This document discusses defect prevention as a way to reduce costs and enhance quality in software development. It notes that preventing defects is better than fixing them later. The key points made include:
- Defects are imperfections that cause software to fail to meet expectations. Most defects are introduced early but found later in the process.
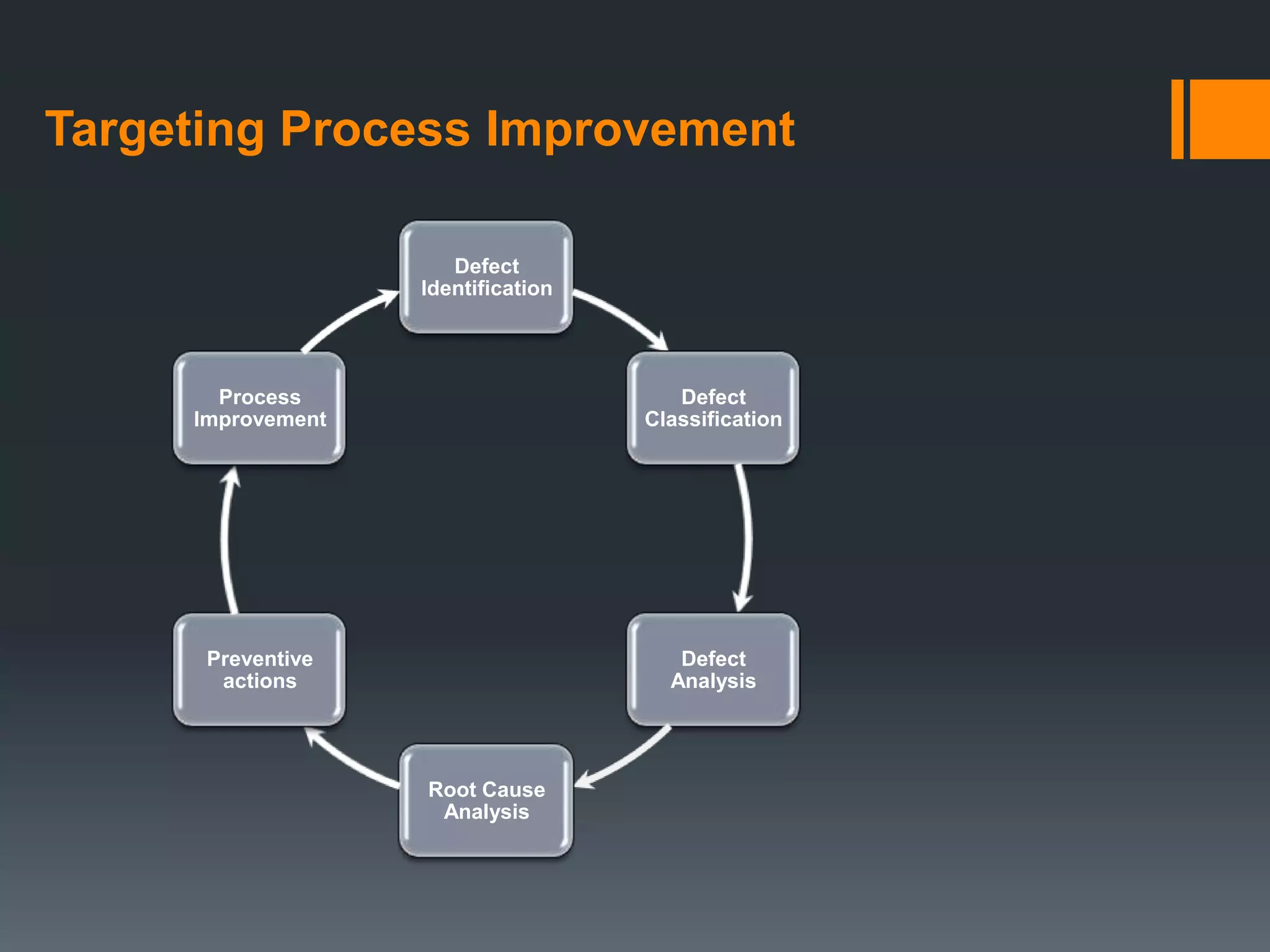
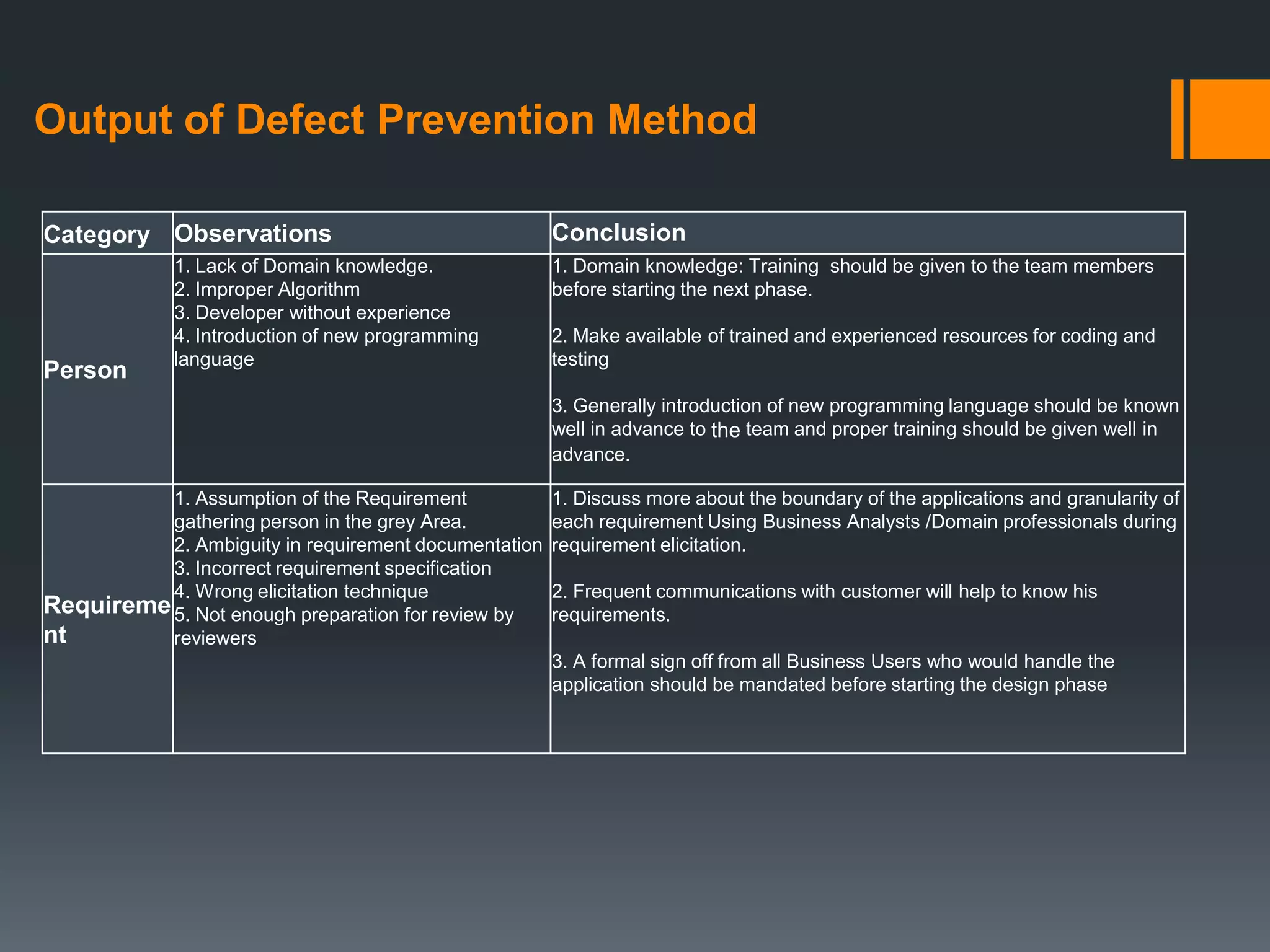
- Defect prevention identifies root causes through analysis of past defects to prevent recurrences. This improves productivity and reduces rework.
