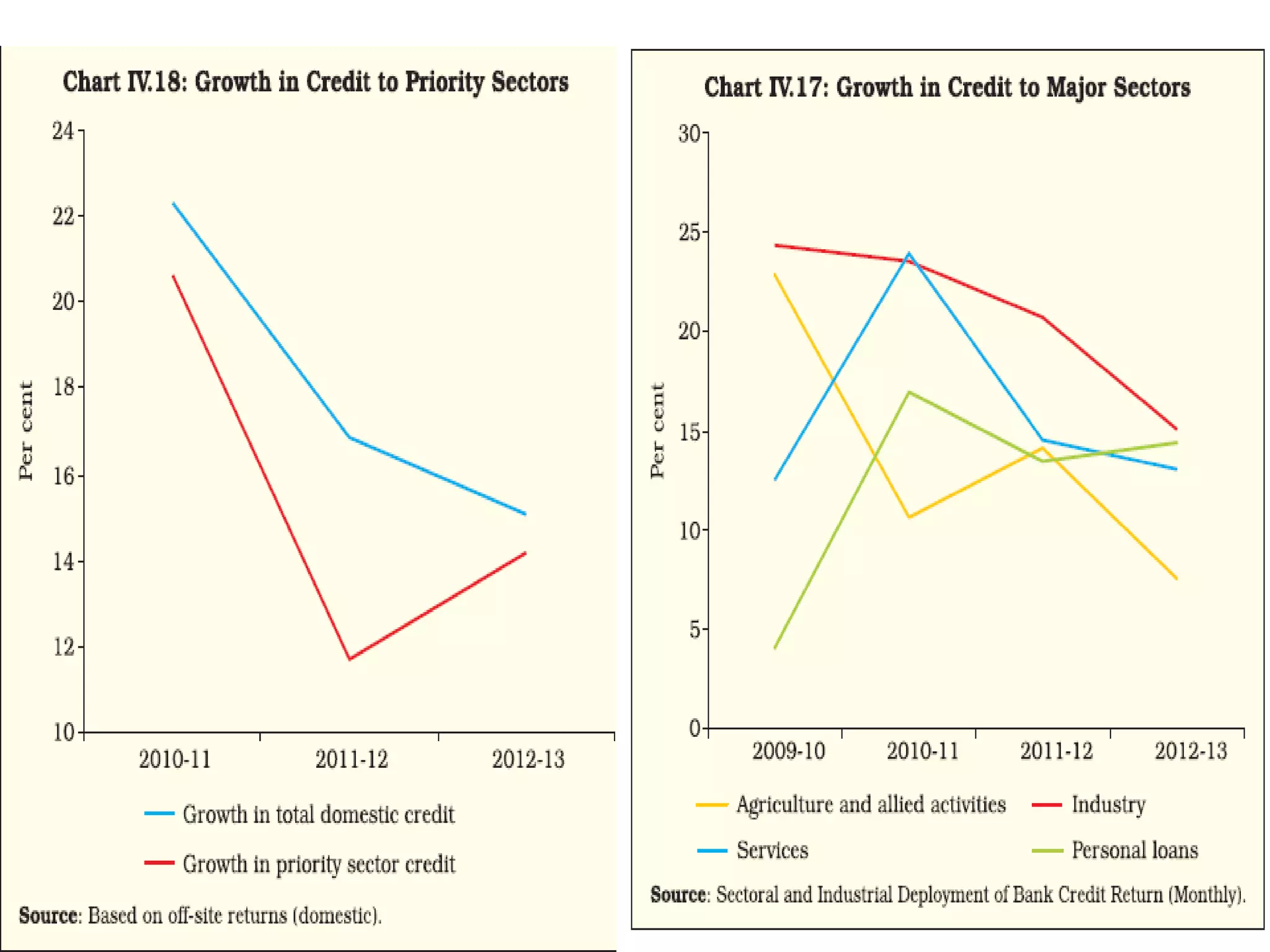
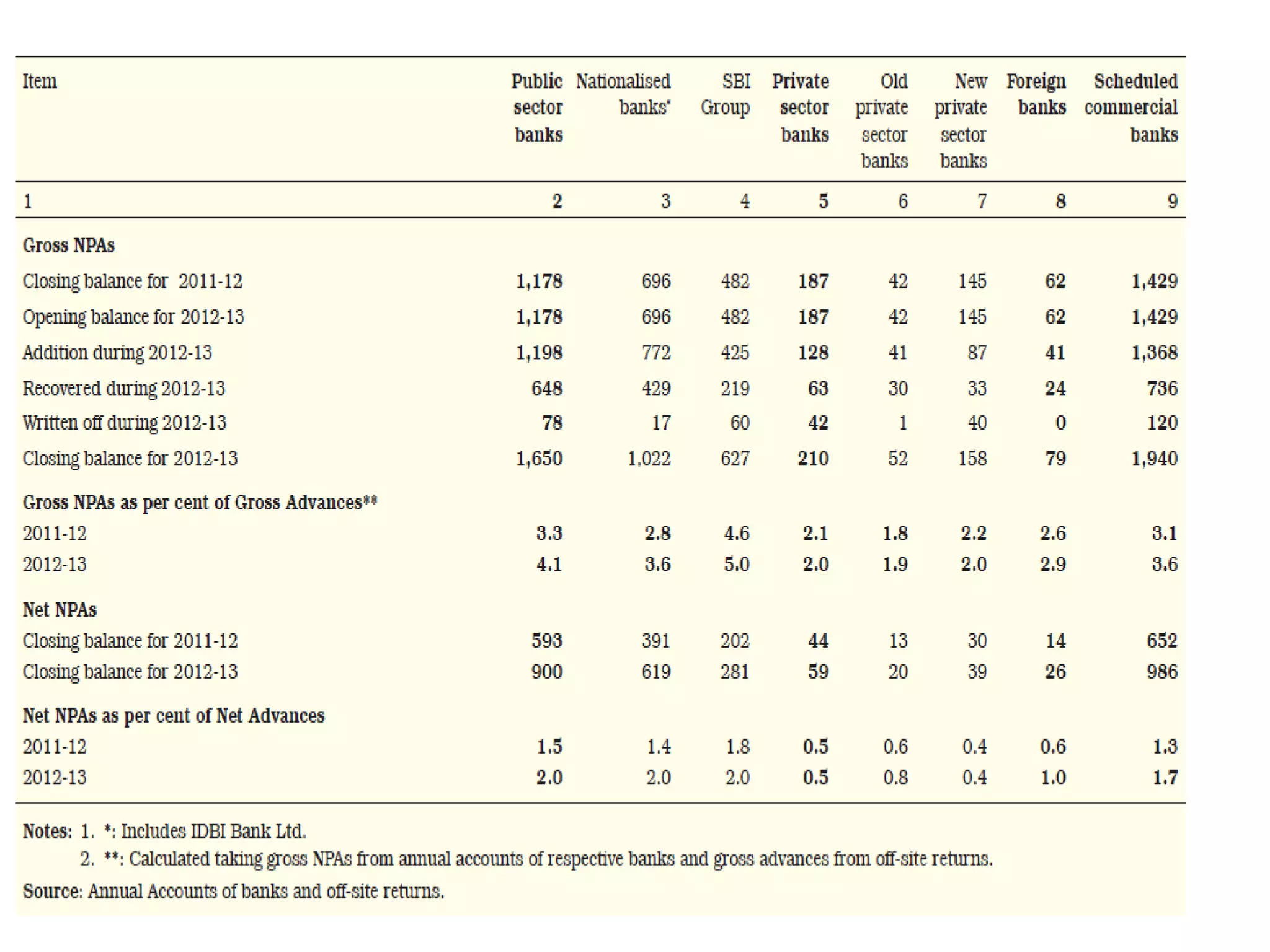
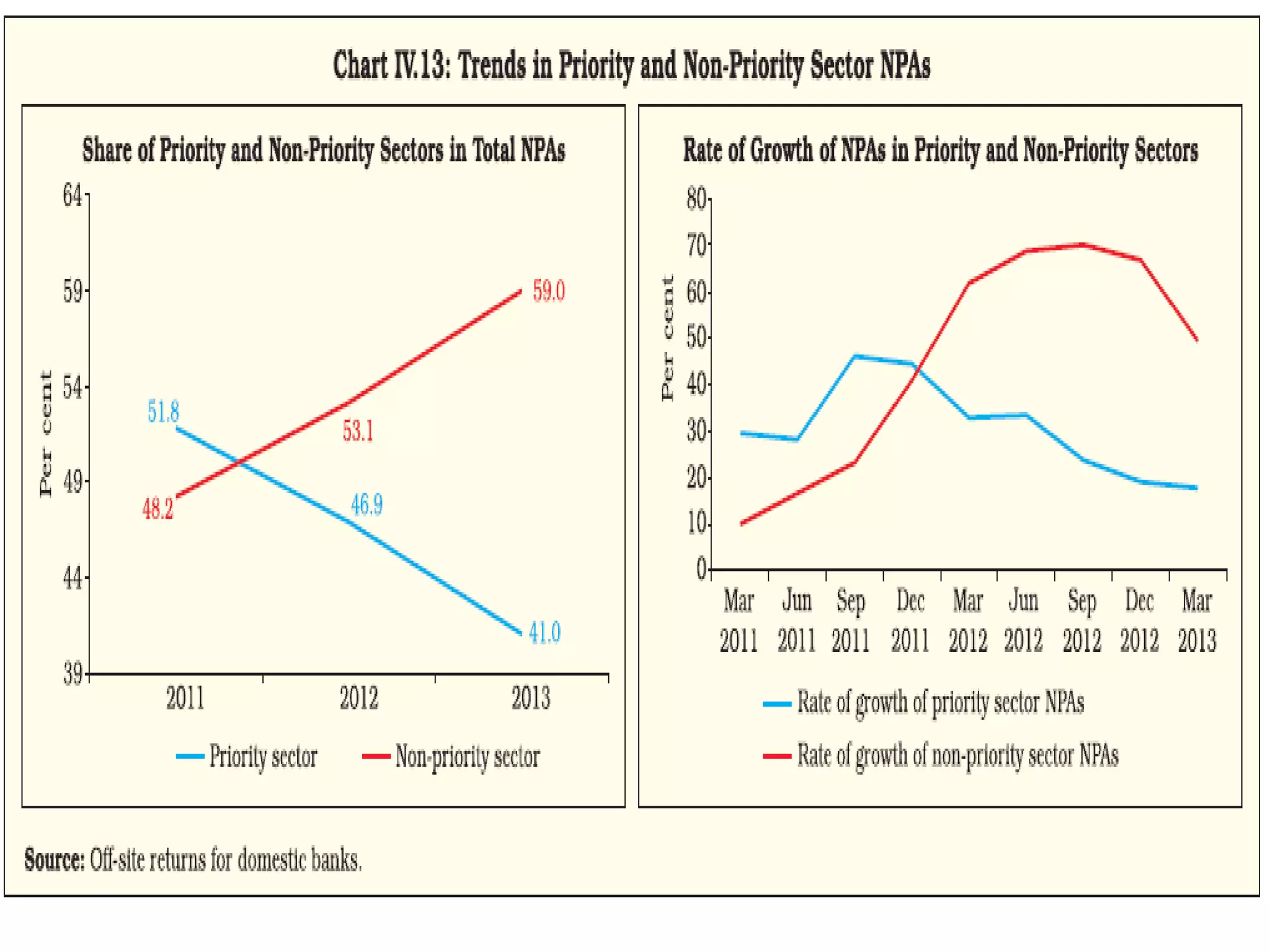
