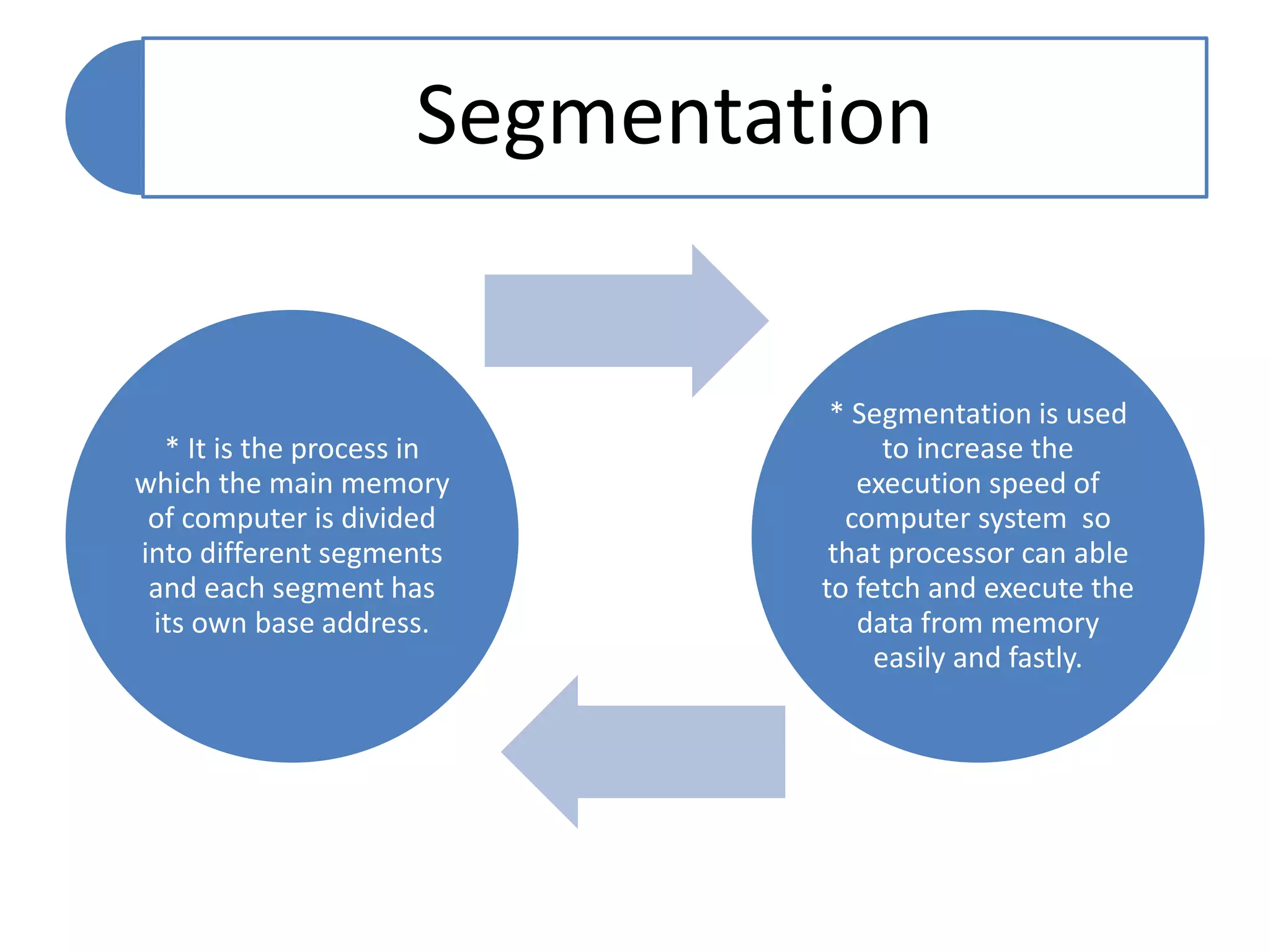
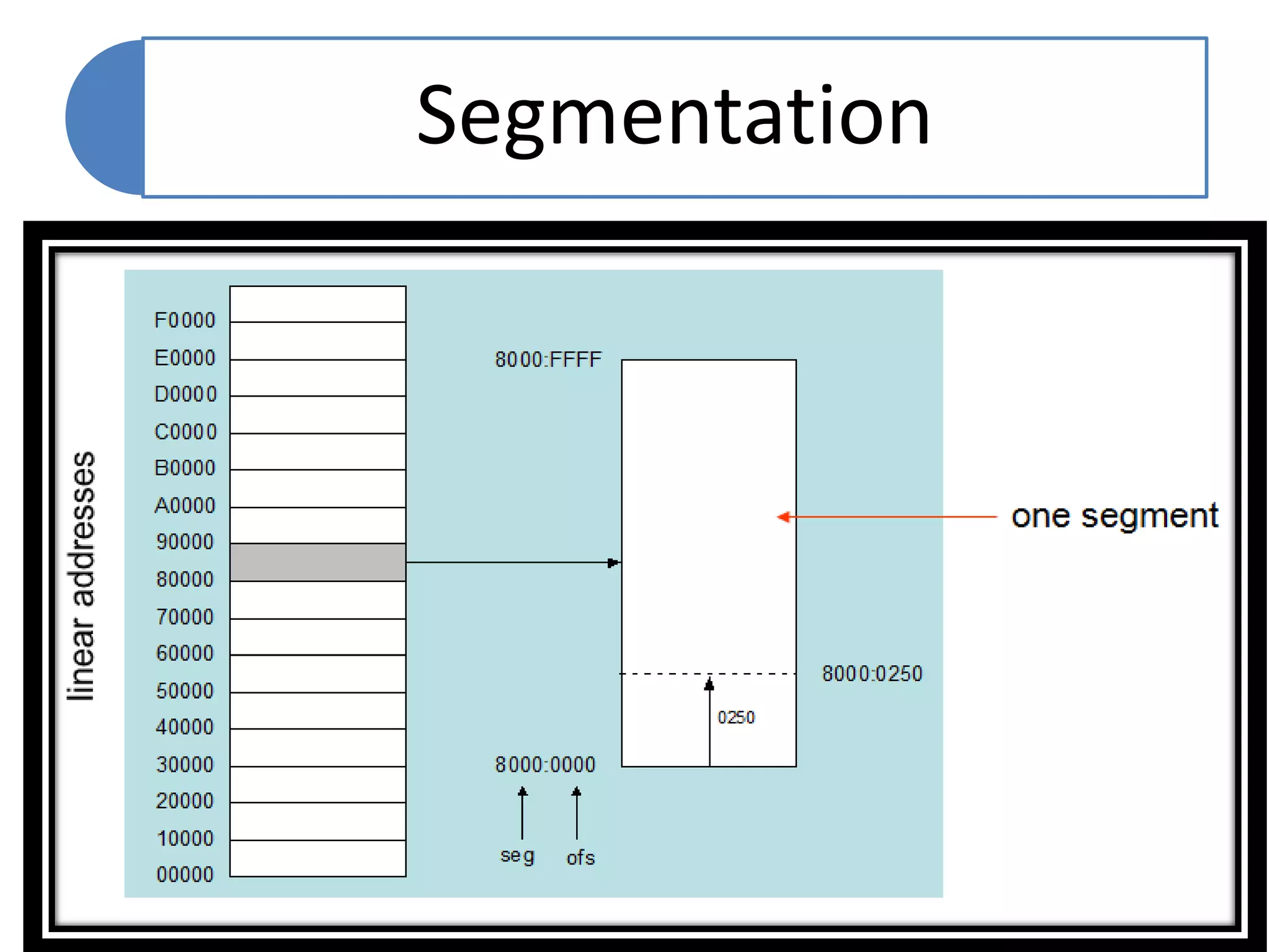
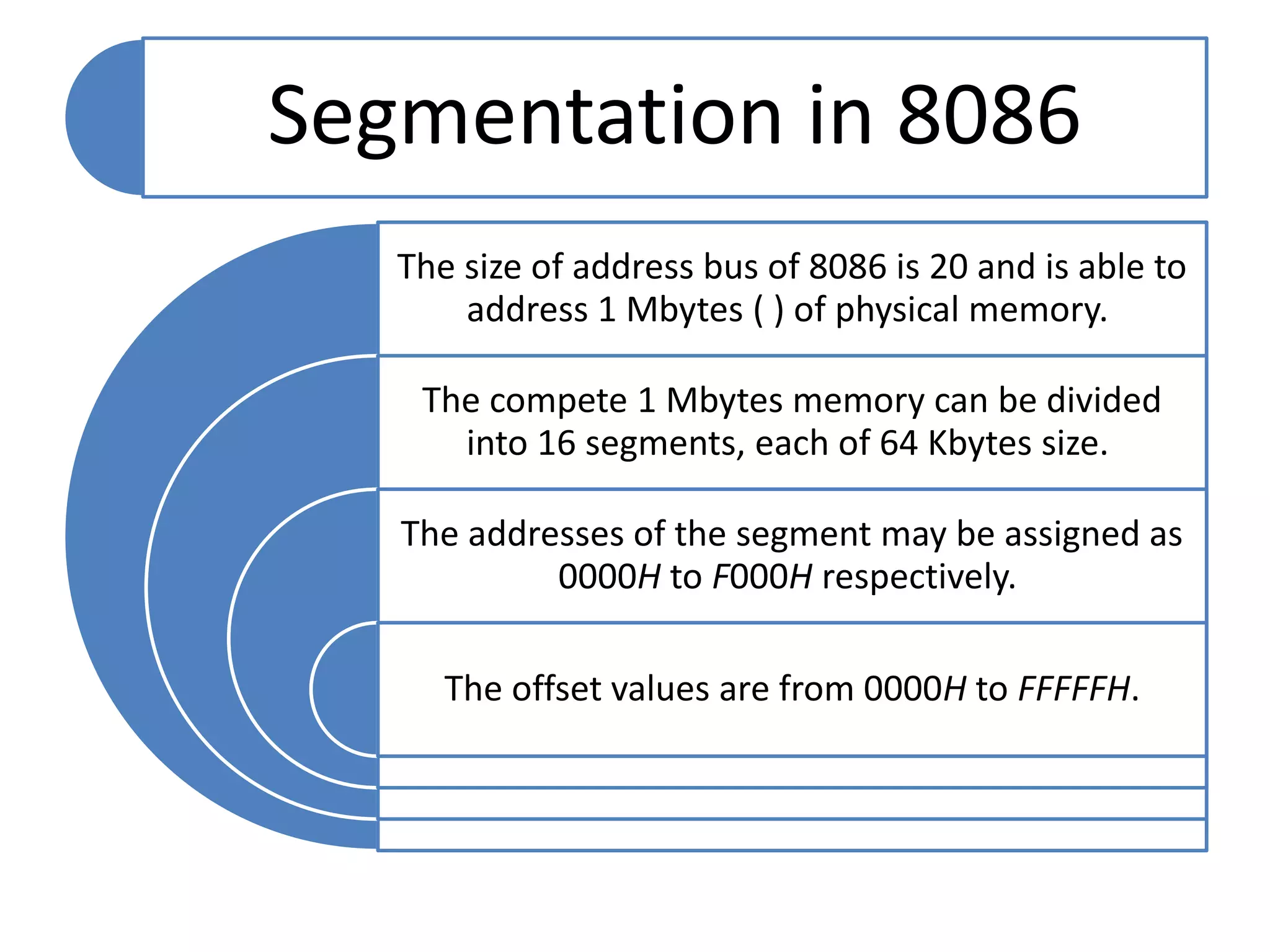
