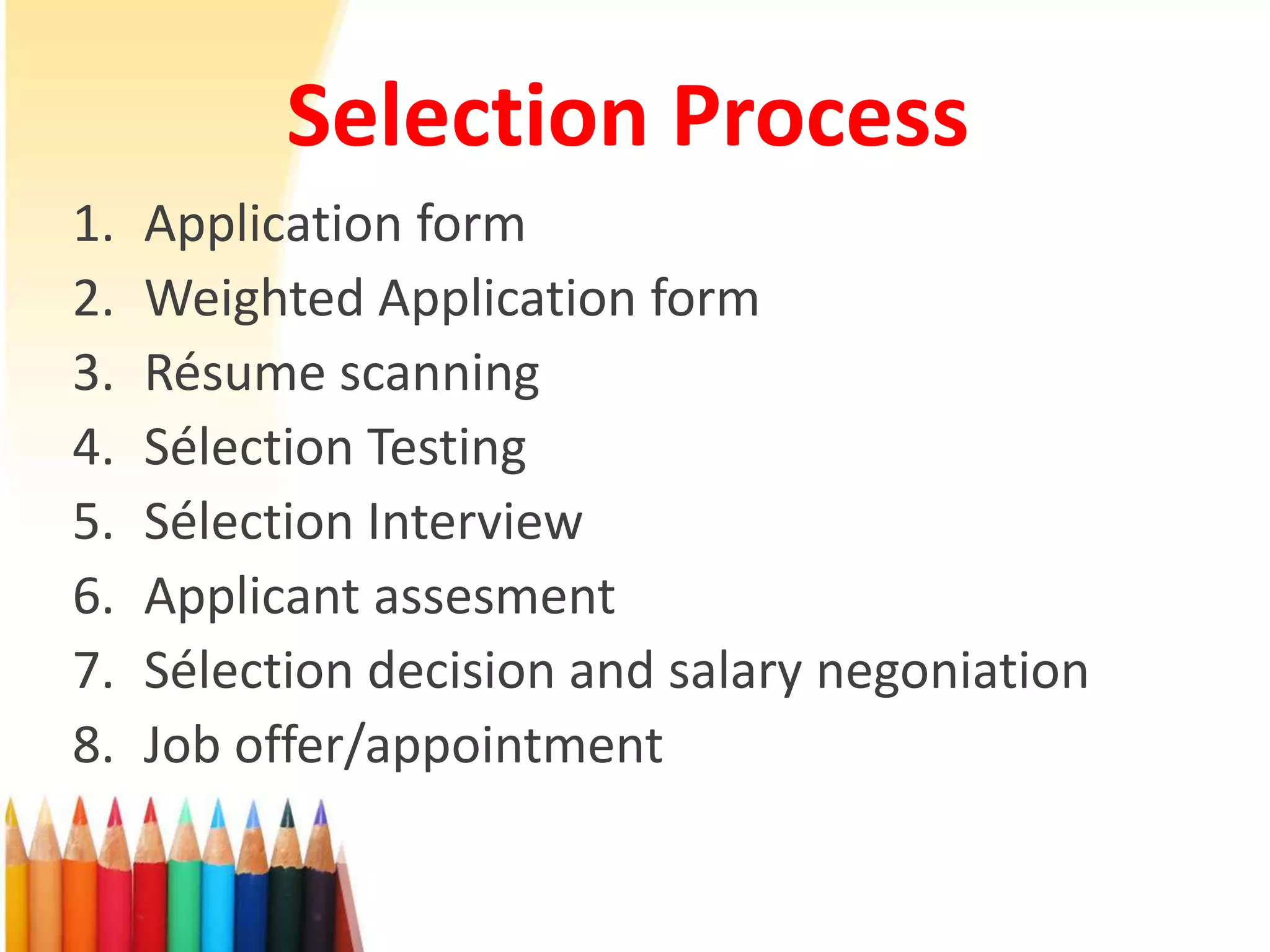
The document discusses the selection and selection process in human resource management. It defines selection as the systematic process of choosing the best qualified candidate for a job based on their qualifications and fit with organizational requirements. The objectives of selection are to identify qualified candidates, reduce hiring costs, and evaluate recruitment efforts. The selection process involves application forms, resume screening, testing, interviews, candidate assessment, making a job offer, and negotiating compensation. Common selection tools include application blanks, weighted application forms, tests of intelligence, aptitude, personality and achievement, and different types of interviews. The goal is to hire the most suitable candidates through a standardized, objective process.