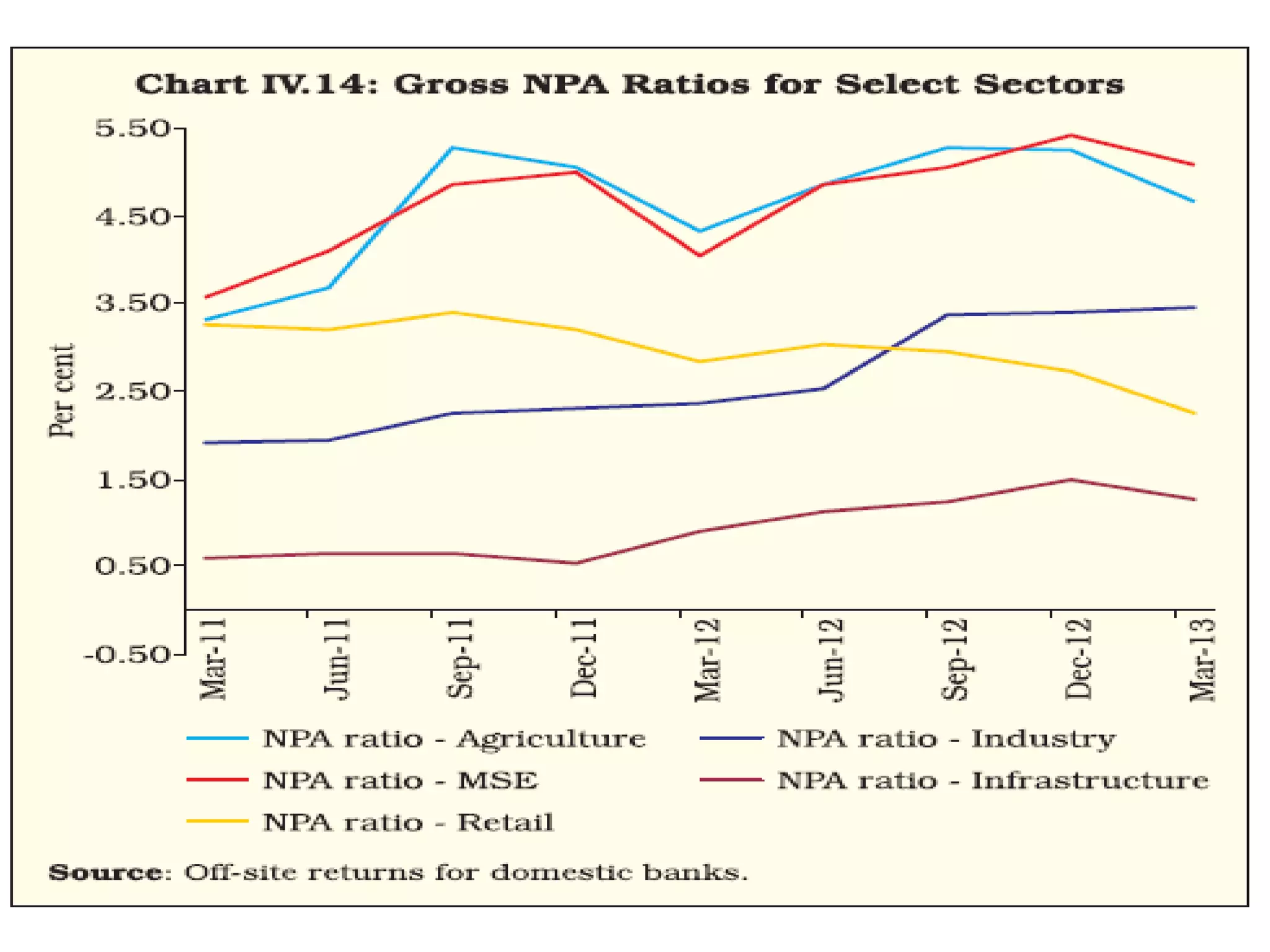
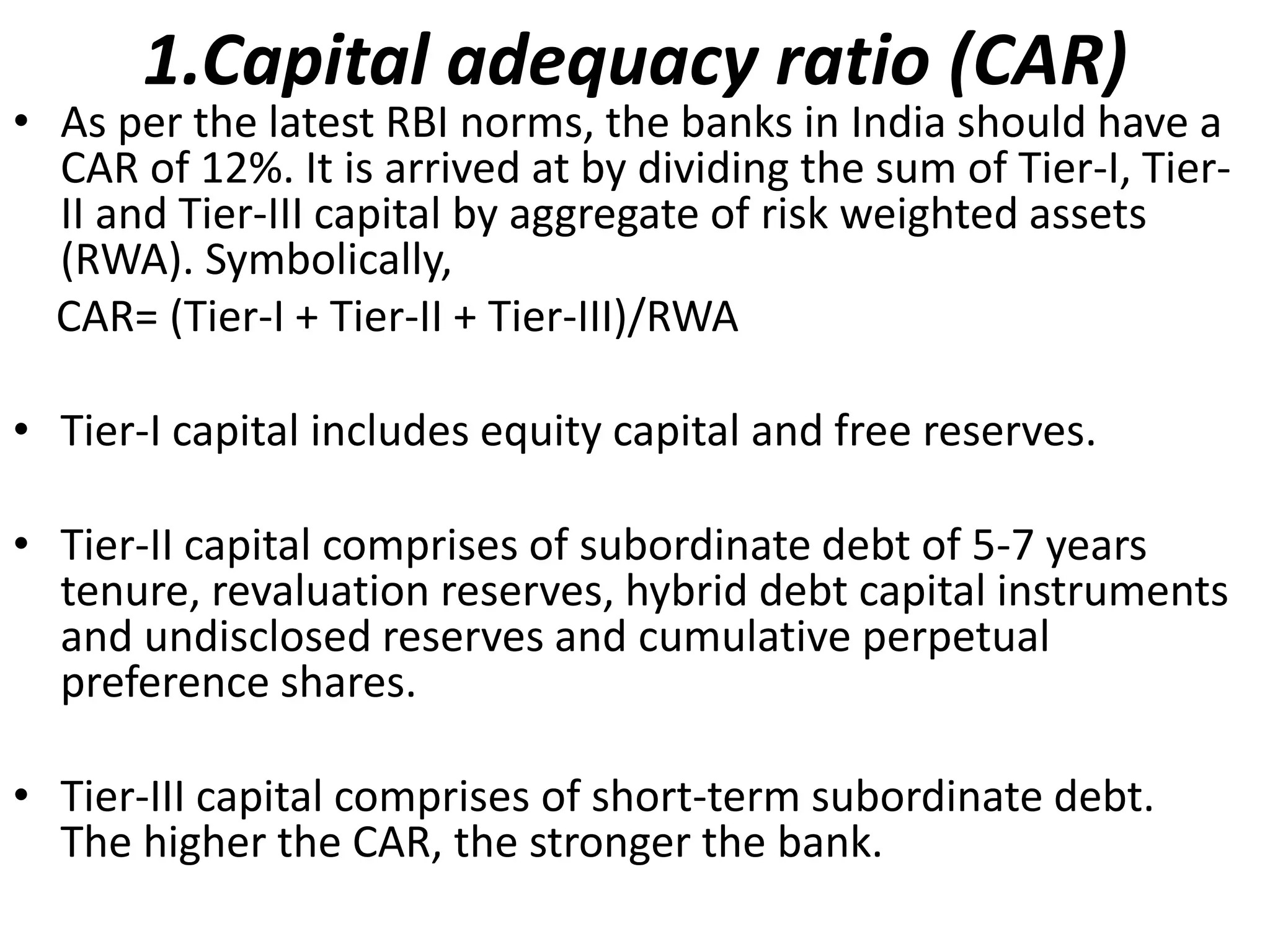
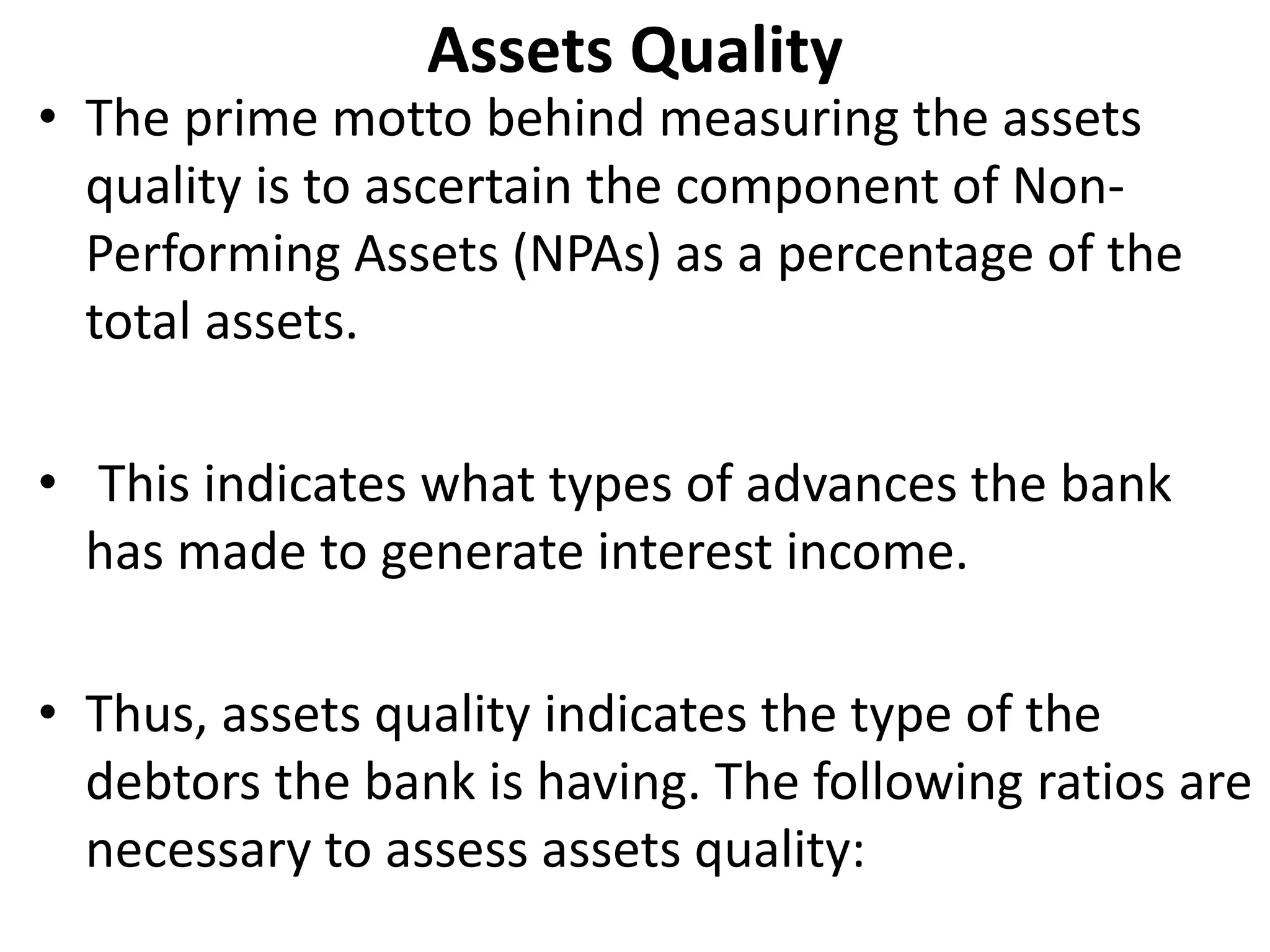