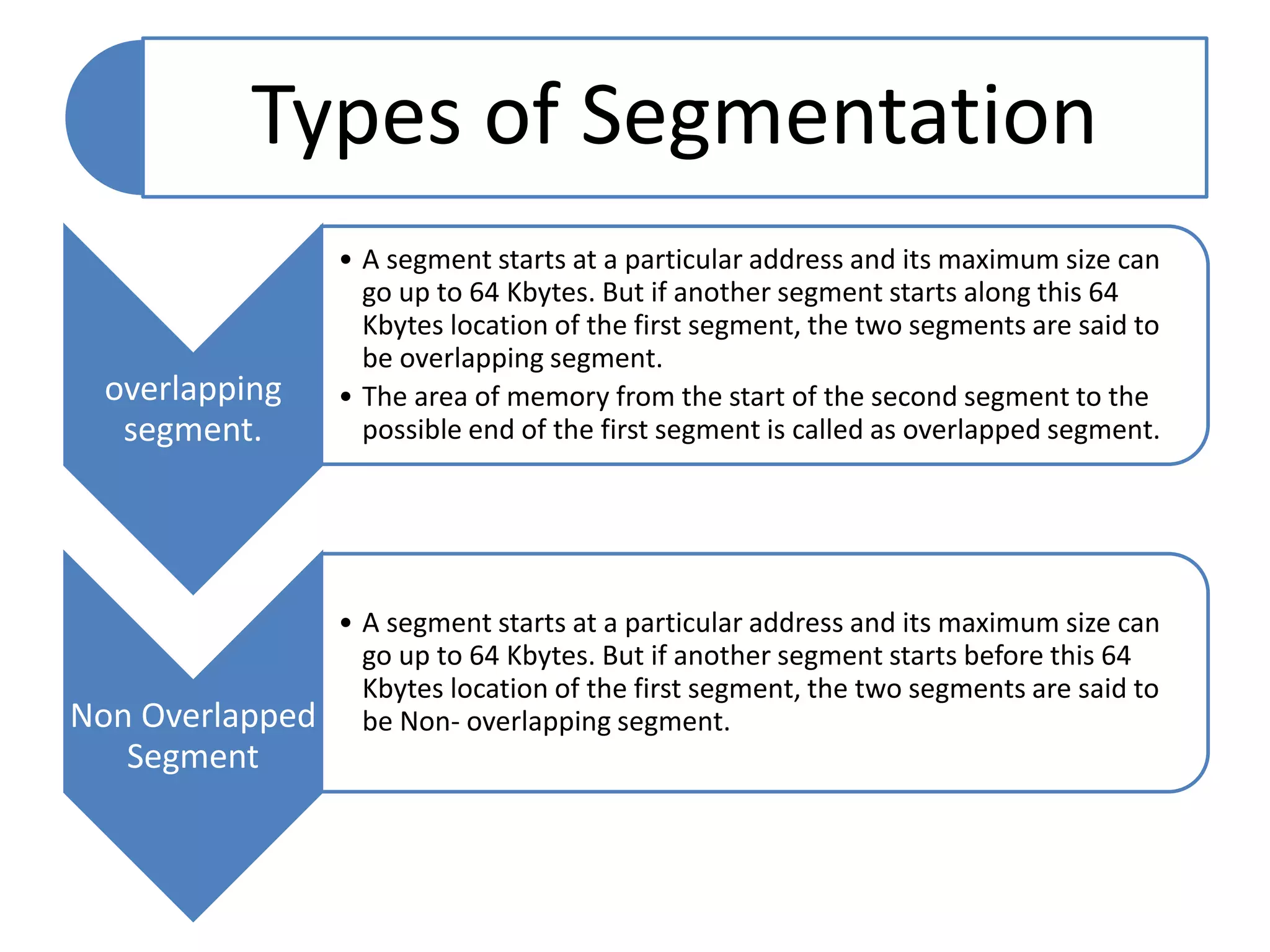
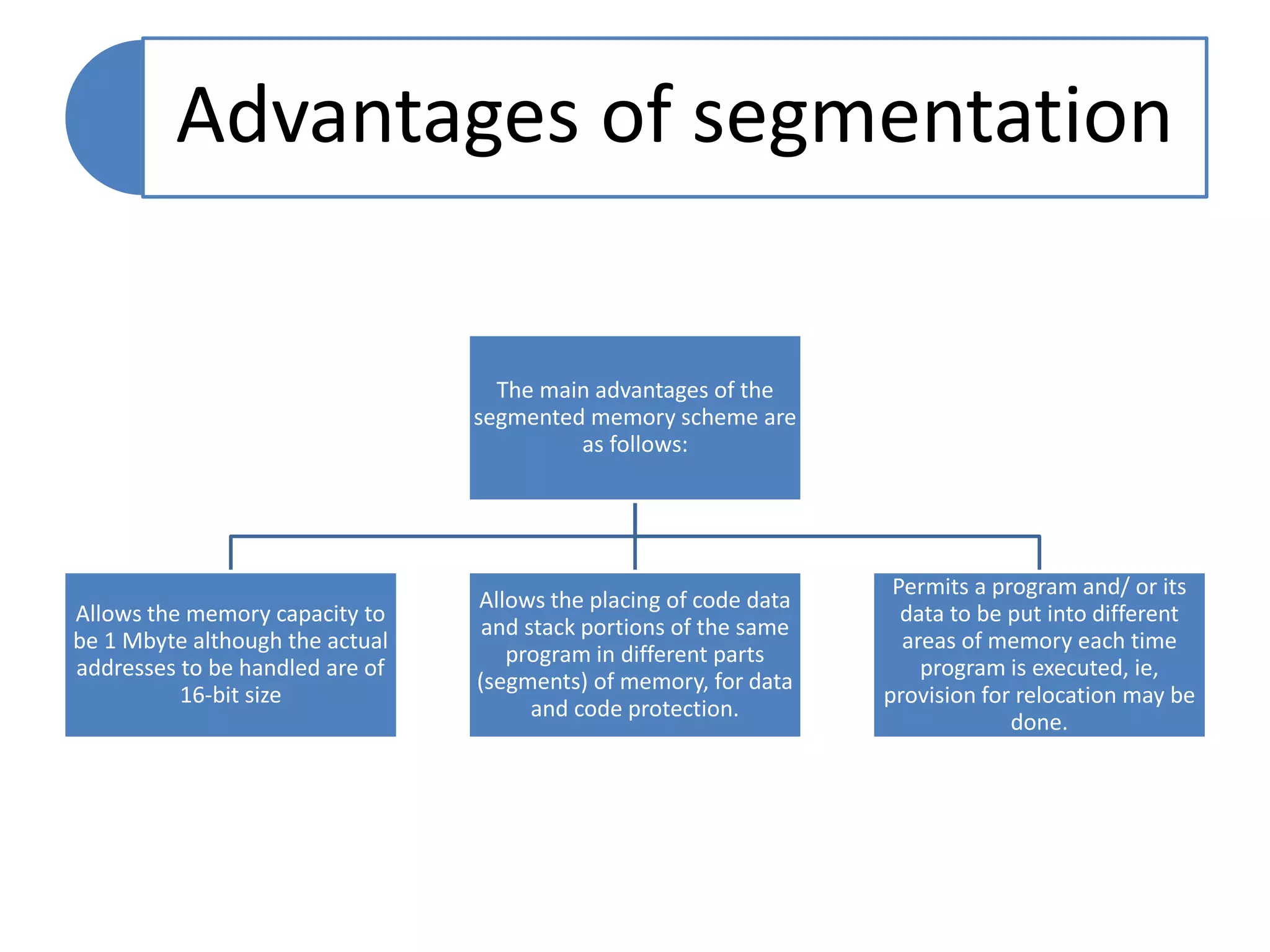
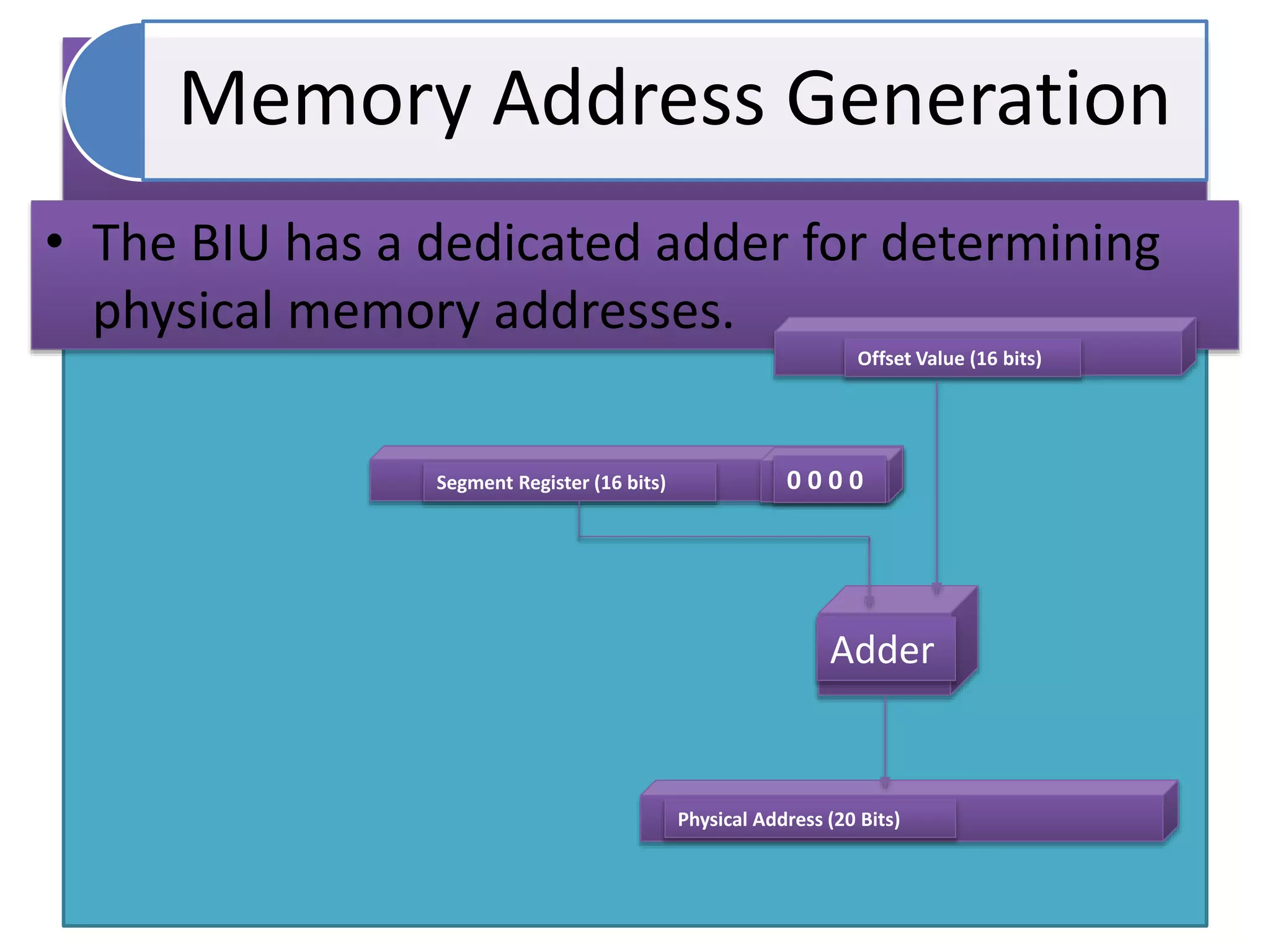
