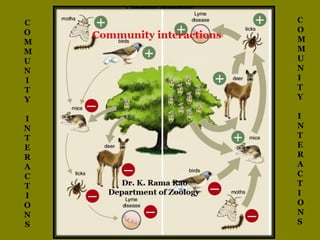
Community interactions
- 2. In ecology, a community is the biotic component of an ecosystem. It consists of populations of different species that live in the same area and interact with one another. The five main forms of interaction between population. The forms are: 1. Mutualism 2. Commensalism 3. Parasitism 4. Competition 5. Predation.
- 3. Populations Interactions Species - A Species - B Name of the Interaction + + Mutualism + 0 Commensalism + - Parasitism - - Competition + - Predation
- 4. 1. Mutualism: It is an interaction that confers benefits to both the interacting species. Examples of mutualism are: a. Lichens represent an intimate mutualistic relationship between a fungus and photosynthesizing algae or cyanobacteria.
- 5. Here, the fungus helps in the absorption of nutrients and provides protection, while algae prepare the food.
- 6. b. Plants need help from animals for pollination and dispersal of seeds. In return, plants provide nectar, pollens and fruits to the pollinators.
- 7. For example, the female wasp uses the fruit not only as an oviposition (egg-laying) site but uses the developing seeds within the fruit for nourishing its larvae.
- 8. The wasp pollinates the fig inflorescence, while searching for suitable egg-laying sites. In return, fig provides the wasp some seeds as food for the developing wasp larvae.
- 9. 2. Commensalism: It is the interaction between two species, where one species is benefitted and the other is neither harmed nor benefitted.
- 10. Examples a. Barnacles growing on the back of whale gets benefitted to move to different locations for food as well as shelter, while the whales are neither benefitted nor harmed.
- 11. b. Egrets always forage close to where the cattle are grazing. Because, the cattle egrets are benefitted by the cattle to detect insects as the cattle stir up the bushes and insects are flushed out from the vegetation to be catched by cattle egrets.
- 13. c. Sea anemone has stinging tentacles and the clown fish lives among them. The fish gets protection from predators, which stay away from the stinging tentacles. The anemone does not appear to derive any benefit by hosting the clown fish.
- 15. 3. Parasitism: It is the mode of interaction between the two species in which one species (parasite) depends on the other species (host) for food and shelter and damages the host. In this process, one organism is benefitted (parasite), while the other being harmed (host).
- 16. (i) Adaptation Methods of a Parasite: (a) Parasite is host-specific in a way that both host and parasite tend to co-evolve. (b) Loss of unnecessary sense organs. (c) Presence of adhesive organs or suckers. (d) Loss of digestive system. (e) High reproductive capacity.
- 17. (ii) The life cycles of parasites are often complex, involving one or two intermediate hosts or vectors to facilitate parasitisation of its primary host. For example (a)Human liver fluke (b)Malarial parasite
- 19. (iii) Majority of parasites harm the host. They reduce the survival, growth and reproduction of the host. They reduce its population density by making it physically weak. (a) Ectoparasites feed on the external surface of the host organism for food and shelter.
- 20. (b) Endoparasites live inside the host’s body at different sites like liver, kidney, lungs, etc., for food and shelter. (c) Brood parasitism is a phenomenon in which one organism (parasite) lays its eggs in the nest of another organism.
- 22. 4. Competition: Competition occurs when closely related species compete for the same resources that are limited: a. It can be best defined as a process in which the fitness of one species (measured in terms of its ‘r’ the intrinsic rate of increase) is significantly lower in the presence of another species.
- 23. b. It is a type of interaction, where both the species suffer. c. Some totally unrelated species could also compete for the same resources c. In interspecific competition, the feeding efficiency of one species might be reduced due to the interfering and inhibitory presence of the other species.
- 24. 5. Predation: It is an interspecific interaction, where an animal called predator kills and consumes the other weaker animal called prey. This is a biological control method . Important roles of predators are:
- 25. (i) They keep prey population under control. (ii) They help in maintaining species diversity in a community by reducing the intensity of competition among prey species. (iii) In absence of predators, prey species could achieve very high population densities and cause instability.
- 26. (iv) When certain exotic species are introduced into a geographical area, they become invasive and start spreading fast. (v) If a predator is too efficient and exploits its prey, then the prey might become extinct. (vi) Prey species have evolved various defence mechanisms to lessen the impact of predation.
- 27. Some species of insects and frogs are cryptically coloured (camouflage) to avoid being detected easily by the predator.