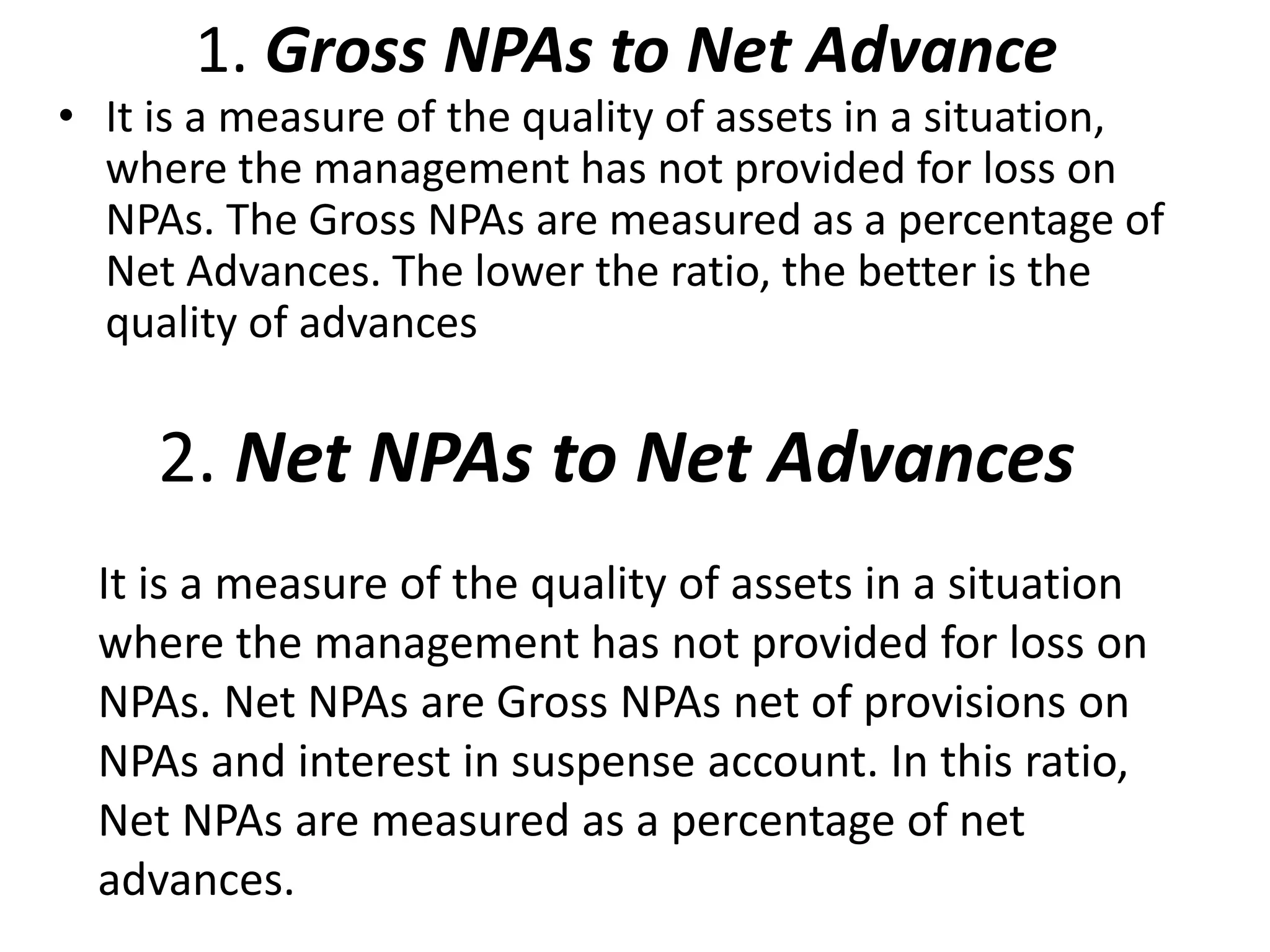
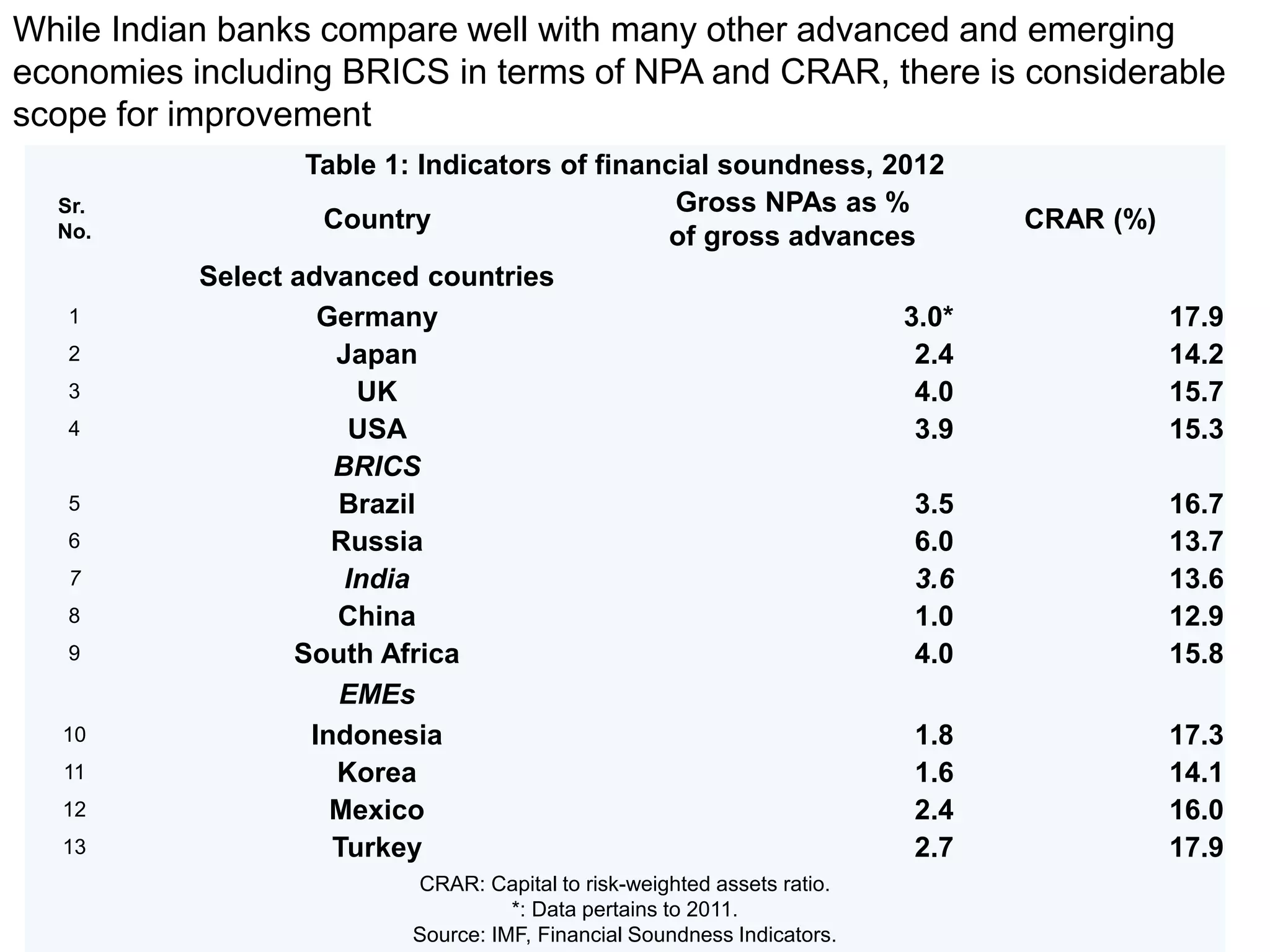
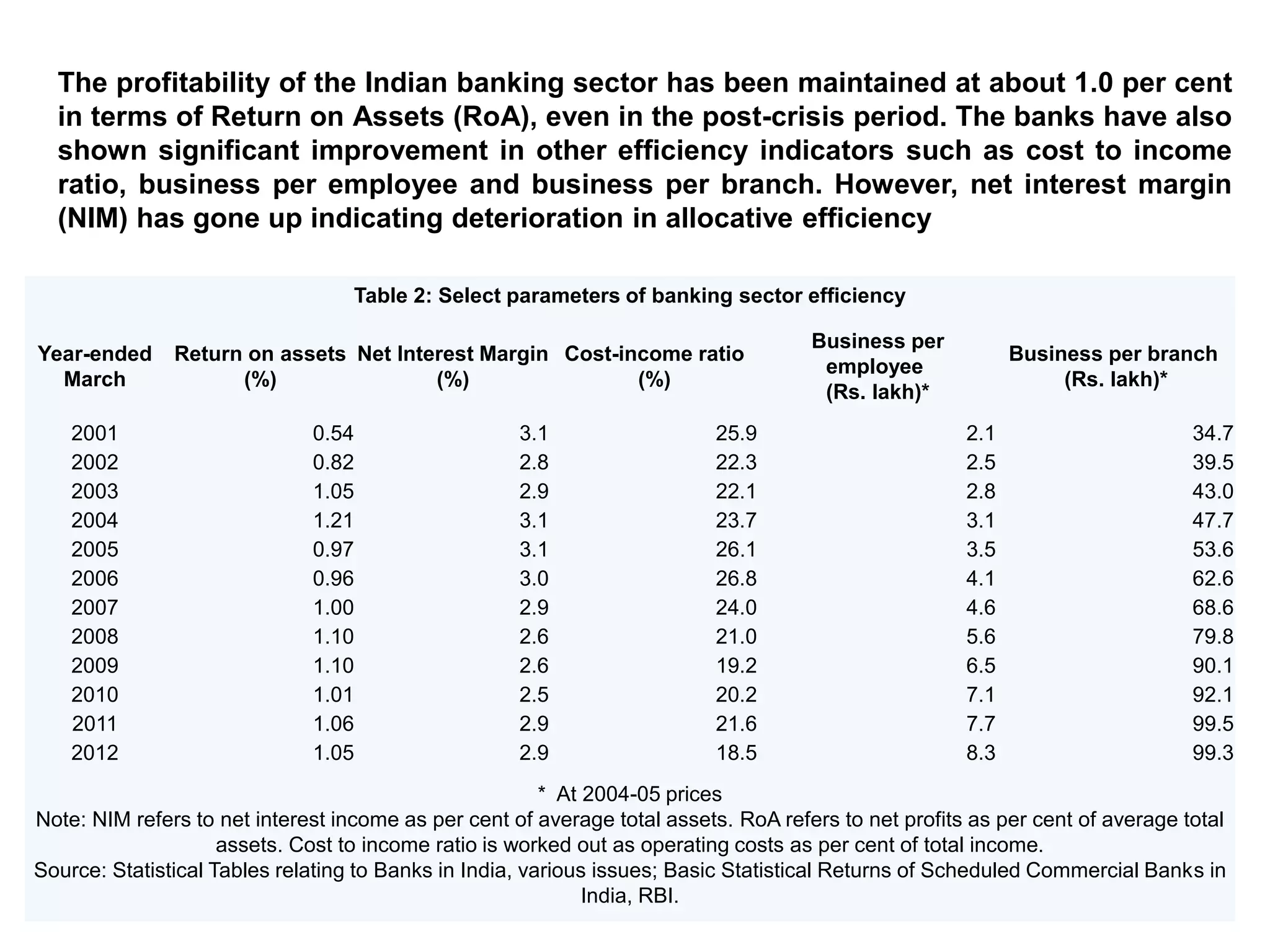