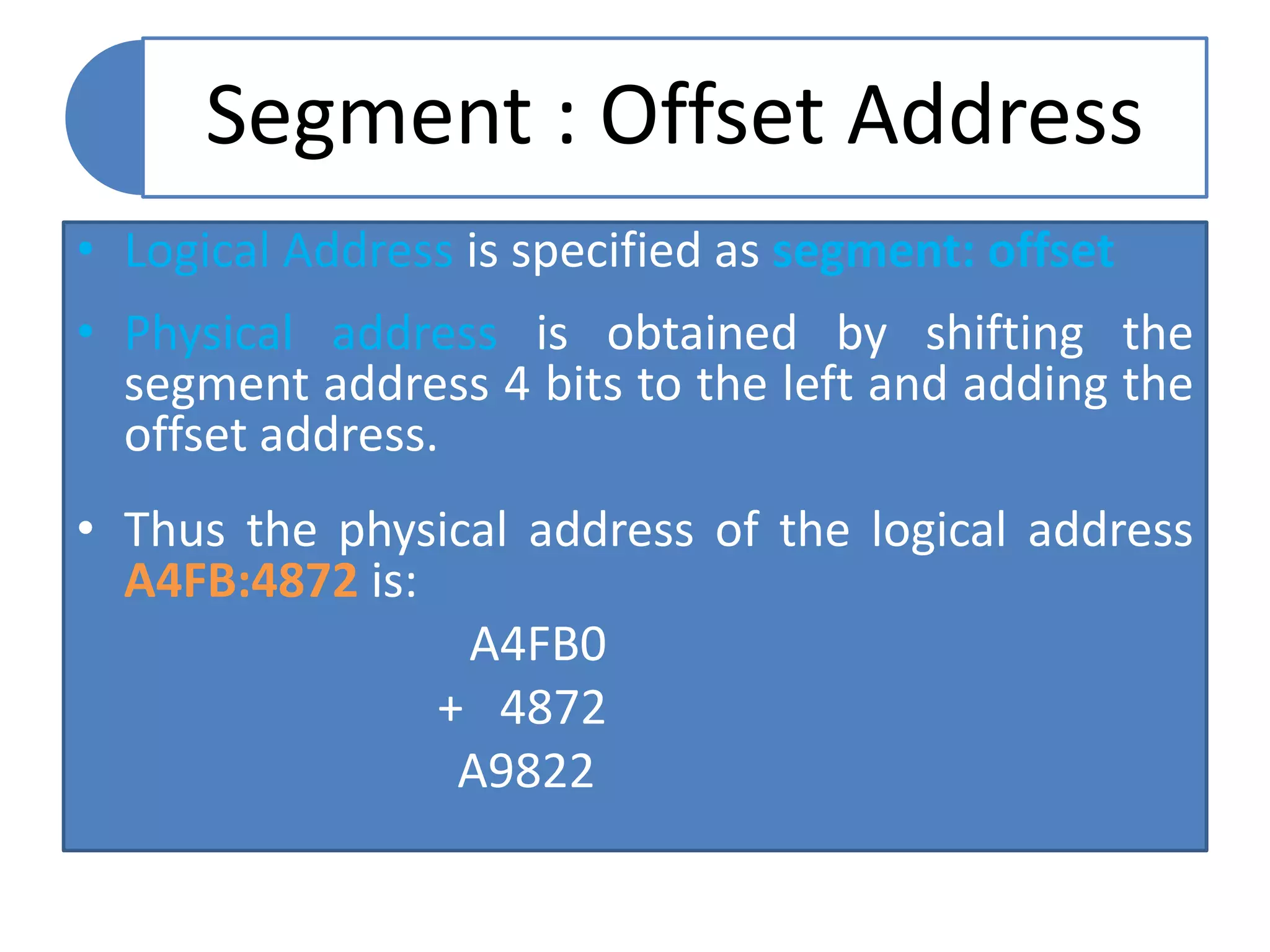
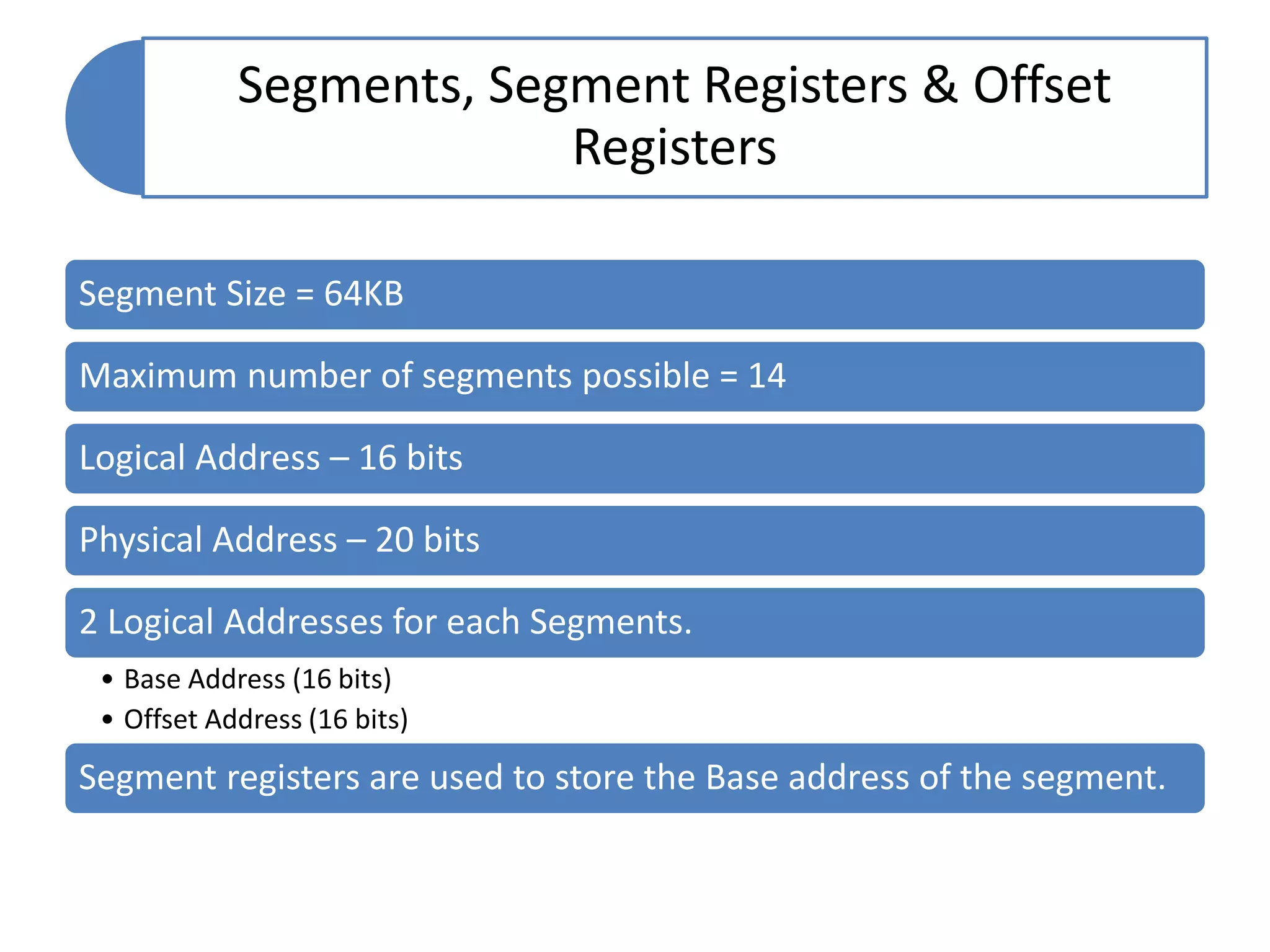
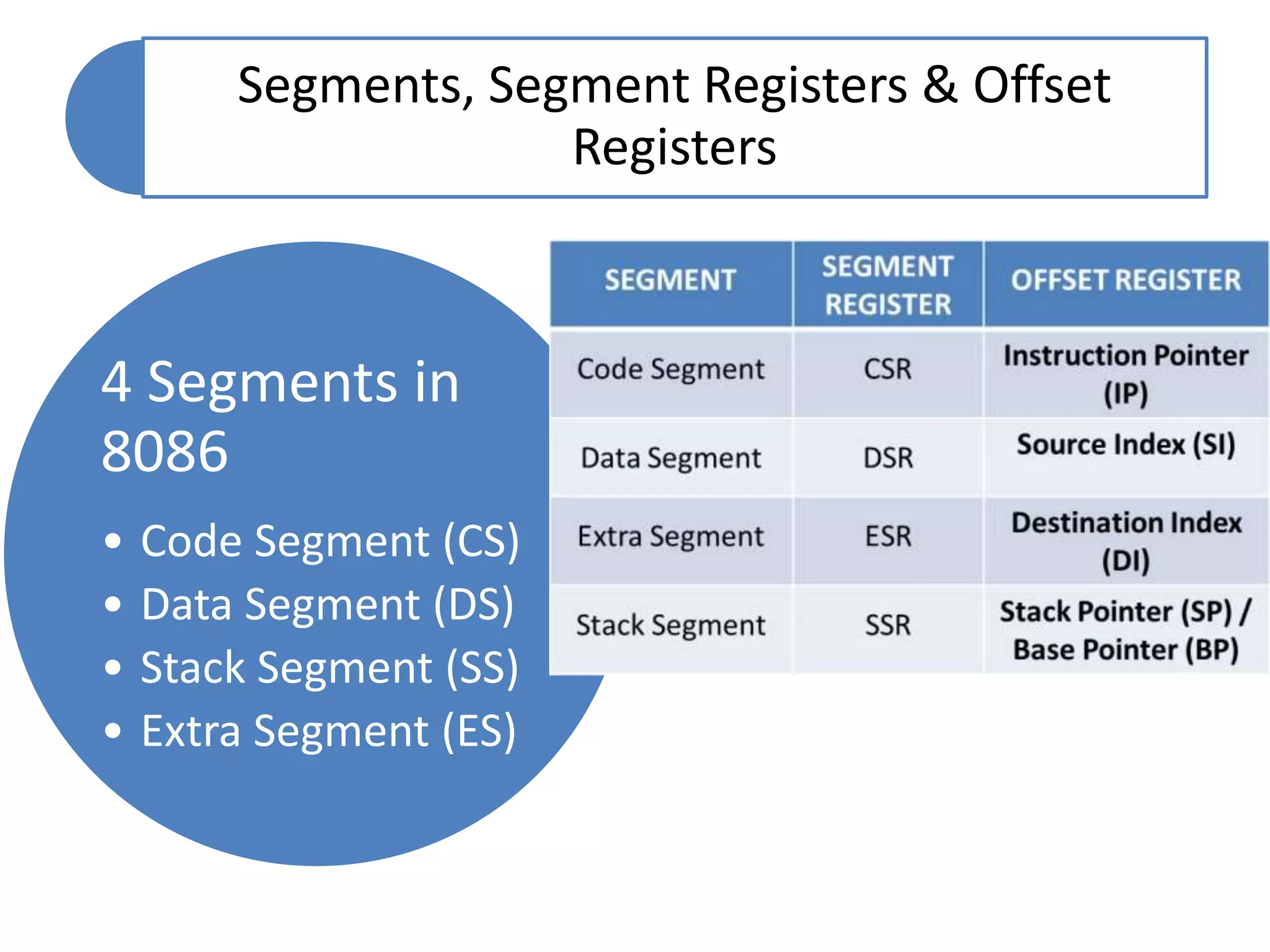