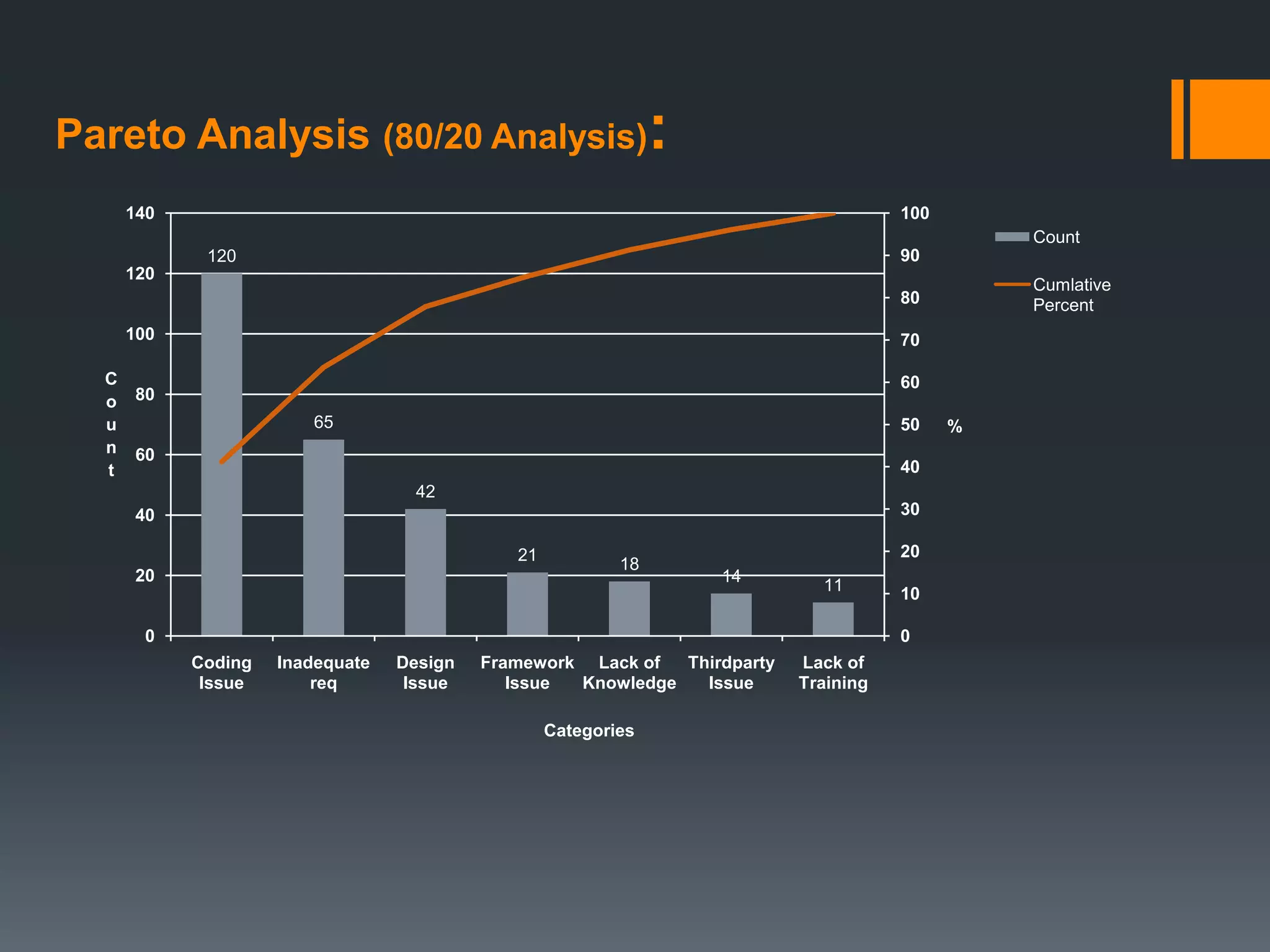
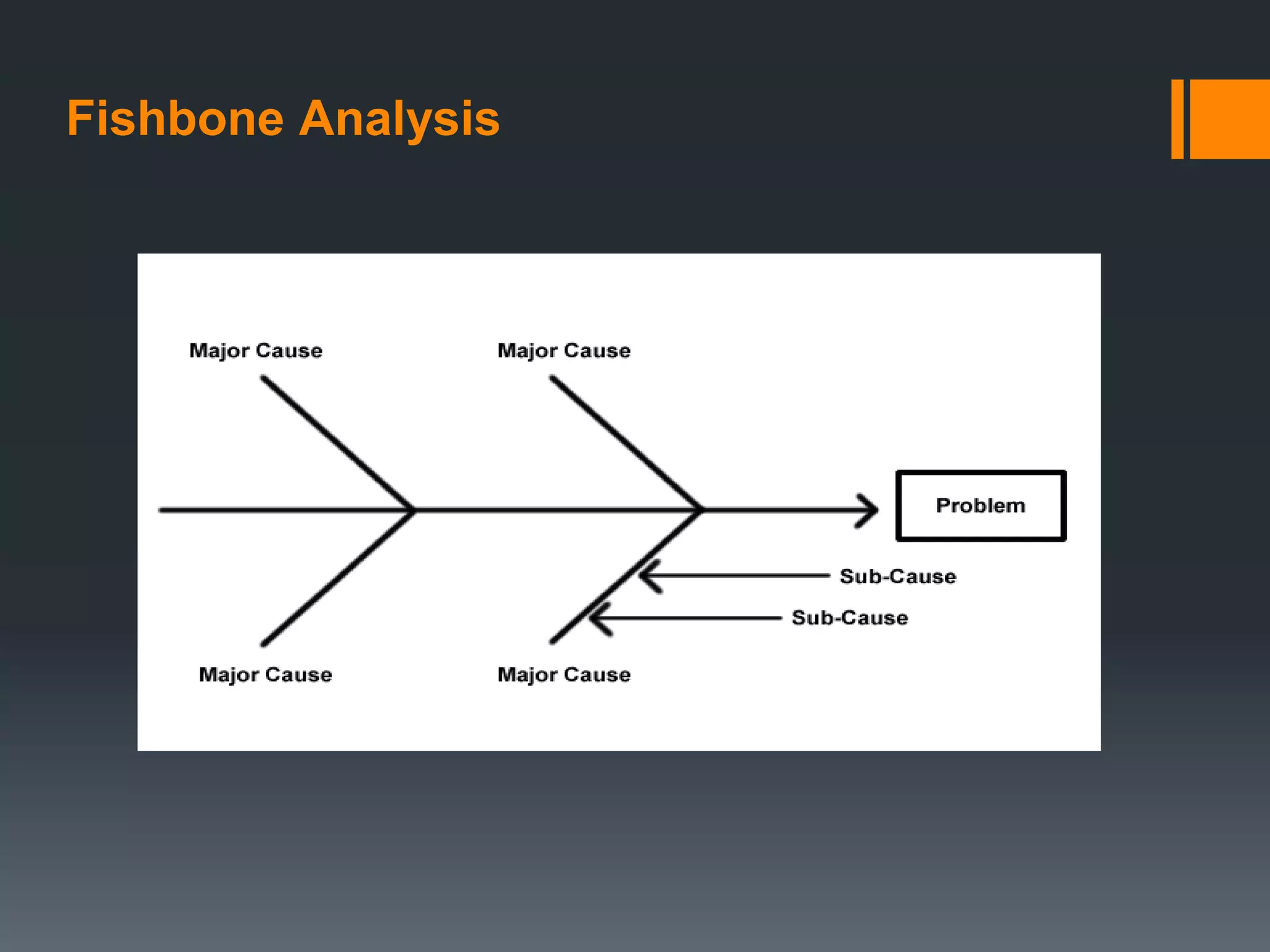
- Fixing defects gets significantly more expensive later in the process, from design to maintenance. Methods of prevention include reviews, inspections, walkthroughs, logging defects, and root cause analysis techniques like Pareto analysis and fishbone diagrams.
-