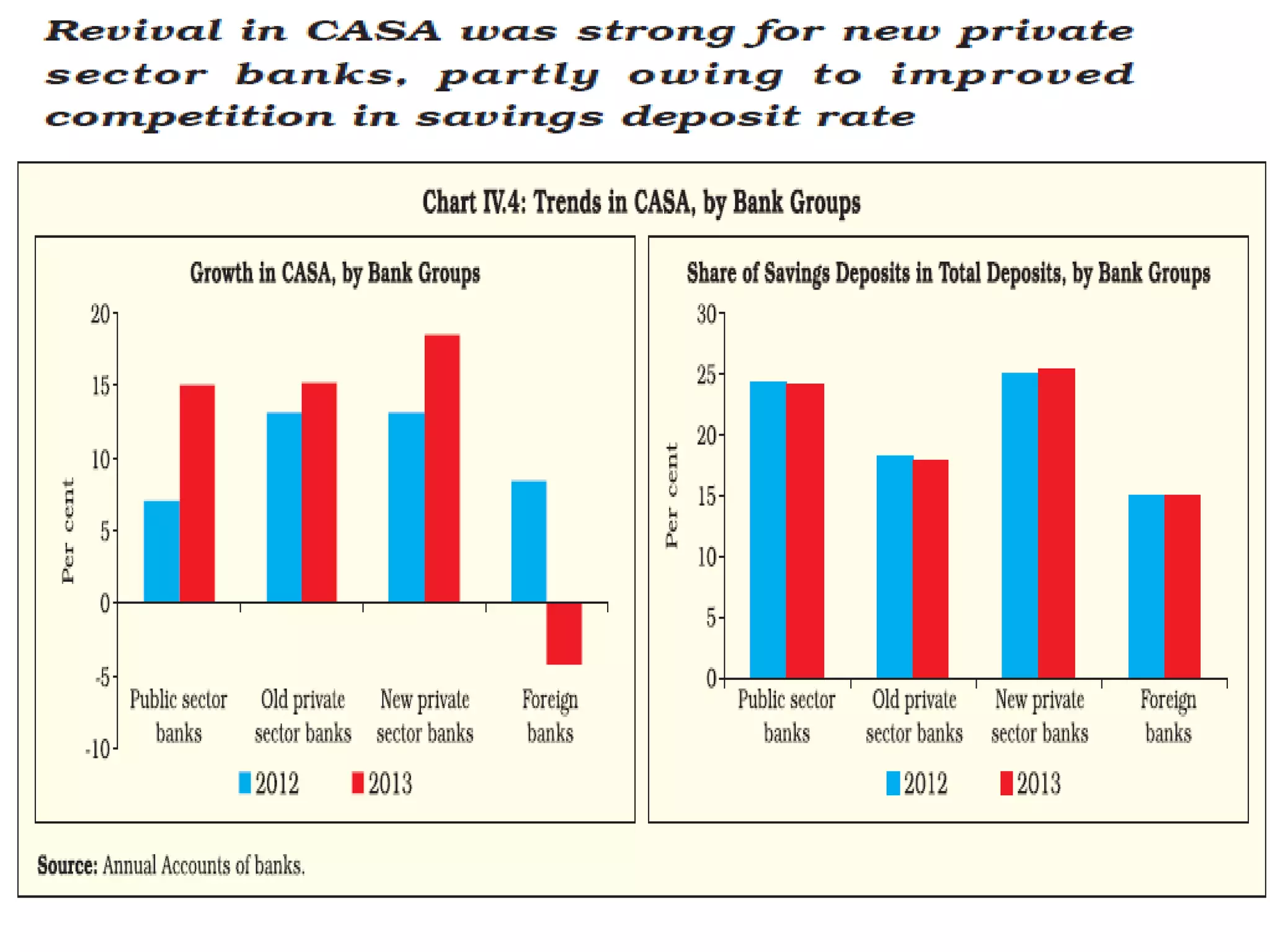
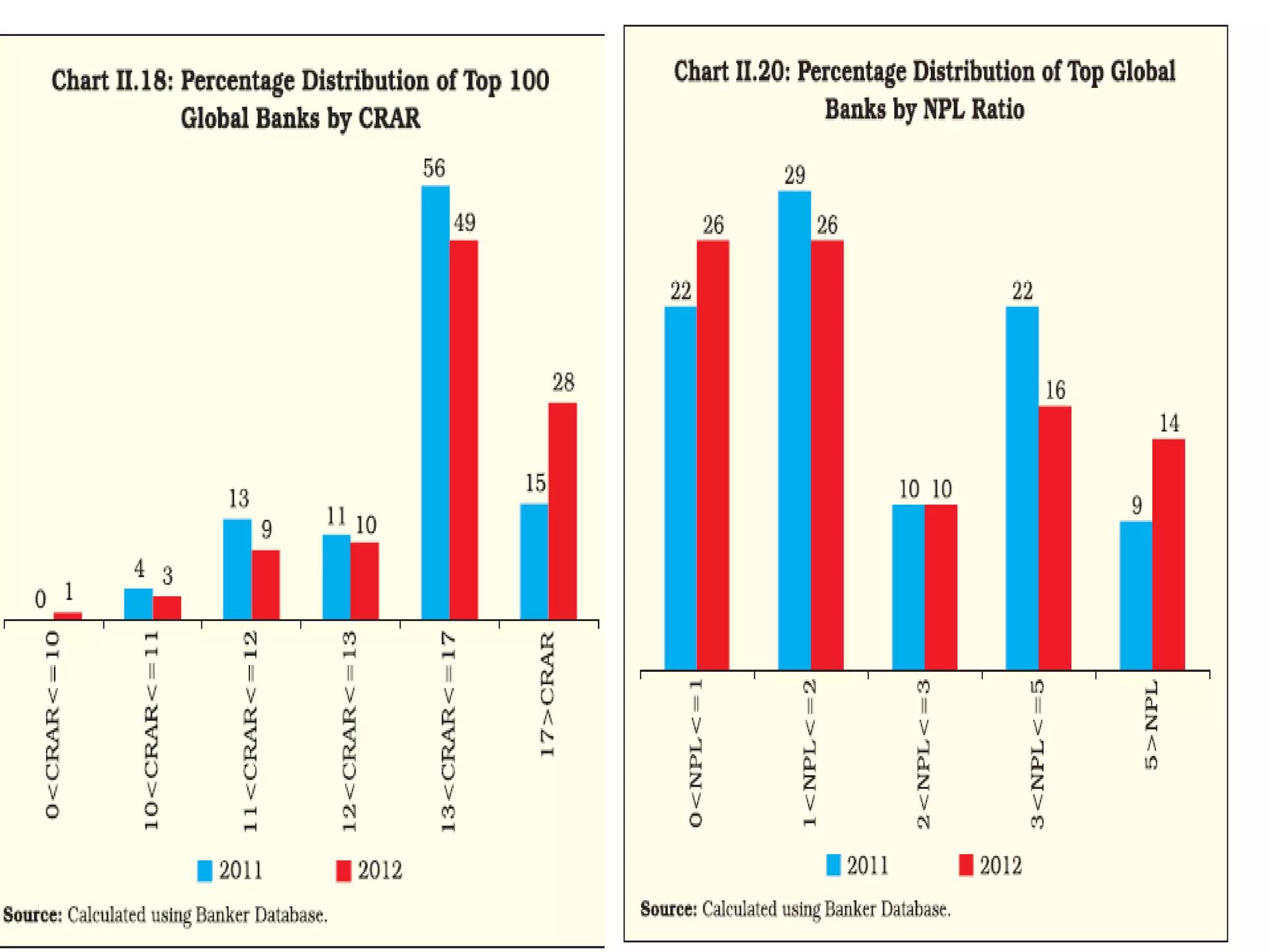
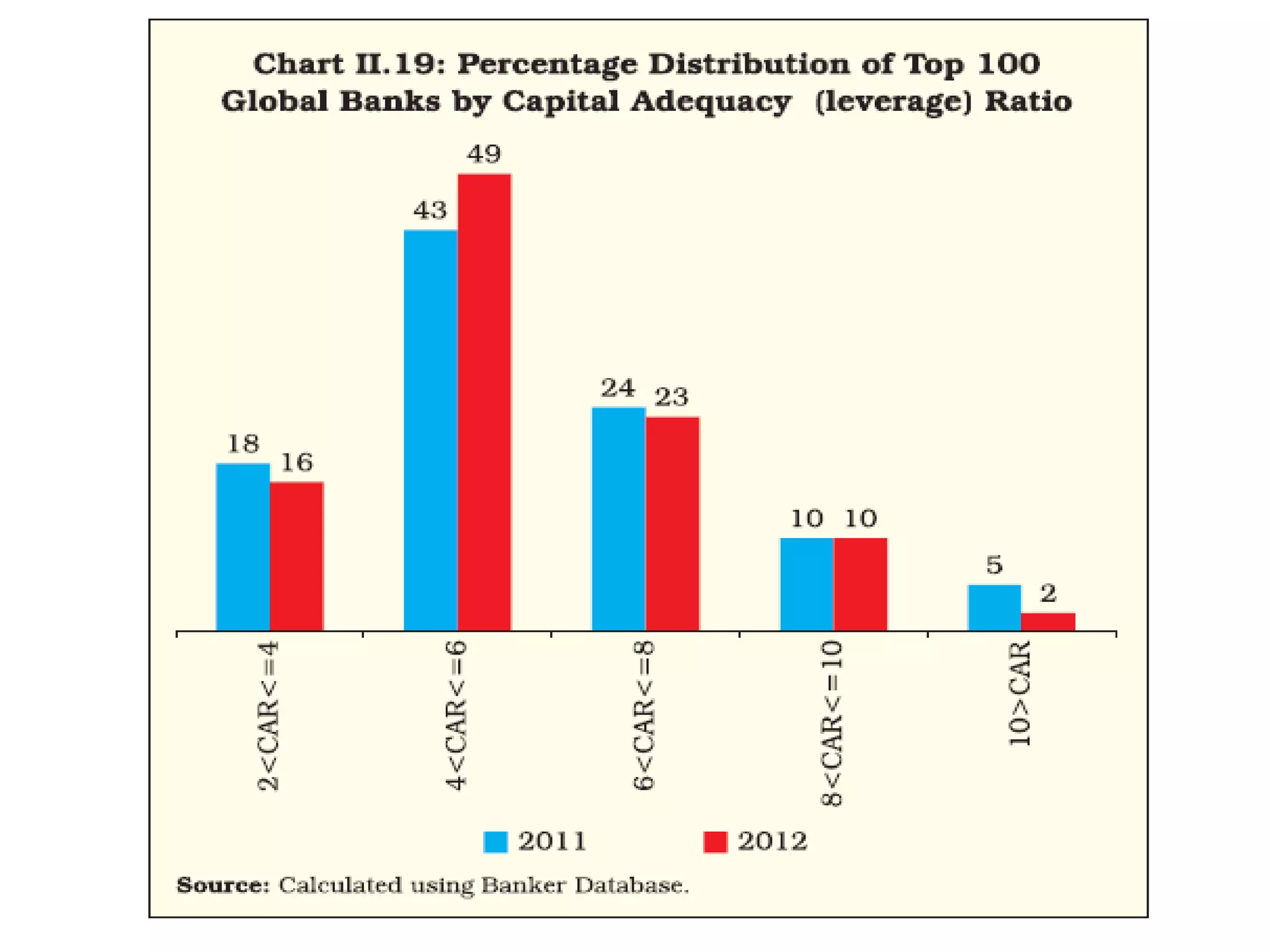
- Banks in India must follow regulations around capital requirements, priority sector lending targets, and controlling non-performing assets.
- Performance is measured using metrics like capital adequacy, asset quality, management efficiency, earnings quality, and more.



































