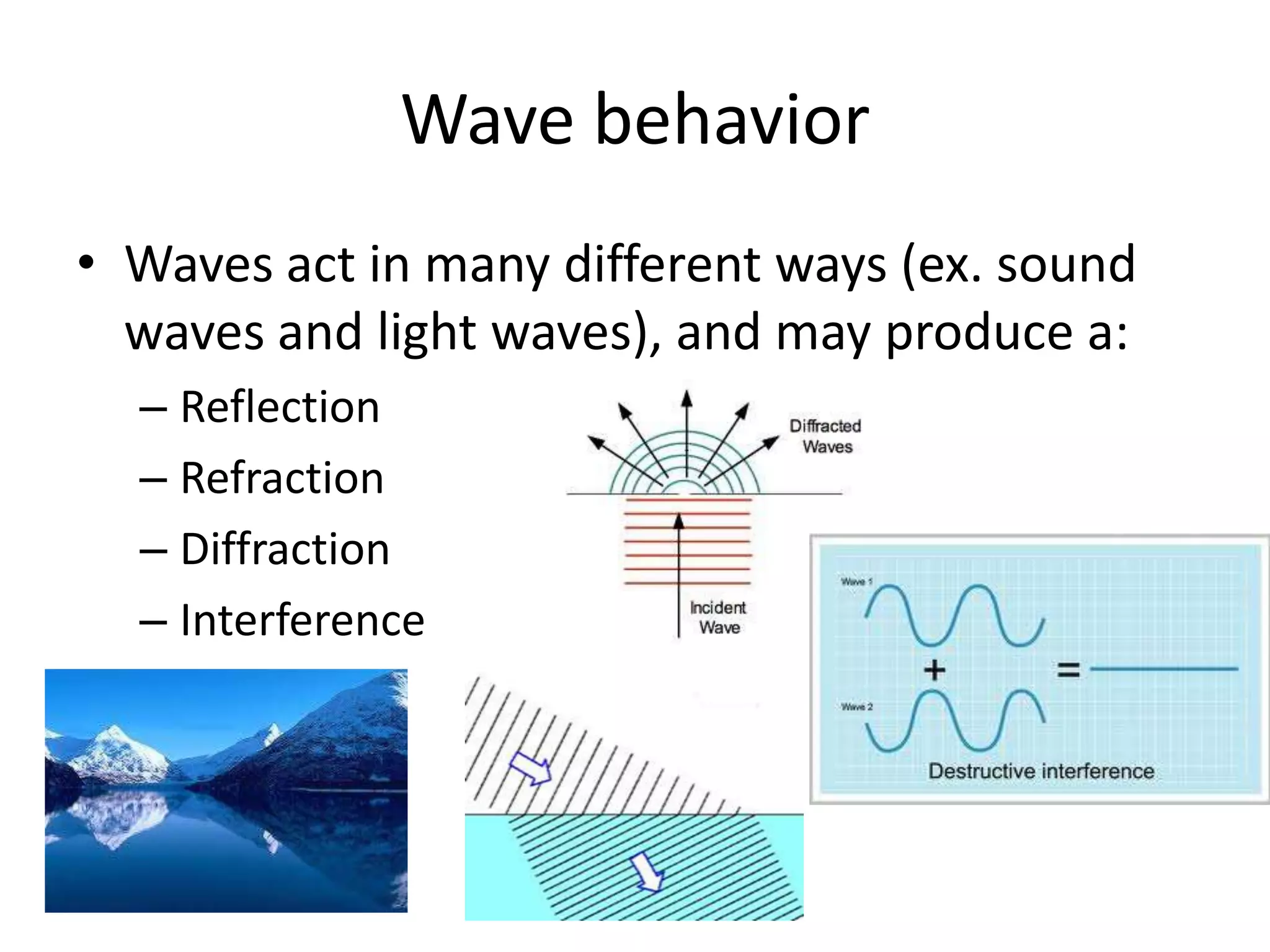
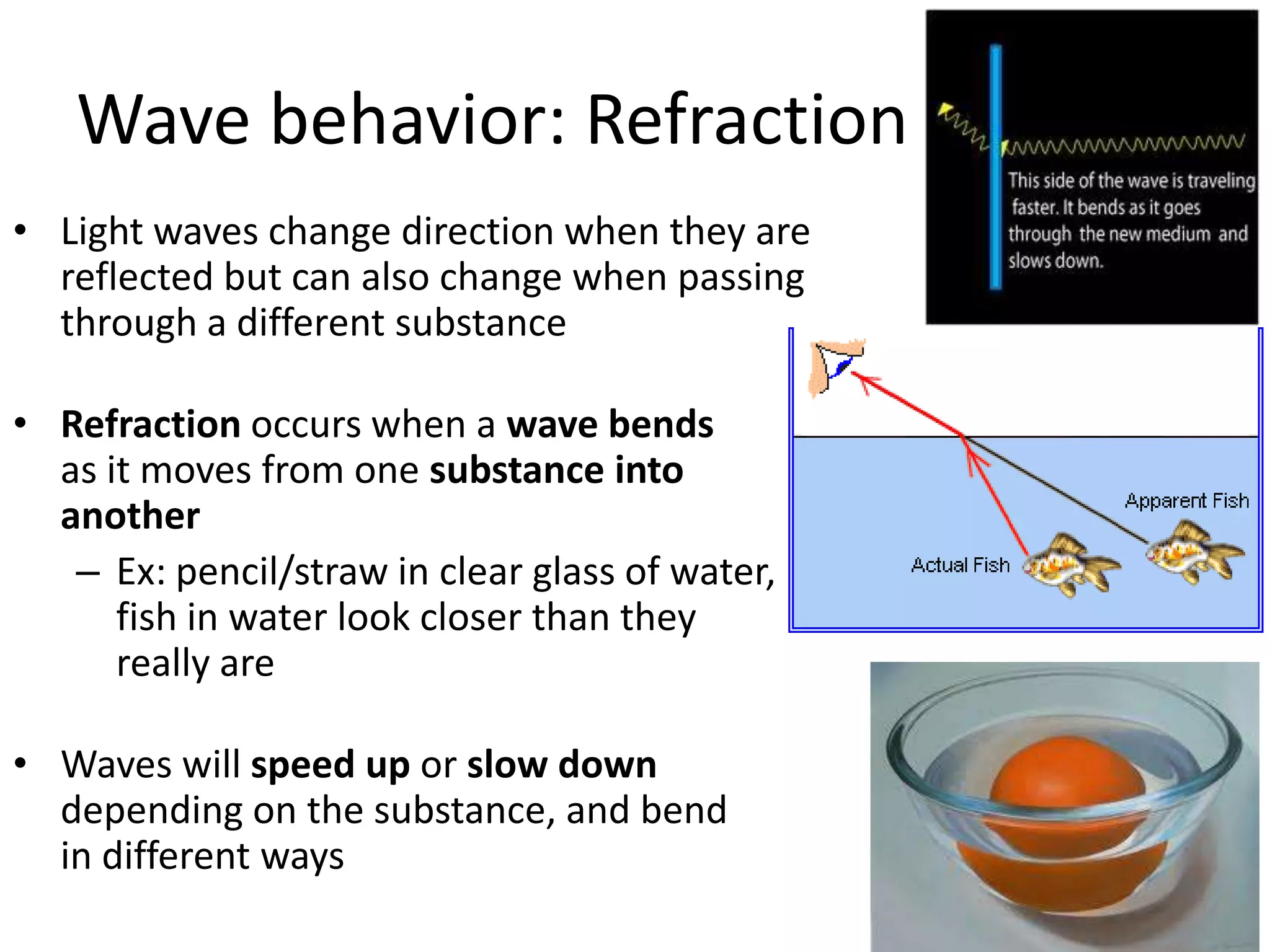
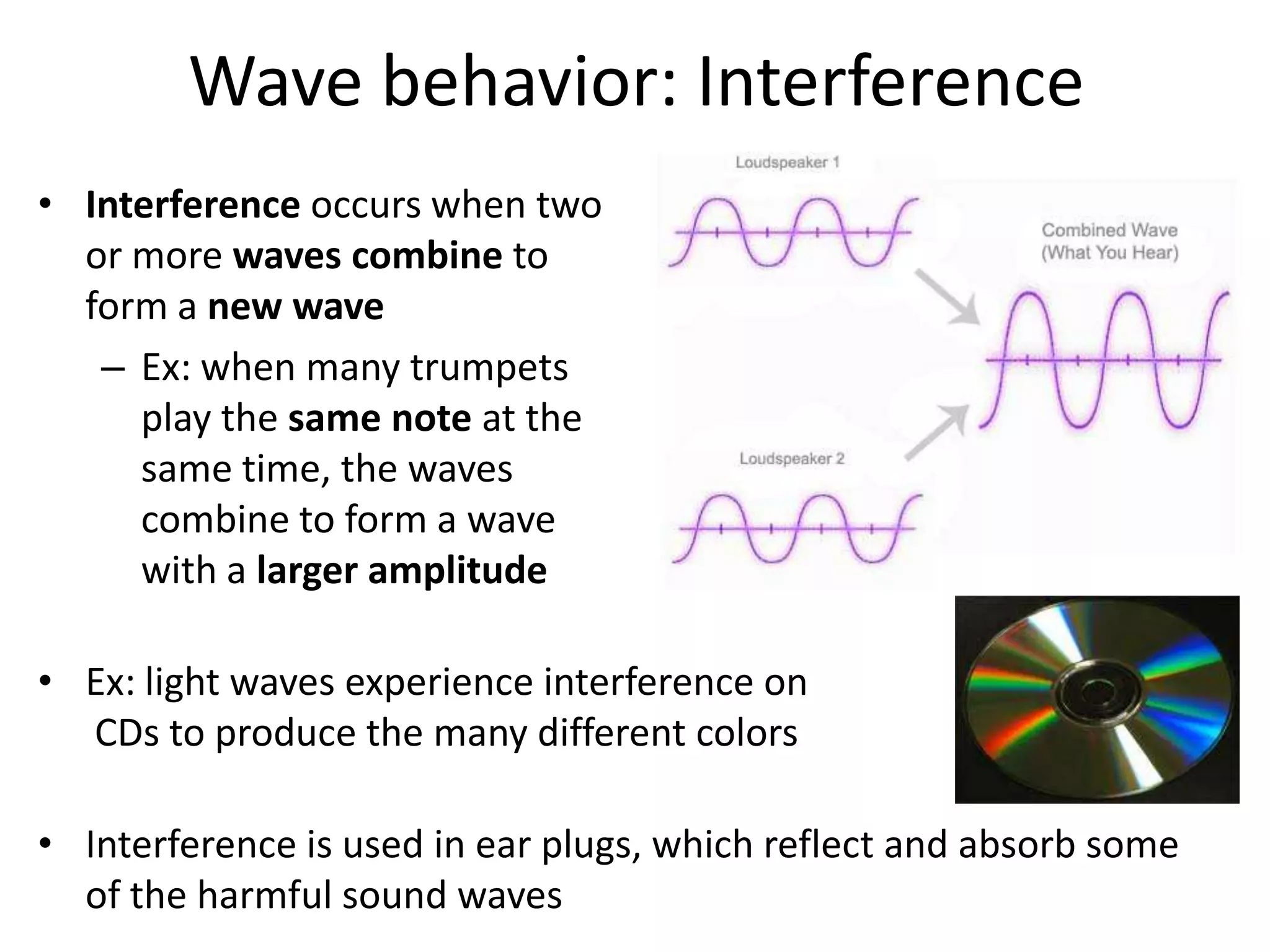
Waves can behave in several ways as they interact with objects and each other. They can reflect off surfaces, refract as they pass between different materials by changing speed and direction, diffract by bending around barriers, and interfere by combining with other waves to form a new wave. Reflection causes echoes, refraction makes underwater objects appear closer, diffraction allows sound to travel around corners, and interference is used in technologies like CDs and ear plugs.