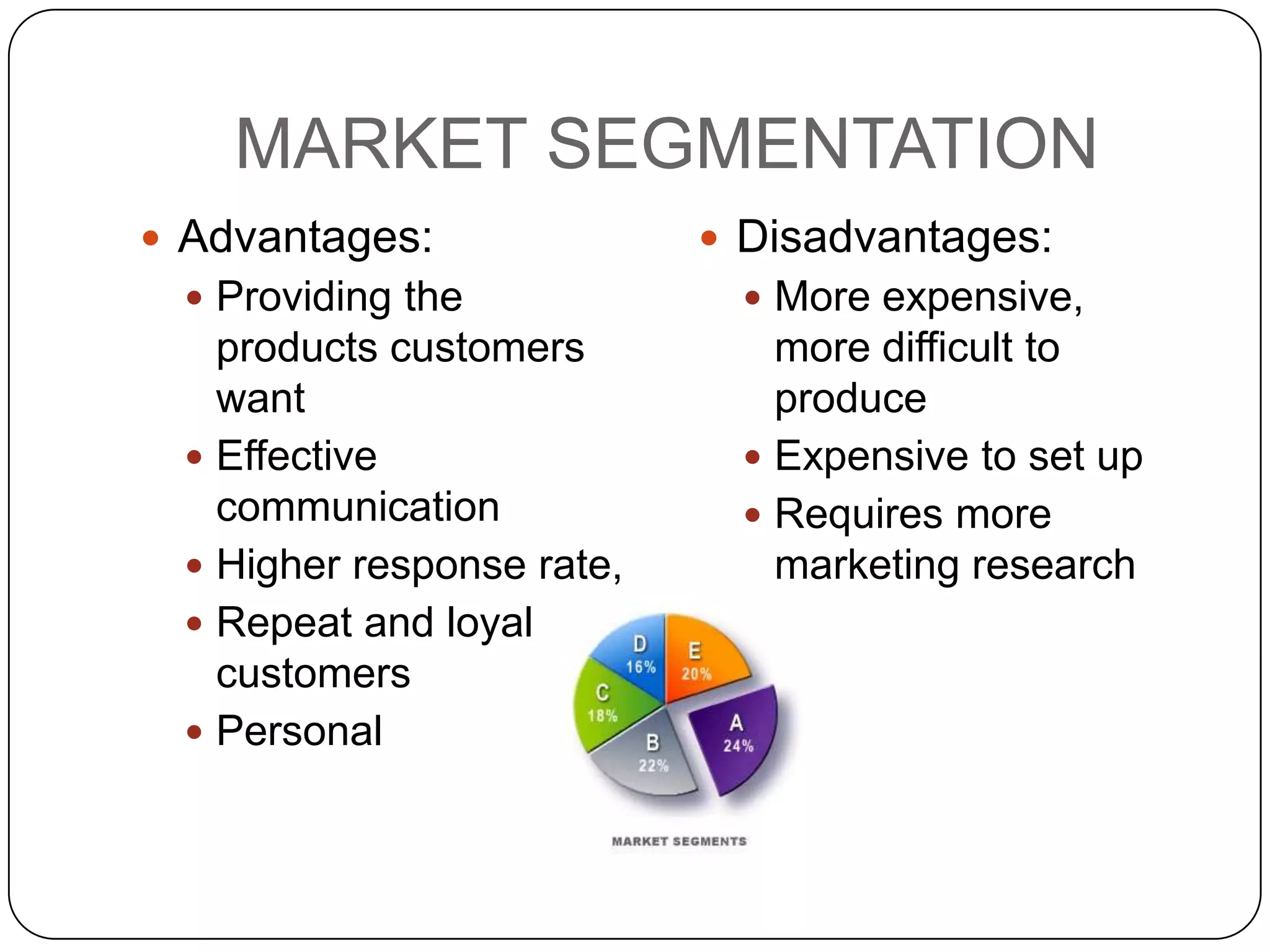
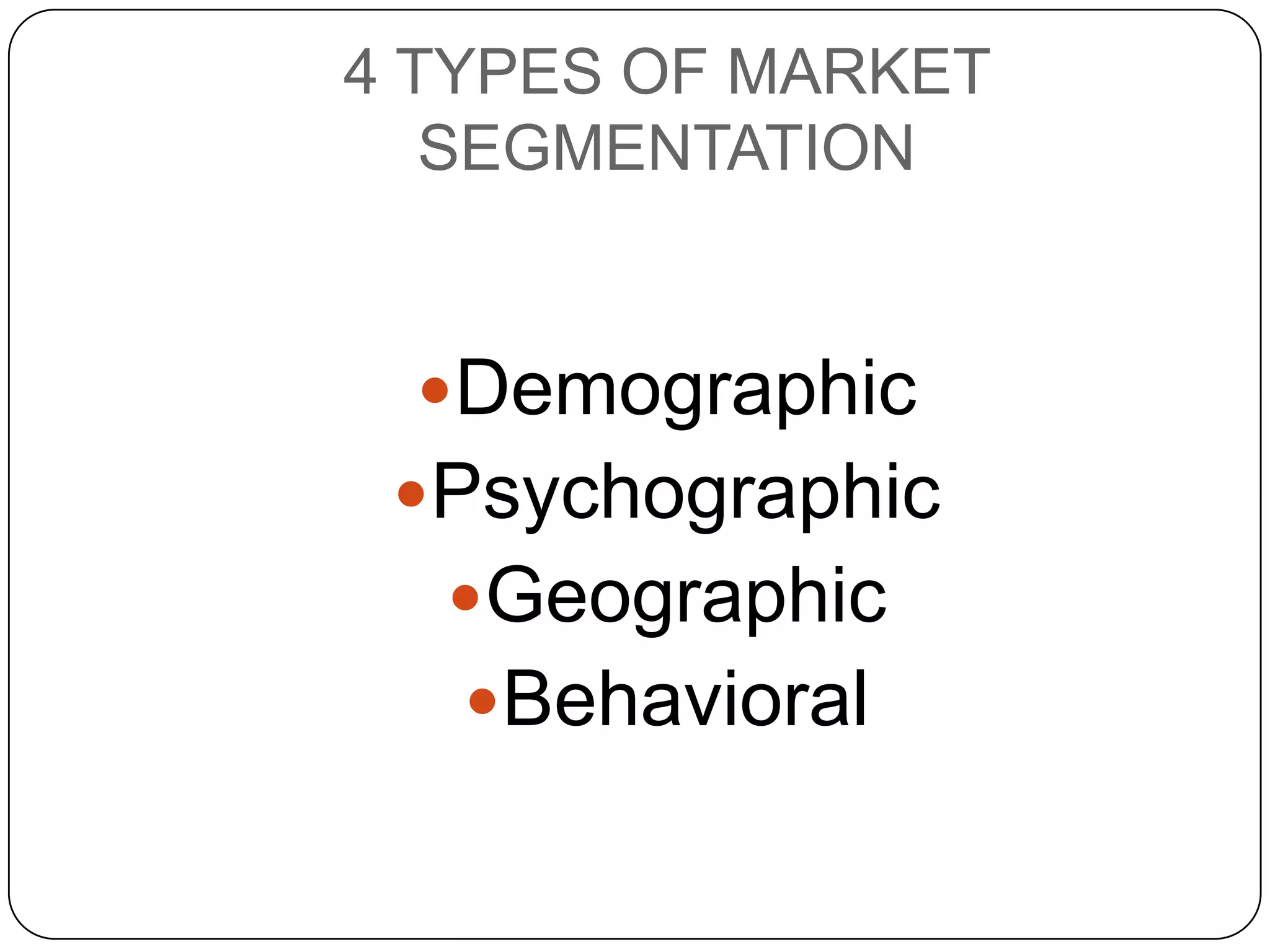
The document discusses marketing strategies and target markets. It explains that the marketing mix includes the 4 P's - product, price, place, promotion. Market segmentation involves dividing a larger market into smaller subgroups that share characteristics. There are four main types of market segmentation: demographic, psychographic, geographic, and behavioral. Understanding segmentation allows businesses to better target their marketing to specific customer groups.