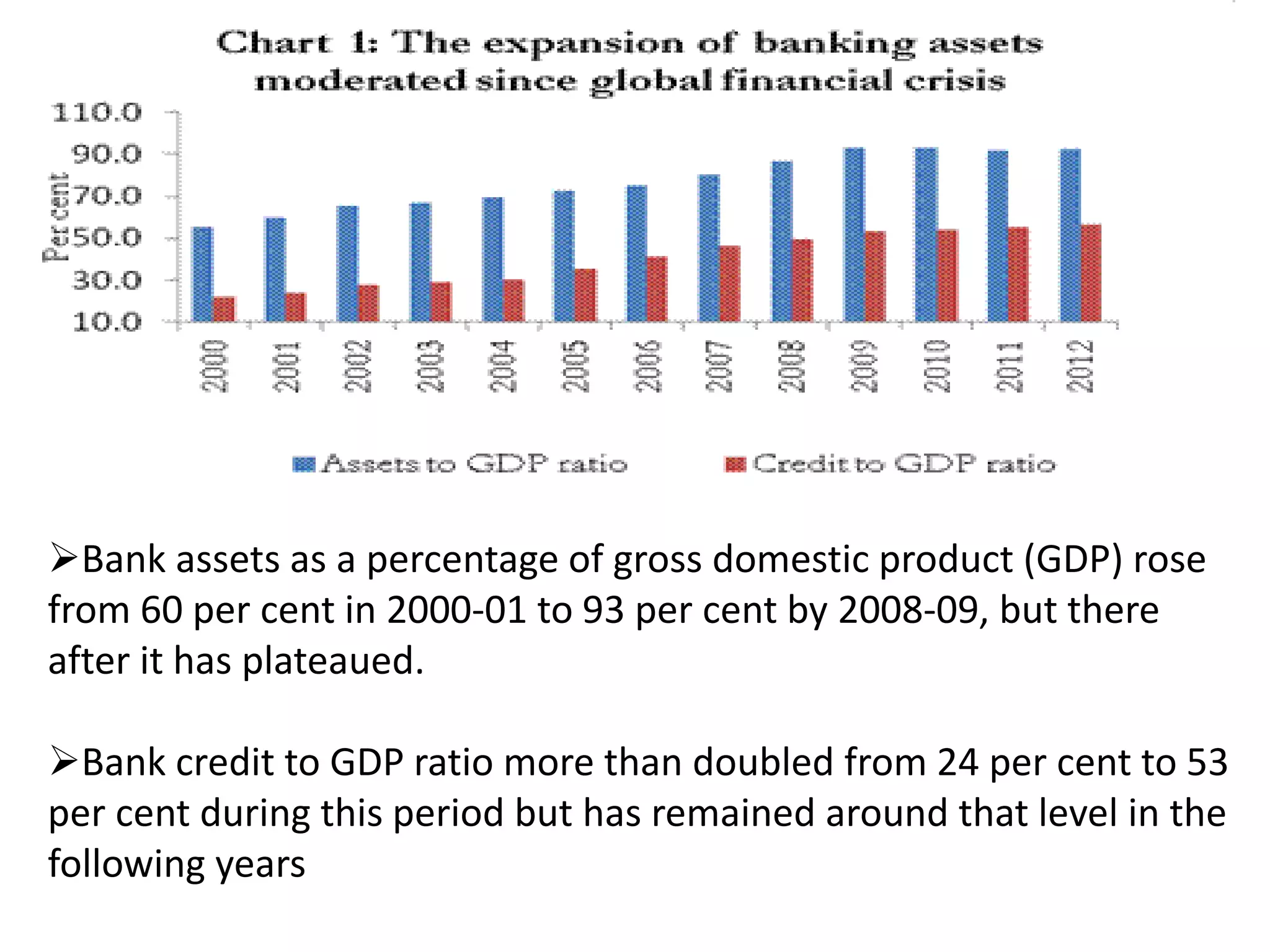
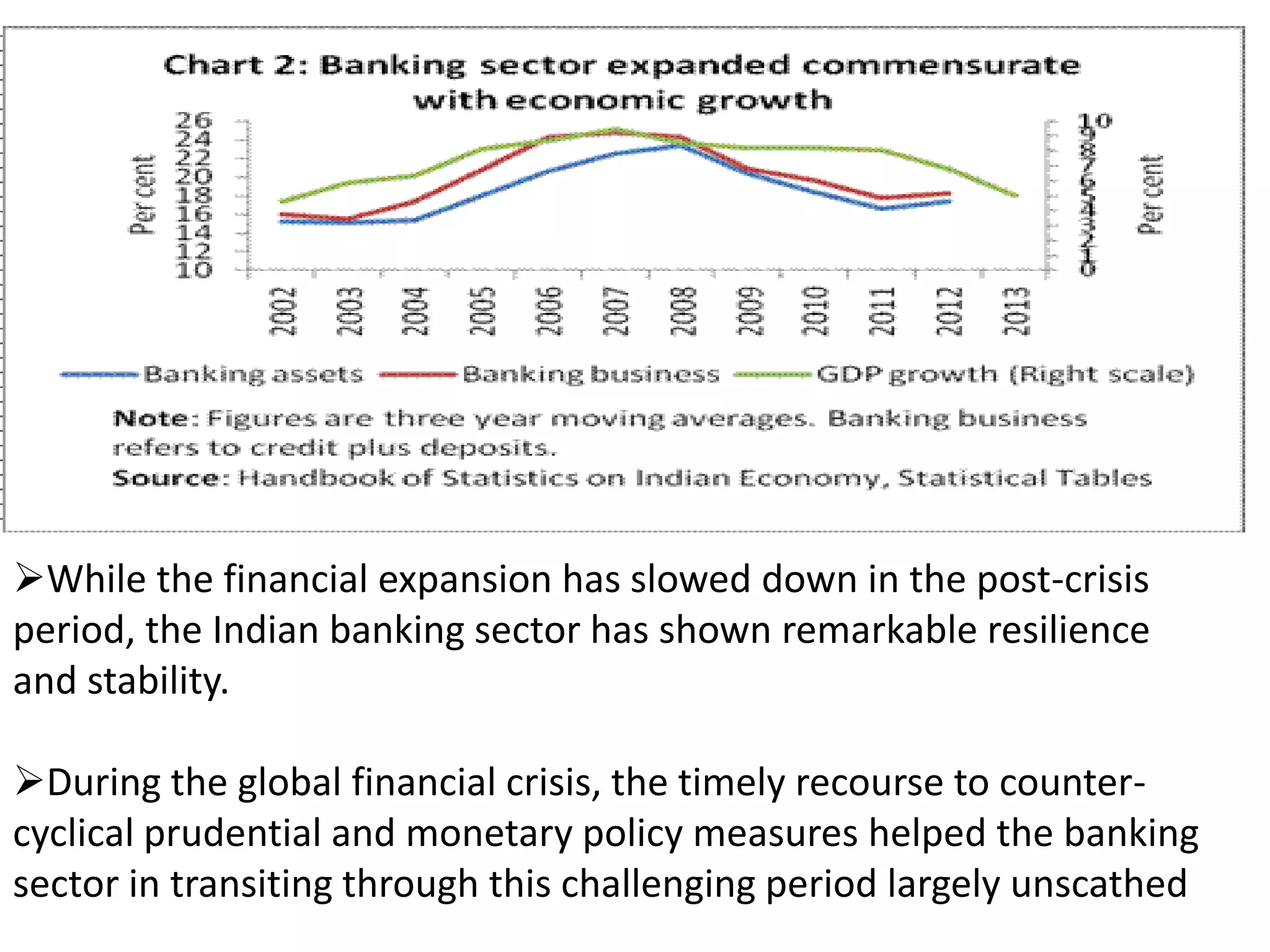
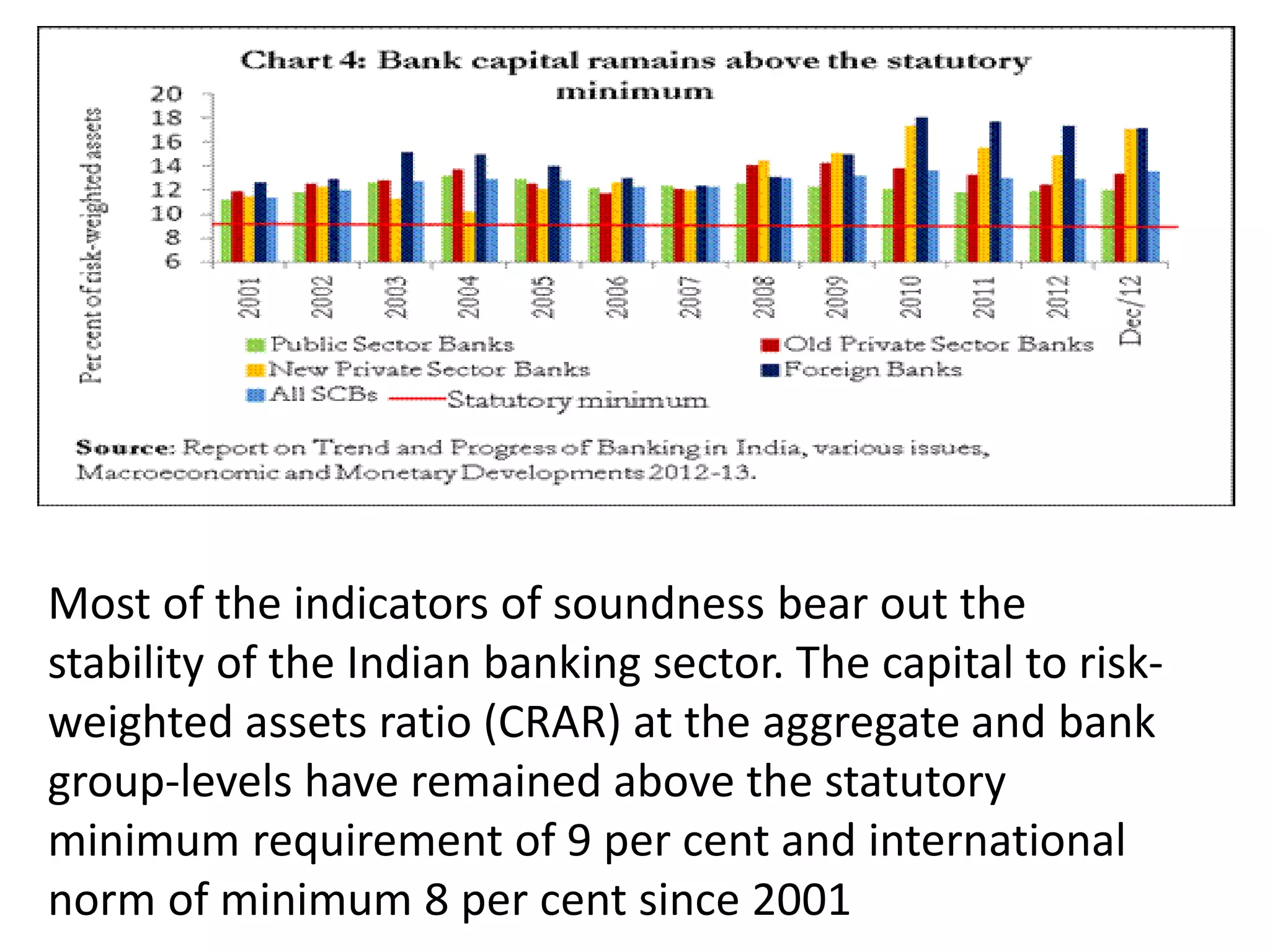
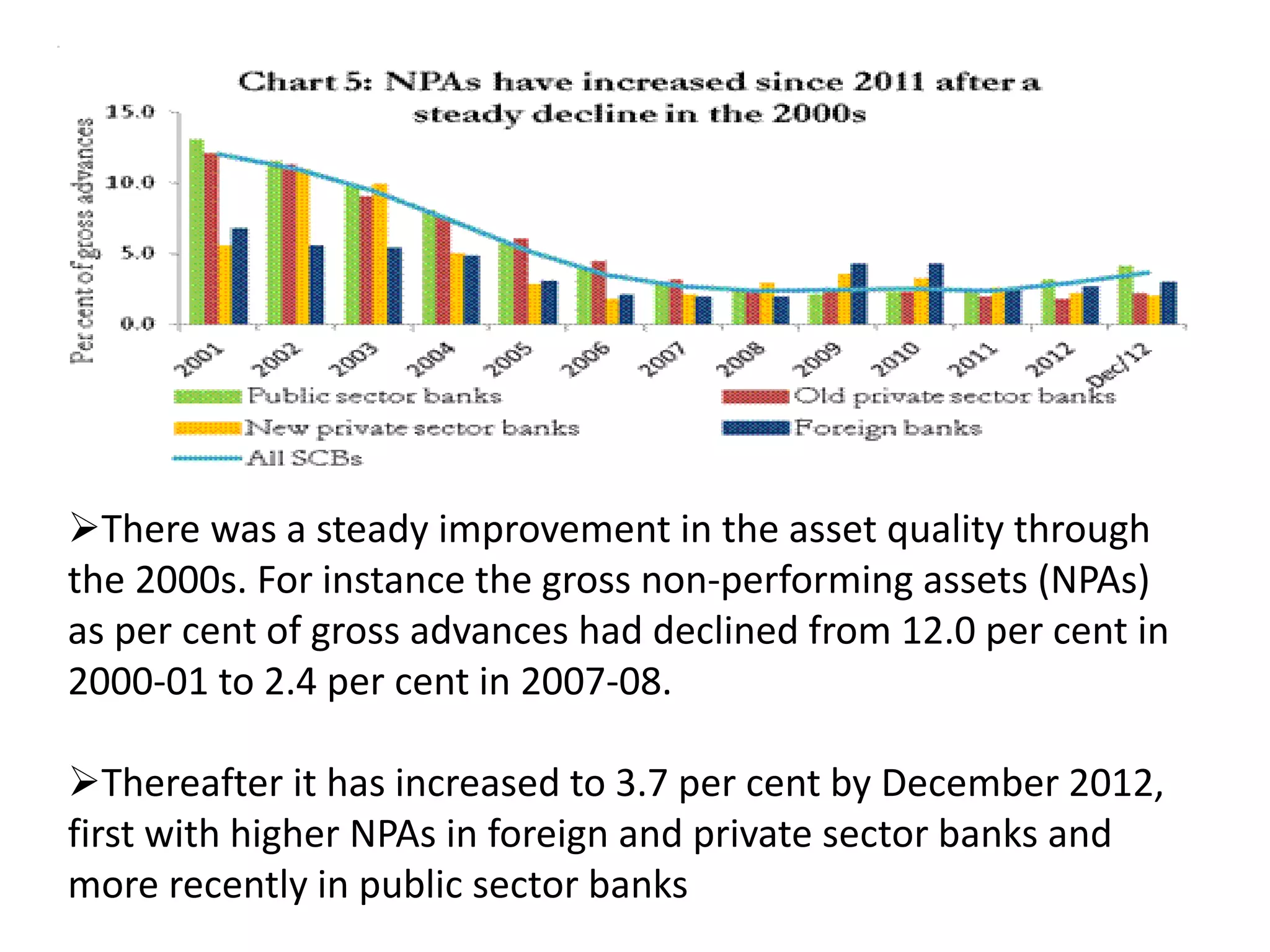





















![Assessment of Non-Fund Based limit
• Computation Showing assessment of Letter of Credit
Particular Amount (Rs)
Projected annual purchase of Raw material (A) *****
Projected annual purchase under LC (B) *****
Projected annual purchase under LC C= (A)*(B) *****
Monthly raw material being purchase through LC [(C)
/12] = (D)
*****
Usance Period (month) (E) *****
Lead Period (month) (F) *****
Amount of LC required G= (D)*(F+F) *****](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bankingindustryinindia-introduction-140918134344-phpapp02/75/Banking-industry-in-india-introduction-84-2048.jpg)