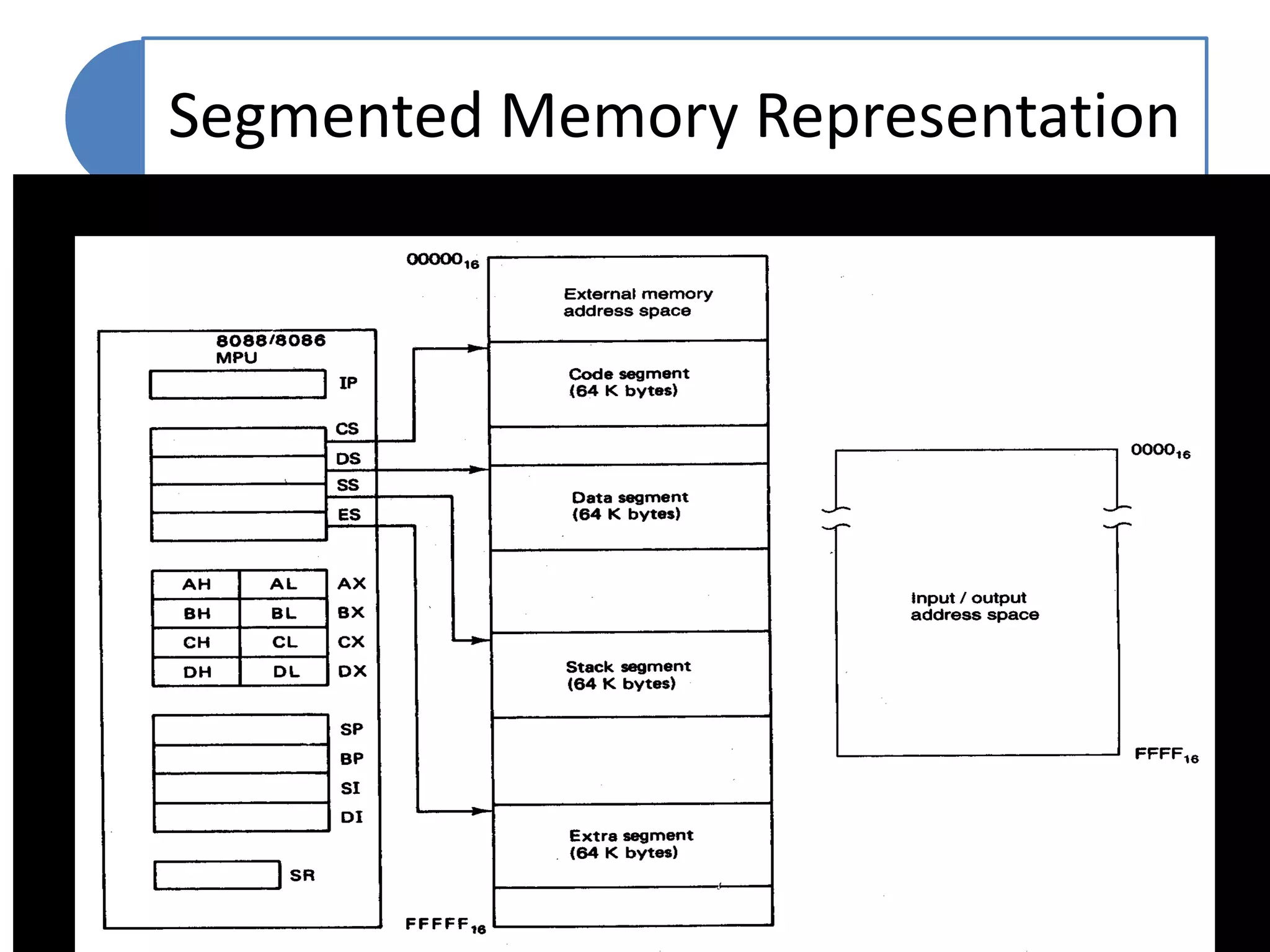
The document discusses memory segmentation in the 8086 microprocessor. It explains that the 8086 has a 20-bit address bus that can address 1MB of physical memory. This memory can be divided into 16 segments of 64KB each, addressed from 0000H to F000H. Segments are accessed using a segment register to provide the base address and an offset value. Logical addresses are specified as segment:offset pairs, which are combined and shifted to generate the 20-bit physical address. Segmentation allows code, data, and stacks to be separated and permits relocation of programs in memory.